Final ID: 4143581
Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitor Linagliptin Improves Cardiac Function, Fibrosis and Apoptosis in a Swine Model of Chronic Myocardial Ischemia
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Interest is increasing in using novel diabetic medications, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, to manage coronary artery disease. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors enhance GLP-1 activity through the same pathway as GLP-1 agonists; however, DPP-4 inhibitors have not been fully evaluated in the setting of ischemic heart disease. We chose to study the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin (LIN) in a swine model of chronic myocardial ischemia (CMI).
Goals:
Study the effect of DPP-4 inhibitor LIN in a clinically relevant swine model of CMI to gain insight into potential therapies for patients with myocardial ischemia.
Methods:
Seventeen Yorkshire swine underwent left thoracotomy and ameroid constrictor placement on the left coronary circumflex (LCx) at age 11 weeks. Two weeks later, swine received either vehicle without drug (CON, n=9, F=4, M=5) or LIN 2.5 mg (n=8, F=5, M=3). After 5 weeks of treatment, swine underwent terminal harvest.
Results:
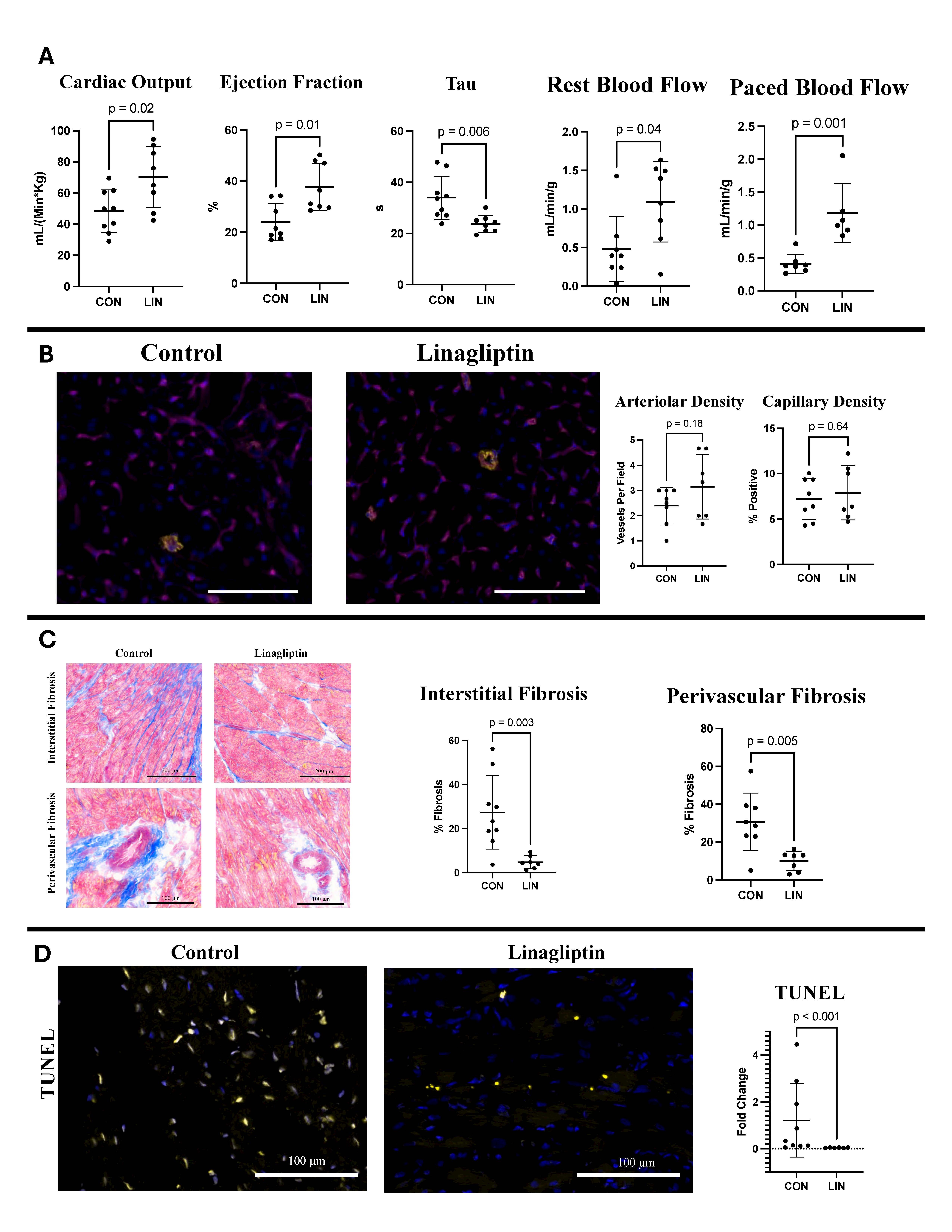
LIN significantly increased cardiac output, stroke volume, ischemic myocardial perfusion at rest, ischemic myocardial perfusion while pacing at 150 beats per minute, and ejection fraction, while decreasing tau (all p<0.05). Trichrome staining showed a marked reduction in ischemic myocardial interstitial and perivascular fibrosis, accompanied by decreased levels of transforming growth factor beta (all p<0.05). Apoptosis, measured by TUNEL, was significantly reduced, along with decreases in apoptosis-inducing factor, Caspase-9, BAD, and cleaved Caspase-9 (all p<0.05). Additionally, there were significant increases in PI3K, phospho-AKT, AMPK, phospho-AMPK, and ENOS, and a significant reduction in collagen 18 and angiostatin (all p<0.05). There were no significant changes in heart rate, arteriolar density, capillary density, or total oxidative stress.
Conclusion:
LIN significantly improved myocardial function and perfusion, likely due to reduced fibrosis and apoptosis. The increased perfusion, independent of vascular density, suggests enhanced vascular reactivity. These benefits in a high-fidelity large animal model of CMI warrant further investigation of LIN to fully understand its potential as a therapy for ischemic heart disease.
Interest is increasing in using novel diabetic medications, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, to manage coronary artery disease. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors enhance GLP-1 activity through the same pathway as GLP-1 agonists; however, DPP-4 inhibitors have not been fully evaluated in the setting of ischemic heart disease. We chose to study the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin (LIN) in a swine model of chronic myocardial ischemia (CMI).
Goals:
Study the effect of DPP-4 inhibitor LIN in a clinically relevant swine model of CMI to gain insight into potential therapies for patients with myocardial ischemia.
Methods:
Seventeen Yorkshire swine underwent left thoracotomy and ameroid constrictor placement on the left coronary circumflex (LCx) at age 11 weeks. Two weeks later, swine received either vehicle without drug (CON, n=9, F=4, M=5) or LIN 2.5 mg (n=8, F=5, M=3). After 5 weeks of treatment, swine underwent terminal harvest.
Results:
LIN significantly increased cardiac output, stroke volume, ischemic myocardial perfusion at rest, ischemic myocardial perfusion while pacing at 150 beats per minute, and ejection fraction, while decreasing tau (all p<0.05). Trichrome staining showed a marked reduction in ischemic myocardial interstitial and perivascular fibrosis, accompanied by decreased levels of transforming growth factor beta (all p<0.05). Apoptosis, measured by TUNEL, was significantly reduced, along with decreases in apoptosis-inducing factor, Caspase-9, BAD, and cleaved Caspase-9 (all p<0.05). Additionally, there were significant increases in PI3K, phospho-AKT, AMPK, phospho-AMPK, and ENOS, and a significant reduction in collagen 18 and angiostatin (all p<0.05). There were no significant changes in heart rate, arteriolar density, capillary density, or total oxidative stress.
Conclusion:
LIN significantly improved myocardial function and perfusion, likely due to reduced fibrosis and apoptosis. The increased perfusion, independent of vascular density, suggests enhanced vascular reactivity. These benefits in a high-fidelity large animal model of CMI warrant further investigation of LIN to fully understand its potential as a therapy for ischemic heart disease.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adverse Outcomes with Cardiac Contractility Modulation: Insights From the MAUDE Registry
Katapadi Aashish, Chelikam Nikhila, Katapadi Aashika, Darden Douglas, Gopinathannair Rakesh, Kabra Rajesh, Atkins Donita, Lakkireddy Dhanunjaya, Pothineni Naga Venkata
Accuracy of Angiographic Identification of Culprit Lesions in Women with MINOCAShwayder Elianna, Li Vincent, Smilowitz Nathaniel, Serrano Claudia, Elbaum Lindsay, Shah Binita, Hochman Judith, Hausvater Anais, Reynolds Harmony