Final ID: MDP1177
AI-Assisted Transseptal Puncture: Visual-Prompt Fine-Tuning of Foundation Models on Low-Dose X-RAY Images
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Transseptal puncture (TSP) is a critical step allowing access from right atrium to left atrium in cardiac interventions. The operation relies heavily on real-time X-ray imaging and often involves subjective decision-making needing experience. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly visual foundation model offer promising solutions to enhance the precision and consistency of TSP.
Research questions
We hypothesize that a foundation model fine-tuned on real TSP images and expert annotations, can accurately predict the optimal puncture site on imaging.
Aims
This study aims to develop and validate an AI method that automatically identifies the ideal TSP site using only the CS catheter as a reference in X-RAY image. This approach seeks to replicate the decision-making process of experienced clinicians, thereby improving the accuracy and safety of the procedure.
Methods
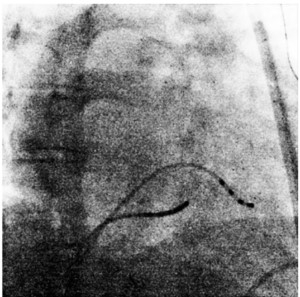
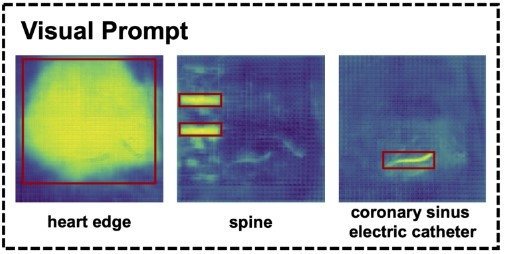
A pilot study enrolled 101 patients in one center. Three experienced senior practitioners are responsible for labeling these images. To learn information from limited X-RAY images, we design a co-training framework based on Segment Anything Model (SAM) to fine-tune the decision module for TSP by combining visual prompts of the three bounding boxes (heart edge, spine, and coronary sinus electrode). The input images are captured before puncture and resized to 512*512. The candidate puncture area is set as a circle centered at actual puncture point with a radius of 10 pixels.
Results
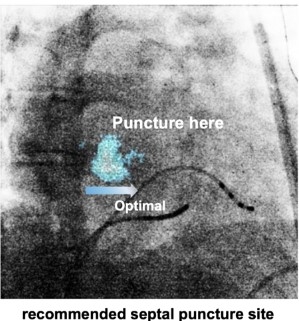
Images from 80 patients were used to fine-tune the decision module, while 21 for validation. The Intersection over Union (IoU) on validation set is 70.22% for the pre-defined candidate TSP circle. In validation, the success rates of the predicted TSP point (the center of the predicted area) falling within radii of 5, 10, 15 pixels cantered on the actual TSP site are 56.30%, 72.01% and 83.54%, respectively.
Conclusions
In this study, we introduce an AI-assisted visual prompt for TSP using SAM-based fine-tuning. With the limited samples, the performance of puncture-site prediction underscores the potential of our framework as an efficient solution for TSP guidance and assistance. The future works include expanding the sample size and testing whether visual prompts can enhance TSP quality and clinical training.
Background
Transseptal puncture (TSP) is a critical step allowing access from right atrium to left atrium in cardiac interventions. The operation relies heavily on real-time X-ray imaging and often involves subjective decision-making needing experience. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly visual foundation model offer promising solutions to enhance the precision and consistency of TSP.
Research questions
We hypothesize that a foundation model fine-tuned on real TSP images and expert annotations, can accurately predict the optimal puncture site on imaging.
Aims
This study aims to develop and validate an AI method that automatically identifies the ideal TSP site using only the CS catheter as a reference in X-RAY image. This approach seeks to replicate the decision-making process of experienced clinicians, thereby improving the accuracy and safety of the procedure.
Methods
A pilot study enrolled 101 patients in one center. Three experienced senior practitioners are responsible for labeling these images. To learn information from limited X-RAY images, we design a co-training framework based on Segment Anything Model (SAM) to fine-tune the decision module for TSP by combining visual prompts of the three bounding boxes (heart edge, spine, and coronary sinus electrode). The input images are captured before puncture and resized to 512*512. The candidate puncture area is set as a circle centered at actual puncture point with a radius of 10 pixels.
Results
Images from 80 patients were used to fine-tune the decision module, while 21 for validation. The Intersection over Union (IoU) on validation set is 70.22% for the pre-defined candidate TSP circle. In validation, the success rates of the predicted TSP point (the center of the predicted area) falling within radii of 5, 10, 15 pixels cantered on the actual TSP site are 56.30%, 72.01% and 83.54%, respectively.
Conclusions
In this study, we introduce an AI-assisted visual prompt for TSP using SAM-based fine-tuning. With the limited samples, the performance of puncture-site prediction underscores the potential of our framework as an efficient solution for TSP guidance and assistance. The future works include expanding the sample size and testing whether visual prompts can enhance TSP quality and clinical training.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multicenter Friedreich Ataxia Registry Identifies Posterior Wall Thickness as a Predictor of Major Adverse Cardiac Events
Lin Kimberly, Johnson Jonathan, Mccormack Shana, Lynch David, Tate Barbara, Feng Yixuan, Huang Jing, Mercer-rosa Laura, Dedio Anna, Mcsweeney Kara, Fournier Anne, Yoon Grace, Payne Ronald, Cripe Linda, Patel Aarti, Niaz Talha
A Case Report of Cardiac Tamponade due to Mycoplasma Pneumoniae-induced Pericarditis - A Rare Complication of a Commonly seen Bacterial InfectionPatel Vidhi, Maharjan Reeju, Okan Tetyana, Singh Bhupinder, Colasacco Joseph