Final ID:
Polygenic Risk Enhances Penetrance and Prognosis in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Insights from a US-based Multi-Ancestry Cohort
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) has traditionally been considered a Mendelian disease driven by pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants of sarcomere encoding genes (SARC-HCM-P/LP), yet these variants explain only a third of the HCM cases. The variable penetrance observed in HCM has suggested a role for polygenic effects. Existing HCM polygenic risk scores (PRSs) have been derived mostly from European-ancestry cohorts, limiting their generalizability. In this study, a multi-ancestry PRS for HCM was developed and evaluated to assess association with HCM penetrance, risk, and outcomes.
Methods: A genome-wide PRS was constructed using summary statistics from the Biobank Japan, and a meta-analysis of seven European-ancestry cohorts, including UK Biobank. Ancestry-optimized weights were derived using PRS-CSx. The score was applied to 205,146 participants from the All of Us Research Program with whole genome sequencing, and values were standardized within ancestry groups. Participants were stratified by PRS risk groups and SARC-HCM-P/LP carrier status. Cox proportional hazard models (with age as time scale) were used to assess associations with heart failure, arrhythmias, and cardiomyopathy to evaluate lifetime risk.
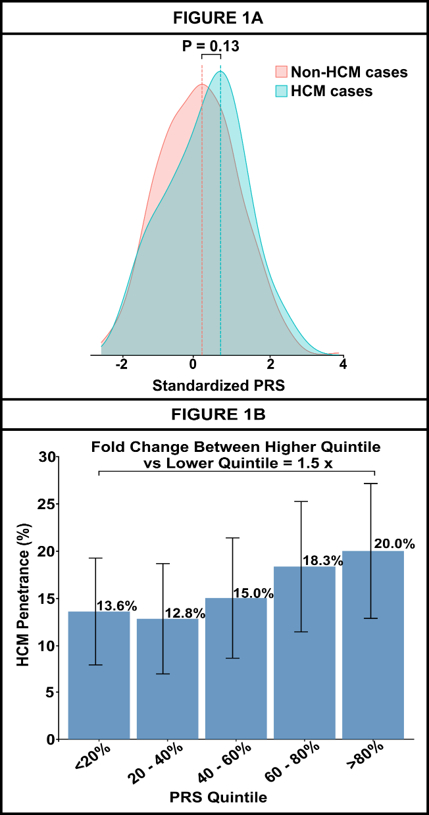
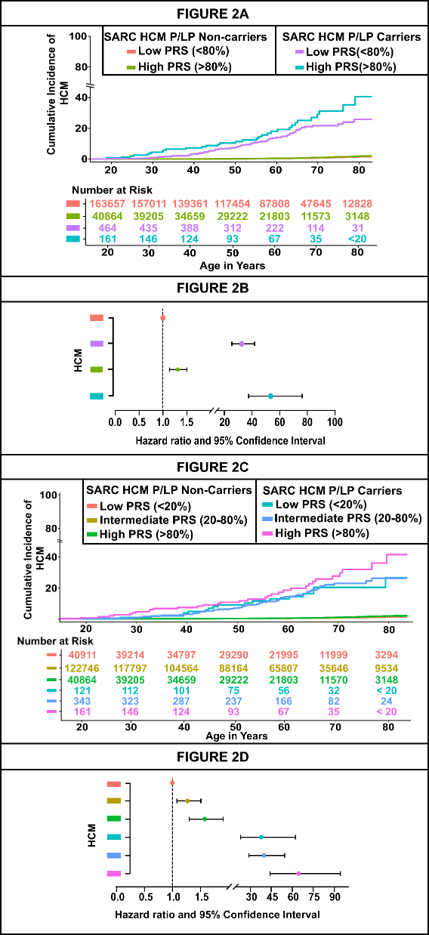
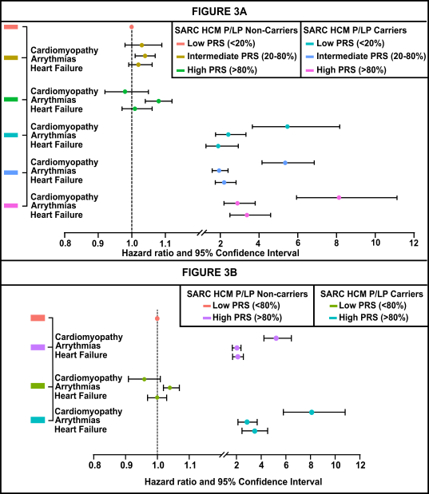
Results: Among 205,146 individuals [median age: 58 years, females: 124,586 (61%), non-European: 76,826 (37.5%)], each standard deviation increase in PRS was associated with higher HCM risk [HR: 1.22 (1.15, 1.29)]. Predictive performance was observed across ancestries (AUC: 0.66 in Europeans, 0.67 in South Asians, 0.63 in Admixed, 0.55 in Africans, 0.56 in East Asians). Among SARC-HCM-P/LP carriers, penetrance increased from 13.6% in the lowest PRS quintile to 20.0% in the highest. A strong additive effect was observed when both SARC-HCM-P/LP and high PRS risk were present [HR: 53.50 (37.51-76.30)] compared to those with SARC-HCM-P/LP carriers [HR: 32.60 (25.40-41.84)] alone and for individuals with high PRS [HR: 1.31 (1.14-1.50)] alone. Higher PRS was associated with increased hazard of cardiovascular outcomes, with markedly elevated risk in SARC-HCM-P/LP carriers compared to non-carriers.
Conclusion: An ancestry-informed PRS for HCM was shown to predict risk across diverse populations, stratify penetrance among SARC-HCM-P/LP carriers, and identify high-risk individuals who are non-carriers. These findings support the integration of PRS into clinical care alongside genetic testing to enhance personalized management of HCM.
Methods: A genome-wide PRS was constructed using summary statistics from the Biobank Japan, and a meta-analysis of seven European-ancestry cohorts, including UK Biobank. Ancestry-optimized weights were derived using PRS-CSx. The score was applied to 205,146 participants from the All of Us Research Program with whole genome sequencing, and values were standardized within ancestry groups. Participants were stratified by PRS risk groups and SARC-HCM-P/LP carrier status. Cox proportional hazard models (with age as time scale) were used to assess associations with heart failure, arrhythmias, and cardiomyopathy to evaluate lifetime risk.
Results: Among 205,146 individuals [median age: 58 years, females: 124,586 (61%), non-European: 76,826 (37.5%)], each standard deviation increase in PRS was associated with higher HCM risk [HR: 1.22 (1.15, 1.29)]. Predictive performance was observed across ancestries (AUC: 0.66 in Europeans, 0.67 in South Asians, 0.63 in Admixed, 0.55 in Africans, 0.56 in East Asians). Among SARC-HCM-P/LP carriers, penetrance increased from 13.6% in the lowest PRS quintile to 20.0% in the highest. A strong additive effect was observed when both SARC-HCM-P/LP and high PRS risk were present [HR: 53.50 (37.51-76.30)] compared to those with SARC-HCM-P/LP carriers [HR: 32.60 (25.40-41.84)] alone and for individuals with high PRS [HR: 1.31 (1.14-1.50)] alone. Higher PRS was associated with increased hazard of cardiovascular outcomes, with markedly elevated risk in SARC-HCM-P/LP carriers compared to non-carriers.
Conclusion: An ancestry-informed PRS for HCM was shown to predict risk across diverse populations, stratify penetrance among SARC-HCM-P/LP carriers, and identify high-risk individuals who are non-carriers. These findings support the integration of PRS into clinical care alongside genetic testing to enhance personalized management of HCM.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Echocardiography Risk Score Predicted Mortality In Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.
Iwakura Katsuomi, Yoshio Yasumura, Hikoso Shungo, Okada Katsuki, Nakatani Daisaku, Sotomi Yohei, Sakata Yasushi, Tanaka Nobuaki, Okada Masato, Okamura Atsunori, Heitaro Watanabe, Seo Masahiro, Hayashi Takaharu, Yano Masamichi, Yamada Takahisa
Cardiac METTL3/METTL14 Complex Mediated m6A Modification is Required for Heart DevelopmentBurke Savanna, Hand Sophie, Li Donna, Li Deqiang, Jang Jihyun