Final ID: 4113997
Semaglutide Improves Myocardial Perfusion and Performance in a Large Animal Model of Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the leading cause of death worldwide. It imposes an enormous symptomatic burden on patients, leaving many with residual disease despite optimal procedural therapy, and up to 1/3rd with debilitating angina amenable neither to procedures, nor to current pharmacologic options. Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide 1 agonist originally approved for management of diabetes, has garnered substantial attention for its capacity to attenuate cardiovascular risk. Although subgroup analyses in patients indicate promise, studies explicitly designed to isolate the impact of semaglutide on the sequelae of CAD are lacking.
Hypothesis: Semaglutide will improve cardiac performance in a clinically relevant large animal model of CAD.
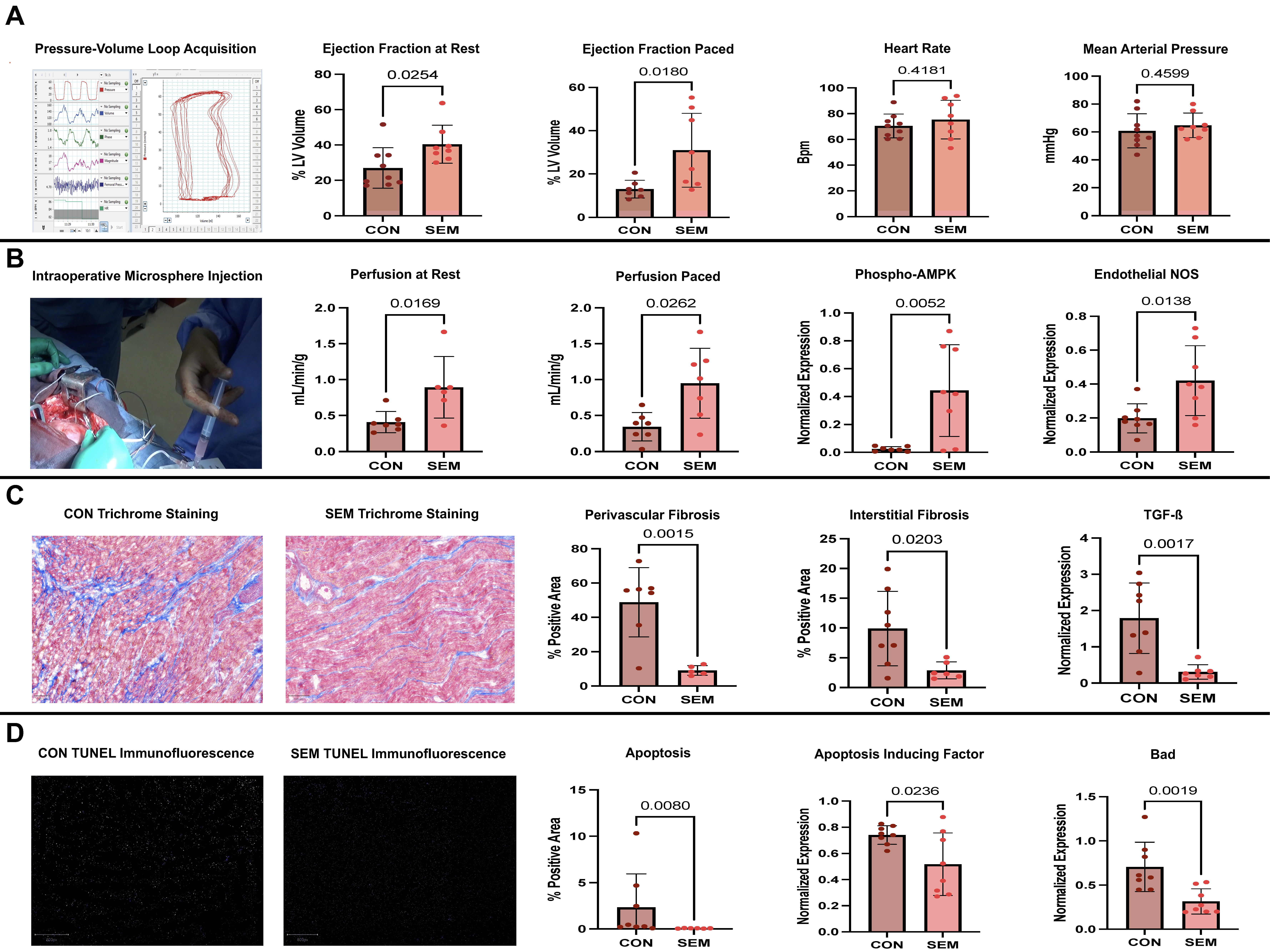
Methods: Yorkshire swine (n=17) underwent placement of an ameroid constrictor around the left circumflex coronary artery to induce CAD. Oral semaglutide was initiated postoperatively at 1.5 mg and scaled up in 2 weeks to 3 mg in treatment animals (SEM, n=8) for a total of 5 weeks, while control animals (CON, n=9) received no drug. All then underwent myocardial harvest with acquisition of perfusion and functional data using microsphere injection and pressure-volume loop catheterization. Immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence were performed on the most ischemic myocardial segments for mechanistic elucidation.
Results: SEM animals exhibited improved left ventricular ejection fraction, both at rest and during rapid myocardial pacing to 150 bpm (both p<0.03), accompanied by increased perfusion to the most ischemic myocardial region at rest and during rapid pacing (both p<0.03); reduced perivascular and interstitial fibrosis (both p <0.03); and apoptosis (p=0.008). These changes were associated with increased activation of the endothelial-protective AMPK pathway (p=0.005), coupled with downstream increases in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (p=0.014).
Conclusions: This study is the first to reveal the capacity of oral semaglutide to augment cardiac function in the chronically ischemic heart in a highly translational large animal model, likely through AMPK-mediated improvement in endothelial function and perfusion to the ischemic myocardium.
Hypothesis: Semaglutide will improve cardiac performance in a clinically relevant large animal model of CAD.
Methods: Yorkshire swine (n=17) underwent placement of an ameroid constrictor around the left circumflex coronary artery to induce CAD. Oral semaglutide was initiated postoperatively at 1.5 mg and scaled up in 2 weeks to 3 mg in treatment animals (SEM, n=8) for a total of 5 weeks, while control animals (CON, n=9) received no drug. All then underwent myocardial harvest with acquisition of perfusion and functional data using microsphere injection and pressure-volume loop catheterization. Immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence were performed on the most ischemic myocardial segments for mechanistic elucidation.
Results: SEM animals exhibited improved left ventricular ejection fraction, both at rest and during rapid myocardial pacing to 150 bpm (both p<0.03), accompanied by increased perfusion to the most ischemic myocardial region at rest and during rapid pacing (both p<0.03); reduced perivascular and interstitial fibrosis (both p <0.03); and apoptosis (p=0.008). These changes were associated with increased activation of the endothelial-protective AMPK pathway (p=0.005), coupled with downstream increases in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (p=0.014).
Conclusions: This study is the first to reveal the capacity of oral semaglutide to augment cardiac function in the chronically ischemic heart in a highly translational large animal model, likely through AMPK-mediated improvement in endothelial function and perfusion to the ischemic myocardium.
More abstracts on this topic:
Large Vessel Recanalization with Thrombolysis Prior to Thrombectomy: Incidence, Outcomes, and Associations With Collateral Status
Skorseth Paige, Colasurdo Marco, Chen Huanwen, Rewinkel Scott, Kim Daniel, Amin Sonesh, Shakal Scott, Priest Ryan, Nesbit Gary, Clark Wayne
A pharmacist-led, population health approach to optimizing care in patients with hypertension and type II diabetes mellitus in minority groupsDoyle Julie, Haftel Elizabeth, Monroe Janet, Chen Zsu-zsu, Benson Mark, Yankama Tuyen, Adam Atif, Rubin Rochelle