Final ID: MP2340
Retinal Vascular and Renal Biomarkers Predict Systemic Cardiovascular and Kidney Disease in the Brazilian Multilabel Ophthalmological Dataset (BRSET)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are leading global causes of morbidity and mortality, often exacerbated by late diagnosis and limited access to early detection methods. Conventional diagnostic tools are frequently invasive or inaccessible in resource-limited settings. Retinal imaging presents a non-invasive alternative, capturing microvascular features that reflect systemic health. However, most validation studies have focused on Asian and Western populations, leaving a gap in South American representation.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that deep learning models trained to predict systemic biomarkers from retinal images in a Korean population could generalize to a Brazilian cohort. Specifically, we examined whether retinal models estimating albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) for CKD, and coronary artery calcium for CVD, could effectively identify affected individuals using data from the Brazilian Multilabel Ophthalmological Dataset (BRSET).
Methods: We applied three retinal image-based models to 16,266 fundus images from 8,524 patients in BRSET. These models infer systemic biomarker values by analyzing retinal vascular and structural features. Ground truth labels were based on disease comorbidity annotations. Model performance was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), sensitivity, and specificity. Thresholds were optimized using the Youden index. Class imbalance (10 CKD cases and 89 CVD cases) in BRSET was preserved to reflect real-world disease prevalence.
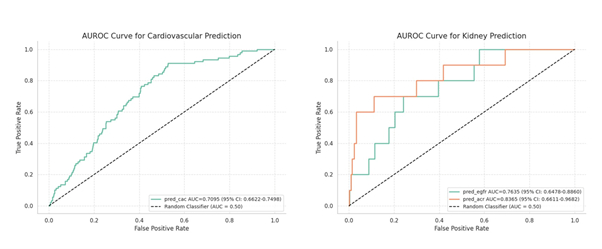
Results: For CKD detection, the ACR model achieved an AUROC of 0.84 (95%CI=0.66-0.97), sensitivity of 0.70, and specificity of 0.89. The eGFR model achieved an AUROC of 0.76 (95%CI=0.65-0.89), sensitivity of 0.70, and specificity of 0.76. For CVD, the coronary artery calcium model showed an AUROC of 0.71(95%CI=0.66-0.75), with high sensitivity (0.91) but lower specificity (0.47).
Conclusion: Deep learning-derived retinal biomarkers demonstrated generalizability from an Asian to a South American cohort, supporting their potential as scalable, non-invasive tools for early systemic disease detection. The ACR model performed best for CKD prediction, while other models showed fair discriminatory ability. Future work should focus on addressing class imbalance, increasing positive case representation, and conducting prospective validation.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that deep learning models trained to predict systemic biomarkers from retinal images in a Korean population could generalize to a Brazilian cohort. Specifically, we examined whether retinal models estimating albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) for CKD, and coronary artery calcium for CVD, could effectively identify affected individuals using data from the Brazilian Multilabel Ophthalmological Dataset (BRSET).
Methods: We applied three retinal image-based models to 16,266 fundus images from 8,524 patients in BRSET. These models infer systemic biomarker values by analyzing retinal vascular and structural features. Ground truth labels were based on disease comorbidity annotations. Model performance was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), sensitivity, and specificity. Thresholds were optimized using the Youden index. Class imbalance (10 CKD cases and 89 CVD cases) in BRSET was preserved to reflect real-world disease prevalence.
Results: For CKD detection, the ACR model achieved an AUROC of 0.84 (95%CI=0.66-0.97), sensitivity of 0.70, and specificity of 0.89. The eGFR model achieved an AUROC of 0.76 (95%CI=0.65-0.89), sensitivity of 0.70, and specificity of 0.76. For CVD, the coronary artery calcium model showed an AUROC of 0.71(95%CI=0.66-0.75), with high sensitivity (0.91) but lower specificity (0.47).
Conclusion: Deep learning-derived retinal biomarkers demonstrated generalizability from an Asian to a South American cohort, supporting their potential as scalable, non-invasive tools for early systemic disease detection. The ACR model performed best for CKD prediction, while other models showed fair discriminatory ability. Future work should focus on addressing class imbalance, increasing positive case representation, and conducting prospective validation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Signature of Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Aging Defines Elevated Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
Perera Sudheesha, Biswas Dhruva, Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Coppi Andreas, Khera Rohan
AI-enabled bone mineral density (AutoBMD AI) measurement in coronary artery calcium (CAC) scans associated with high CAC score independently of conventional risk factors: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)Naghavi Morteza, Atlas Kyle, Zhang Chenyu, Reeves Anthony, Atlas Thomas, Henschke Claudia, Yankelevitz David, Roy Sion, Budoff Matthew