Final ID: 4124277
Resorcimoline, a Novel Free Radical Scavenger, Exhibits Cardioprotective Effects Following Coronary Ischemia-reperfusion Injury
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Ischemic heart disease remains the leading cause of death worldwide. Early coronary revascularization is the most important treatment. Recent findings have revealed that reactive oxygen species (ROS) can lead to tissue damage following coronary artery revascularization, known as ischemia-reperfusion injury. In this study, we focused on a novel free radical scavenger, resorcimoline (RML). Last year, we reported the scavenging activity of RML in vitro against multiple ROS, confirmed by the electron spin resonance spectrometry.
Hypothesis
Resorcimoline might reduce ROS damage in cardiomyocytes, thereby exerting cardioprotective effects following coronary ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Methods
Nine-to-eleven-week-old male Wistar rats were subjected to acute myocardial ischemia induced by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery for 30 minutes. Rats received intravenous injections of RML at 6 mg/kg before the ligation release or saline as a control. The heart sections were double-stained at 24-hour reperfusion with Evans blue and triphenyltetrazolium chloride to assess the infarct area. Cardiac function was evaluated at 2-day and 7-day reperfusion with echocardiography. Myocardial fibrosis was assessed at 7-day reperfusion by Masson’s trichrome staining. Primary cultured rat cardiomyocytes were treated with 10 μM angiotensin II for 3.5 hours and then exposed to RML for 30 minutes. Cellular ROS assay kits were used to assess the levels of ROS in the cardiomyocytes.
Results
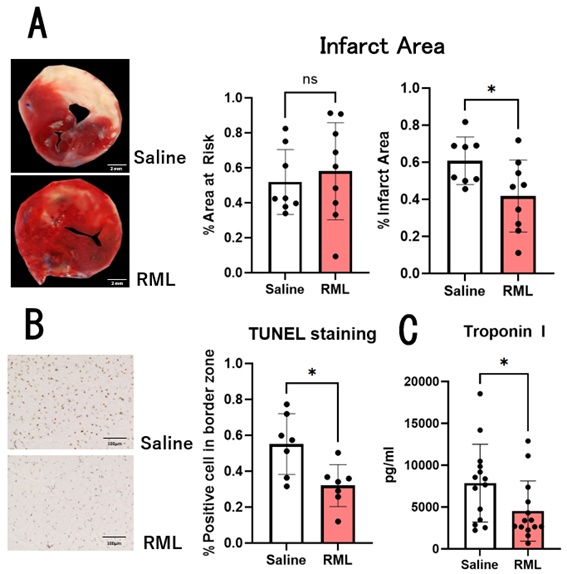
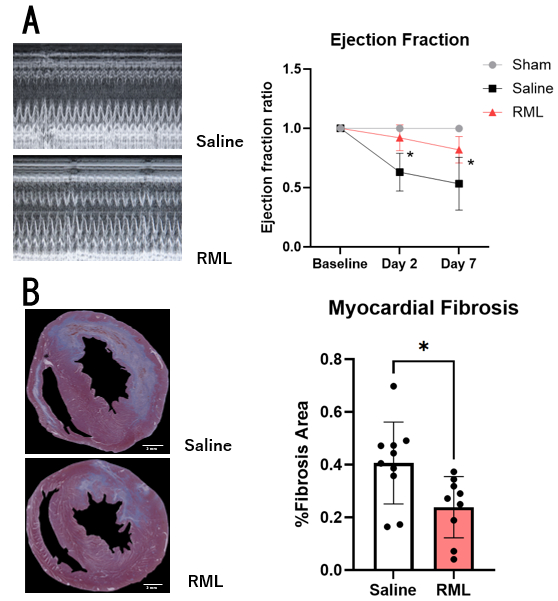
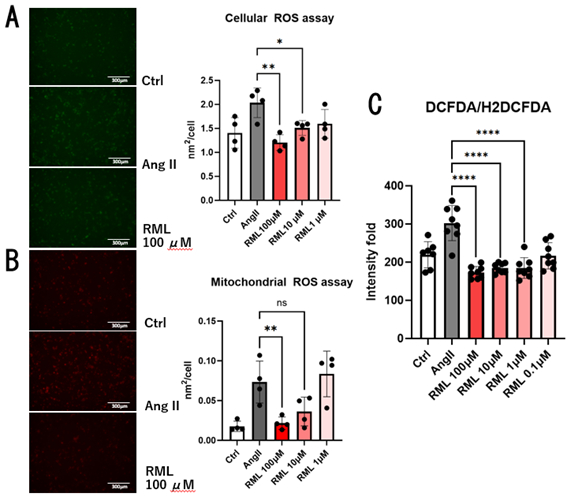
Infarct size in RML-treated animals was significantly smaller than in control animals (41.8±19.4% vs. 60.8±12.9%, p=0.03, Fig. 1A). Apoptotic cells in the border zone were significantly reduced in RML-treated animals (32.0±11.7% vs. 55.1±16.9%, p=0.01, Fig. 1B). Troponin I level in RML-treated animals was significantly lower than in control animals (p=0.04, Fig. 1C). Ejection fraction in RML-treated animals was significantly preserved at 2-day reperfusion and 7-day reperfusion when compared to control animals (p=0.001, p=0.003, Fig. 2A). Myocardial fibrosis area in RML-treated animals was significantly smaller than in control animals (23.9±11.7% vs. 40.6±15.6%, p=0.01, Fig. 2B). RML significantly reduced angiotensin II-induced ROS in cardiomyocytes in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 3A,B,C).
Conclusion
Resorcimoline exhibits cardioprotective effects following coronary ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing the infarct size and ROS damage in cardiomyocytes.
Background
Ischemic heart disease remains the leading cause of death worldwide. Early coronary revascularization is the most important treatment. Recent findings have revealed that reactive oxygen species (ROS) can lead to tissue damage following coronary artery revascularization, known as ischemia-reperfusion injury. In this study, we focused on a novel free radical scavenger, resorcimoline (RML). Last year, we reported the scavenging activity of RML in vitro against multiple ROS, confirmed by the electron spin resonance spectrometry.
Hypothesis
Resorcimoline might reduce ROS damage in cardiomyocytes, thereby exerting cardioprotective effects following coronary ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Methods
Nine-to-eleven-week-old male Wistar rats were subjected to acute myocardial ischemia induced by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery for 30 minutes. Rats received intravenous injections of RML at 6 mg/kg before the ligation release or saline as a control. The heart sections were double-stained at 24-hour reperfusion with Evans blue and triphenyltetrazolium chloride to assess the infarct area. Cardiac function was evaluated at 2-day and 7-day reperfusion with echocardiography. Myocardial fibrosis was assessed at 7-day reperfusion by Masson’s trichrome staining. Primary cultured rat cardiomyocytes were treated with 10 μM angiotensin II for 3.5 hours and then exposed to RML for 30 minutes. Cellular ROS assay kits were used to assess the levels of ROS in the cardiomyocytes.
Results
Infarct size in RML-treated animals was significantly smaller than in control animals (41.8±19.4% vs. 60.8±12.9%, p=0.03, Fig. 1A). Apoptotic cells in the border zone were significantly reduced in RML-treated animals (32.0±11.7% vs. 55.1±16.9%, p=0.01, Fig. 1B). Troponin I level in RML-treated animals was significantly lower than in control animals (p=0.04, Fig. 1C). Ejection fraction in RML-treated animals was significantly preserved at 2-day reperfusion and 7-day reperfusion when compared to control animals (p=0.001, p=0.003, Fig. 2A). Myocardial fibrosis area in RML-treated animals was significantly smaller than in control animals (23.9±11.7% vs. 40.6±15.6%, p=0.01, Fig. 2B). RML significantly reduced angiotensin II-induced ROS in cardiomyocytes in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 3A,B,C).
Conclusion
Resorcimoline exhibits cardioprotective effects following coronary ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing the infarct size and ROS damage in cardiomyocytes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acetylcholine-loaded Nanoparticles Protect Against Myocardial Injury In In Vitro Cardiac Spheroids and In an In Vivo Myocardial Infarction Murine Model
Liu Chung Ming Clara, Patil Runali, Refaat Ahmed, Vettori Laura, Couttas Timothy, Beck Dominik, Wang Xiaowei, Gentile Carmine
ACS-Specific Gut Microbial and Metabolic Profiles Reveal Diagnostic and Recovery MarkersXu Jing, Fu Jingyuan, Dai Die, Yang Yanan, Yang Jingang, Gao Shanshan, Wu Chongming, He Jiumin, Chen Weihua, Yang Yue-jin