Final ID: MP27
Timing of Carbohydrate Intake and Cardiovascular Disease: The Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL)
Abstract Body: Introduction: Dietary carbohydrates (CHOs) can substantially impact cardiometabolic risk. Given the circadian rhythm of metabolism, CHO intake timing may also impact CVD risk.
Hypothesis: The association of CHO intake with CVD risk varies depending on CHO quality intake timing.
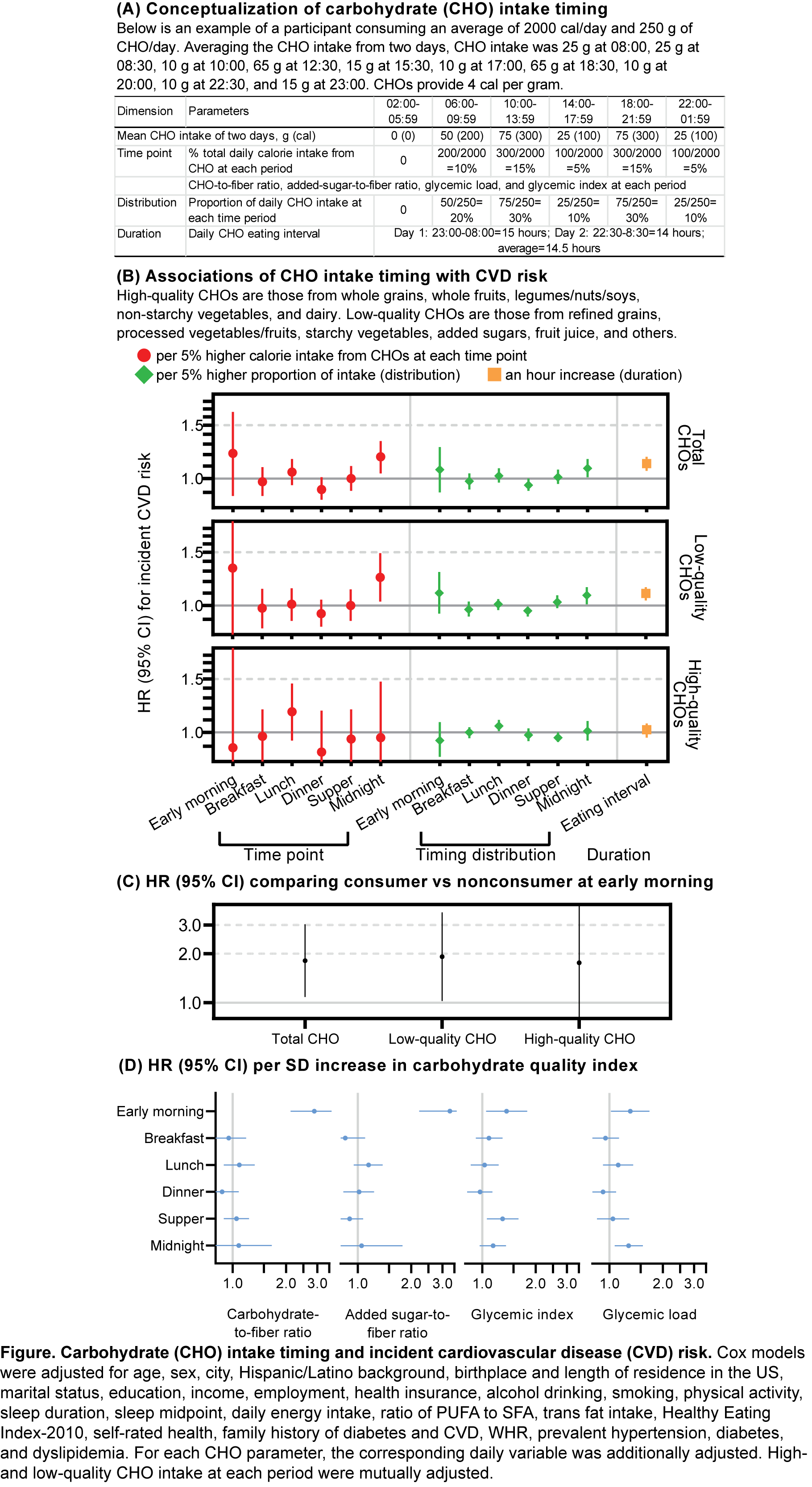
Methods: Among 12,401 HCHS/SOL participants free of CVD and cancer at baseline (2008-11), CHO intake timing was assessed by two 24-h dietary recalls: absolute CHO intake at each period (time point), proportion of CHO intake at each period (timing distribution), and CHO intake duration (Fig A). We also considered CHO quality by examining high- and low-quality carbohydrate intake (based on food sources, Fig B), carbohydrate-to-fiber ratio, added-sugar-to-fiber ratio, and glycemic load and index at each period. Associations of CHO intake timing with adjudicated incident CVD (including CHD, stroke, and heart failure) were tested by Cox models adjusted for sociodemographic, lifestyle, dietary, and health covariates.
Results: Over a median follow-up of 9.7 y, 217 CVD cases occurred. At midnight, a 5% higher daily calorie intake from total and low-quality CHOs was associated with an HR of 1.18 (95% CI 1.04-1.33) and 1.24 (1.03-1.49) for CVD risk, respectively (Fig B). In early morning, HRs comparing consumption to no consumption of total and low-quality CHOs were 1.81 (1.09-3.02) and 1.92 (1.03-3.58) for CVD risk (Fig C), and poorer carbohydrate quality indices were associated with higher CVD risk (Fig D). A one-hour longer intake interval for total and low-quality CHOs was associated with an HR of 1.12 (1.06-1.18) and 1.10 (1.04-1.15) for CVD risk (Fig B). Timing of high-quality carbohydrate intake showed minimal association with CVD risk (Fig B&C).
Conclusion: Higher CHO intake at midnight and early morning, along with longer CHO intake duration, particularly from low-quality sources, is associated with higher CVD risk in US Hispanic/Latino adults. CHO intake timing might need to be included in future dietary recommendations for CVD prevention.
Hypothesis: The association of CHO intake with CVD risk varies depending on CHO quality intake timing.
Methods: Among 12,401 HCHS/SOL participants free of CVD and cancer at baseline (2008-11), CHO intake timing was assessed by two 24-h dietary recalls: absolute CHO intake at each period (time point), proportion of CHO intake at each period (timing distribution), and CHO intake duration (Fig A). We also considered CHO quality by examining high- and low-quality carbohydrate intake (based on food sources, Fig B), carbohydrate-to-fiber ratio, added-sugar-to-fiber ratio, and glycemic load and index at each period. Associations of CHO intake timing with adjudicated incident CVD (including CHD, stroke, and heart failure) were tested by Cox models adjusted for sociodemographic, lifestyle, dietary, and health covariates.
Results: Over a median follow-up of 9.7 y, 217 CVD cases occurred. At midnight, a 5% higher daily calorie intake from total and low-quality CHOs was associated with an HR of 1.18 (95% CI 1.04-1.33) and 1.24 (1.03-1.49) for CVD risk, respectively (Fig B). In early morning, HRs comparing consumption to no consumption of total and low-quality CHOs were 1.81 (1.09-3.02) and 1.92 (1.03-3.58) for CVD risk (Fig C), and poorer carbohydrate quality indices were associated with higher CVD risk (Fig D). A one-hour longer intake interval for total and low-quality CHOs was associated with an HR of 1.12 (1.06-1.18) and 1.10 (1.04-1.15) for CVD risk (Fig B). Timing of high-quality carbohydrate intake showed minimal association with CVD risk (Fig B&C).
Conclusion: Higher CHO intake at midnight and early morning, along with longer CHO intake duration, particularly from low-quality sources, is associated with higher CVD risk in US Hispanic/Latino adults. CHO intake timing might need to be included in future dietary recommendations for CVD prevention.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of the Mediterranean Diet with White Matter Integrity Among Hispanics/Latinos. Final Results from the Study of Latinos-Investigation of Neurocognitive Aging-MRI (SOL-INCA-MRI) Ancillary Study
Trifan Gabriela, Talavera Gregory, Maillard Pauline, Daviglus Martha, Gonzalez Hector M, Decarli Charles, Testai Fernando, Moustafa Bayan, Isasi Carmen, Lipton Richard, Sotres-alvarez Daniela, Cai Jianwen, Tarraf Wassim, Stickel Ariana, Mattei Josiemer
Assessment of Dietary Recall Plausibility Using an Updated Formula that Considers Energy Intake Measured by Doubly-Labeled WaterSantos Baez Leinys, Ravelli Michele N., Diaz-rizzolo Diana A., Popp Collin, Cheng Bin, Gallagher Dympna, Schoeller Dale, Laferrere Blandine