Final ID: MP793
Association of TTR-Targeted Therapies with Cardiovascular Outcomes in Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy: A Real-World Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) is a progressive, infiltrative disease caused by deposition of misfolded transthyretin (TTR) amyloid fibrils in the myocardium. TTR-targeted therapies, including TTR stabilizers and gene silencers, have shown clinical benefit in randomized clinical trials. However, data on cardiovascular outcomes associated with these therapies in real-world settings remain limited.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study utilized electronic health record data from the TriNetX Research Network (2019–2025). Adults with a diagnosis of ATTR-CM were categorized into three groups based on prescription records: TTR stabilizers (e.g., tafamidis, acoramidis), TTR gene silencers (e.g., vutrisiran, eplontersen, patisiran, inotersen), or standard medical therapy. The primary outcome was a composite of ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF), cardiac arrest, or all-cause mortality. Cox proportional hazards models with inverse probability weighting (IPW) were used to estimate adjusted associations.
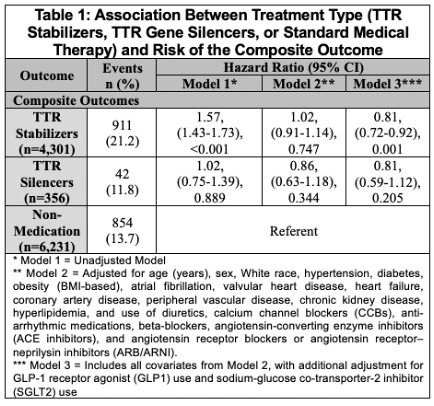
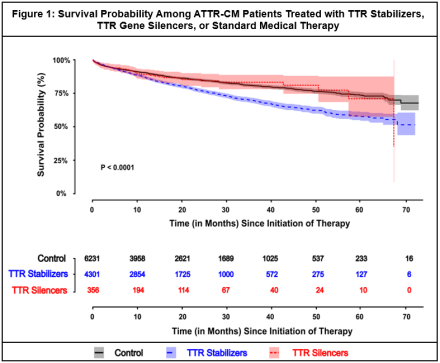
Results: Among 10,888 patients with ATTR-CM (34.8% female; median age 73 years [IQR 64–80]), 4,301 received a TTR stabilizer, 356 received a TTR gene silencer, and 6,231 were managed with standard therapy. In adjusted analyses using IPW, TTR stabilizer use was associated with a lower risk of the composite outcome compared with standard therapy (HR = 0.81; 95% CI: 0.72–0.92; p = 0.001). A non-significant association was observed for TTR gene silencers relative to standard therapy (HR = 0.81; 95% CI: 0.59–1.12; p = 0.205). (Table 1, Figure 1)
Conclusions: In this large, real-world analysis of patients with ATTR-CM, use of TTR stabilizers was associated with a lower incidence of major cardiovascular events compared with standard care. TTR gene silencers showed a similar directional association, though limited by a smaller sample size. These findings support further investigation in prospective studies to better understand the relationship between TTR-targeted therapies and clinical outcomes.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study utilized electronic health record data from the TriNetX Research Network (2019–2025). Adults with a diagnosis of ATTR-CM were categorized into three groups based on prescription records: TTR stabilizers (e.g., tafamidis, acoramidis), TTR gene silencers (e.g., vutrisiran, eplontersen, patisiran, inotersen), or standard medical therapy. The primary outcome was a composite of ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF), cardiac arrest, or all-cause mortality. Cox proportional hazards models with inverse probability weighting (IPW) were used to estimate adjusted associations.
Results: Among 10,888 patients with ATTR-CM (34.8% female; median age 73 years [IQR 64–80]), 4,301 received a TTR stabilizer, 356 received a TTR gene silencer, and 6,231 were managed with standard therapy. In adjusted analyses using IPW, TTR stabilizer use was associated with a lower risk of the composite outcome compared with standard therapy (HR = 0.81; 95% CI: 0.72–0.92; p = 0.001). A non-significant association was observed for TTR gene silencers relative to standard therapy (HR = 0.81; 95% CI: 0.59–1.12; p = 0.205). (Table 1, Figure 1)
Conclusions: In this large, real-world analysis of patients with ATTR-CM, use of TTR stabilizers was associated with a lower incidence of major cardiovascular events compared with standard care. TTR gene silencers showed a similar directional association, though limited by a smaller sample size. These findings support further investigation in prospective studies to better understand the relationship between TTR-targeted therapies and clinical outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Focus for Improvement - Factors for Lab Adherence in a Pediatric Preventive Cardiology Program
Holsinger Hunter, Porterfield Ronna, Taylor Makenna, Dresbach Bethany, Seipel Brittany, Igwe Chukwuemeka, Alvarado Chance, Tran Andrew
A Simple One-Item Nursing Falls Assessment Predicts Outcomes For Patients With Stage D Heart Failure Undergoing Surgical Advanced TherapiesSalvador Vincent, Perez Jaime Abraham, Hudec Paige, Gorodeski Eiran, Oneill Thomas