Final ID: Tu028
NADPH Oxidase Inhibition Antagonizes Endothelial Pro-inflammatory and Pro-oxidant Signaling Resulting in Enhanced Coronary Vasorelaxation in Diabetic Models
Abstract Body: Introduction: NADPH oxidase (NOX) overactivation and reactive oxygen species amplification may underlie worse cardiac outcomes in patients with diabetes. Our group has shown impaired endothelium-dependent coronary vasodilation in diabetes, with restored endothelial function following NOX inhibition. Persistently high levels of oxidative stress may be driving this impaired coronary microvascular reactivity by altering small-conductance potassium channel activity. We hypothesized that NADPH oxidase inhibition would be vasoprotective through reductions in pro-oxidant and pro-inflammatory signaling.
Methods: Human coronary arterial endothelial cells (HCAECs) were obtained from diabetic (D) and nondiabetic (C) patients (N = 4 per group). HCAECs were cultured in normo- or hyperglycemic conditions, with one hyperglycemic group receiving NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin (DT). Molecular signaling was assessed using immunoblotting.
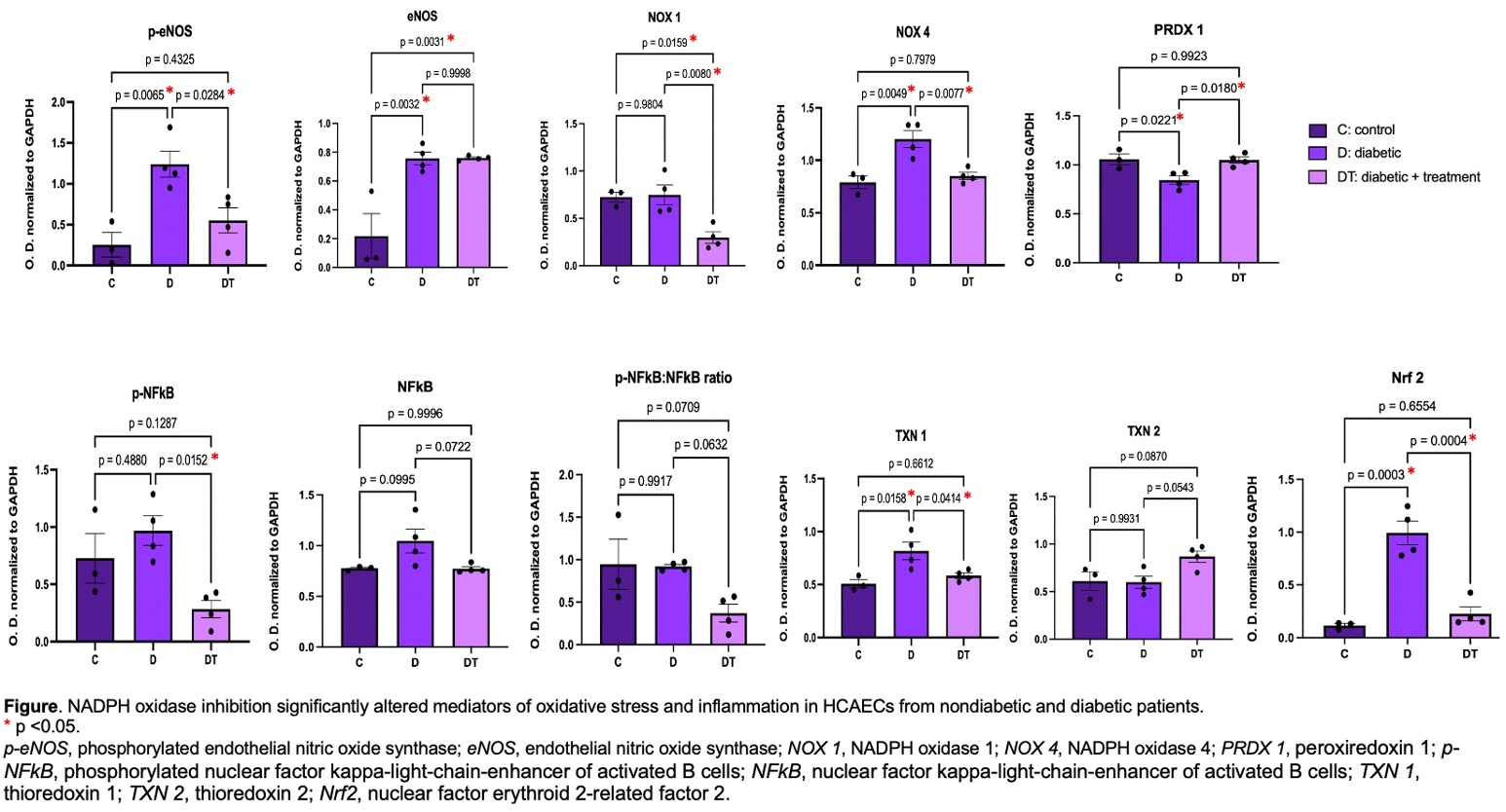
Results: Diabetes resulted in significantly increased pro-oxidant markers, including NOX 4 (p = 0.005), phosphorylated endothelial nitric oxide synthase (p-eNOS) (p = 0.007), and eNOS (p = 0.003). Pro-inflammatory Nrf2 was also increased (p = 0.0003), with a trend toward increased NFkB (p = 0.09) in D compared to C. Antioxidant peroxiredoxin (PRDX) 1 was significantly reduced in D compared to C (p = 0.02). NOX inhibition rescued these effects, with reversed trends in NOX 4 (p = 0.008), p-eNOS (p = 0.03), and PRDX 1 (p = 0.02) following apocynin treatment. NOX inhibition resulted in de novo decrease in NOX 1 in DT when compared to D (p = 0.008) and C (p = 0.02), and decrease in phosphorylated NFkB (p-NFkB) when compared to D (p = 0.02). There was a trend toward decreased total NFkB (p = 0.07) and p-NFkB:NFkB ratio (p = 0.06) and increased antioxidant thioredoxin (TXN) 2 (p = 0.05) in diabetic cells following treatment. Antioxidant superoxide dismutase (SOD) 2 (p = 0.01) and TXN 1 (p = 0.02) were increased in D when compared to C, while apocynin treatment reversed these changes (SOD 2, p = 0.0006; TXN 1, p = 0.04). There were no significant differences in NOX 2, SOD 1, catalase, PRDX 2, or PRDX 3 between the groups.
Conclusions: Apocynin overall suppressed pro-oxidant and pro-inflammatory signaling in human diabetic coronary endothelial cells, resulting in improved coronary endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. Cardioprotective strategies that incorporate NADPH oxidase inhibition in the setting of diabetes warrant further investigation.
Methods: Human coronary arterial endothelial cells (HCAECs) were obtained from diabetic (D) and nondiabetic (C) patients (N = 4 per group). HCAECs were cultured in normo- or hyperglycemic conditions, with one hyperglycemic group receiving NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin (DT). Molecular signaling was assessed using immunoblotting.
Results: Diabetes resulted in significantly increased pro-oxidant markers, including NOX 4 (p = 0.005), phosphorylated endothelial nitric oxide synthase (p-eNOS) (p = 0.007), and eNOS (p = 0.003). Pro-inflammatory Nrf2 was also increased (p = 0.0003), with a trend toward increased NFkB (p = 0.09) in D compared to C. Antioxidant peroxiredoxin (PRDX) 1 was significantly reduced in D compared to C (p = 0.02). NOX inhibition rescued these effects, with reversed trends in NOX 4 (p = 0.008), p-eNOS (p = 0.03), and PRDX 1 (p = 0.02) following apocynin treatment. NOX inhibition resulted in de novo decrease in NOX 1 in DT when compared to D (p = 0.008) and C (p = 0.02), and decrease in phosphorylated NFkB (p-NFkB) when compared to D (p = 0.02). There was a trend toward decreased total NFkB (p = 0.07) and p-NFkB:NFkB ratio (p = 0.06) and increased antioxidant thioredoxin (TXN) 2 (p = 0.05) in diabetic cells following treatment. Antioxidant superoxide dismutase (SOD) 2 (p = 0.01) and TXN 1 (p = 0.02) were increased in D when compared to C, while apocynin treatment reversed these changes (SOD 2, p = 0.0006; TXN 1, p = 0.04). There were no significant differences in NOX 2, SOD 1, catalase, PRDX 2, or PRDX 3 between the groups.
Conclusions: Apocynin overall suppressed pro-oxidant and pro-inflammatory signaling in human diabetic coronary endothelial cells, resulting in improved coronary endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. Cardioprotective strategies that incorporate NADPH oxidase inhibition in the setting of diabetes warrant further investigation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessing Diagnostic Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Machine Learning-Based Fractional Flow Reserve versus Traditional Invasive Fractional Flow Reserve for Coronary Artery Stenosis Evaluation
Jain Shubhika, Panchal Viraj, Adams Mariah, Singh Mansunderbir, Goyal Samarth, Joshi Divya Dinesh, Vyas Rahul, Thotamgari Sahith Reddy, Brar Vijaywant
An Epigenetic Drug, GSK126 Mitigates Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition Attenuating Atherosclerosis in DiabetesAziz Misbah, Jandeleitdahm Karin, Khan Abdul Waheed