Final ID: MP1075
Trimethylamine N-oxide Promotes Atrial Arrhythmia Susceptibility via Neuroglial IL-1β-Driven Inflammatory Activation of the Left Stellate Ganglion
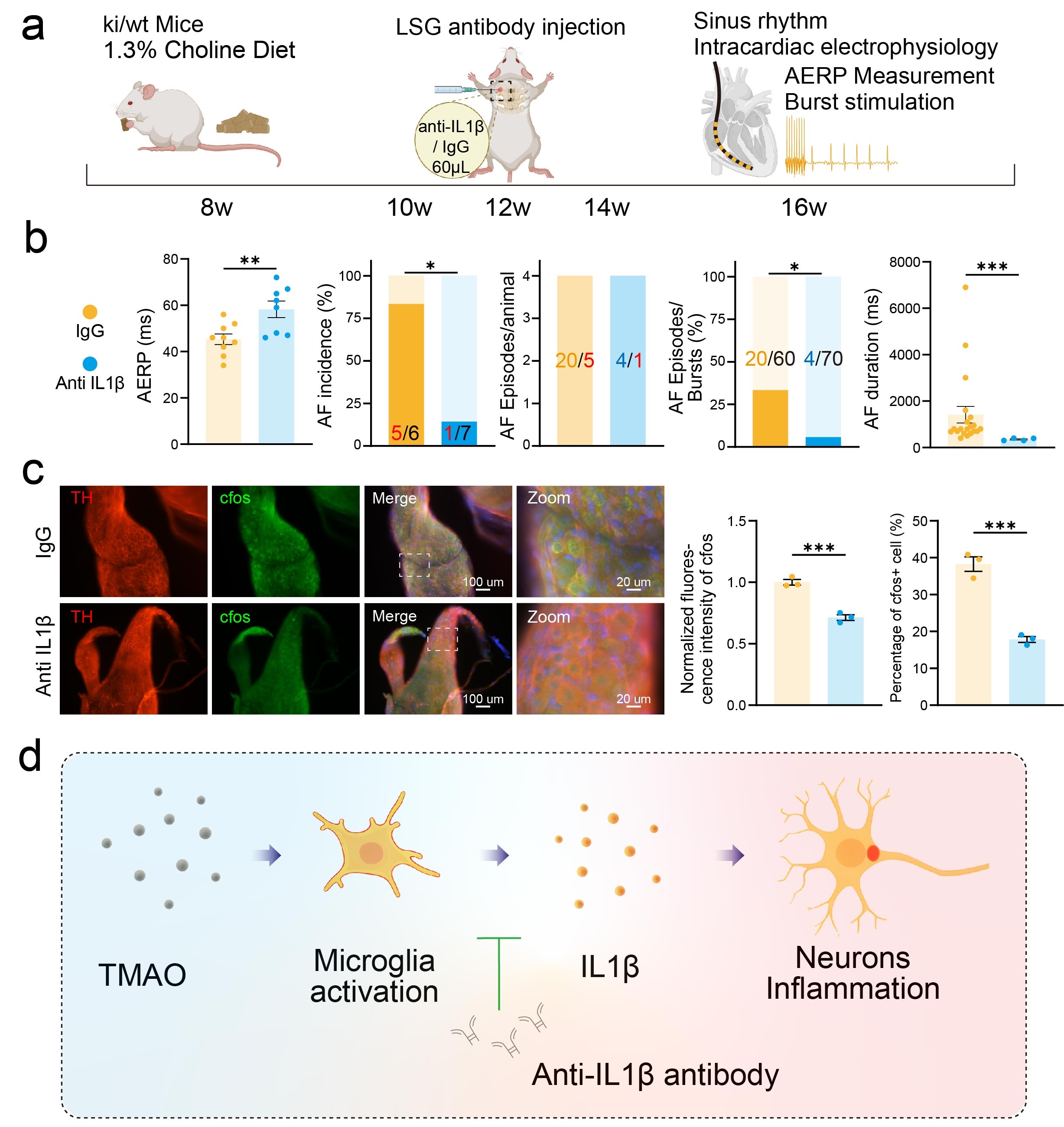
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Dietary choline intake has been epidemiologically linked to an increased risk of atrial fibrillation (AF); however, the mechanistic underpinnings of this association remain poorly understood. Among the metabolites derived from choline, trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) has emerged as a key pro-arrhythmic molecule, implicated in a variety of cardiovascular pathologies. In this study, we utilized a cardiac-specific CREM-IbΔC-X transgenic mouse model, which spontaneously develops AF, to explore the impact of chronic choline supplementation and subacute TMAO exposure on atrial electrophysiological stability. Chronic administration of a high-choline diet significantly accelerated the onset of spontaneous AF, increased the frequency of atrial premature beats, and exacerbated overall AF burden. In a parallel model, intraperitoneal injection of TMAO heightened AF susceptibility, an effect mediated through activation of the left stellate ganglion (LSG). This pro-arrhythmic effect was effectively abrogated by local LSG blockade with hexamethonium bromide, suggesting that autonomic modulation plays a central role. To further elucidate the molecular mechanisms, we performed bulk RNA sequencing of LSG tissue and observed a marked upregulation of inflammatory signaling pathways, with interleukin-1 (IL-1) signaling emerging as a dominant feature in TMAO-treated mice. In vitro studies confirmed that TMAO selectively induced IL-1β expression in neuroglial cells, which in turn activated co-cultured hippocampal neurons, highlighting a neuron–glia crosstalk mechanism. Critically, in vivo microinjection of an IL-1β monoclonal antibody into the LSG significantly attenuated high-choline diet-induced ganglionic activation and reduced AF susceptibility. These findings identify neuroglial IL-1β–mediated inflammation within the LSG as a novel mechanistic link between dietary choline metabolism and atrial arrhythmogenesis. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that TMAO enhances atrial arrhythmia vulnerability in a spontaneous AF mouse model via neuroglial IL-1β–driven inflammatory activation of the left stellate ganglion, providing new insights into the diet–gut–brain–heart axis in AF pathophysiology.
More abstracts on this topic:
The Effects of Dietary Patterns and Sodium Reduction on Blood Pressure in Type 2 Diabetes: Results of the DASH4D Randomized Trial
Pilla Scott, Yeh Hsin-chieh, Mitchell Christine, Wang Nae-yuh, Appel Lawrence
A Comparison of Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients with and without Adult Congenital Heart Disease Undergoing Catheter Ablation for Ventricular TachycardiaFutela Pragyat, Poddar Aastha, Kowlgi Gurukripa