Final ID: Su2078
Cardiac Rehabilitation In a Safety Net Population (CRISP): Functional Outcomes Assessed by 6-Minute Walk Test
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) is recommended for secondary prevention following a range of cardiovascular insults and is proven to improve functional status and mobility in clinical trials. However, the feasibility and impact of CR in socioeconomically disadvantaged and ethnically diverse safety net populations remain understudied. This study evaluates changes in 6-minute walk test (6MWT) distances following CR in a safety-net healthcare system of the Department of Health Services (DHS) for the county of Los Angeles.
Methods:
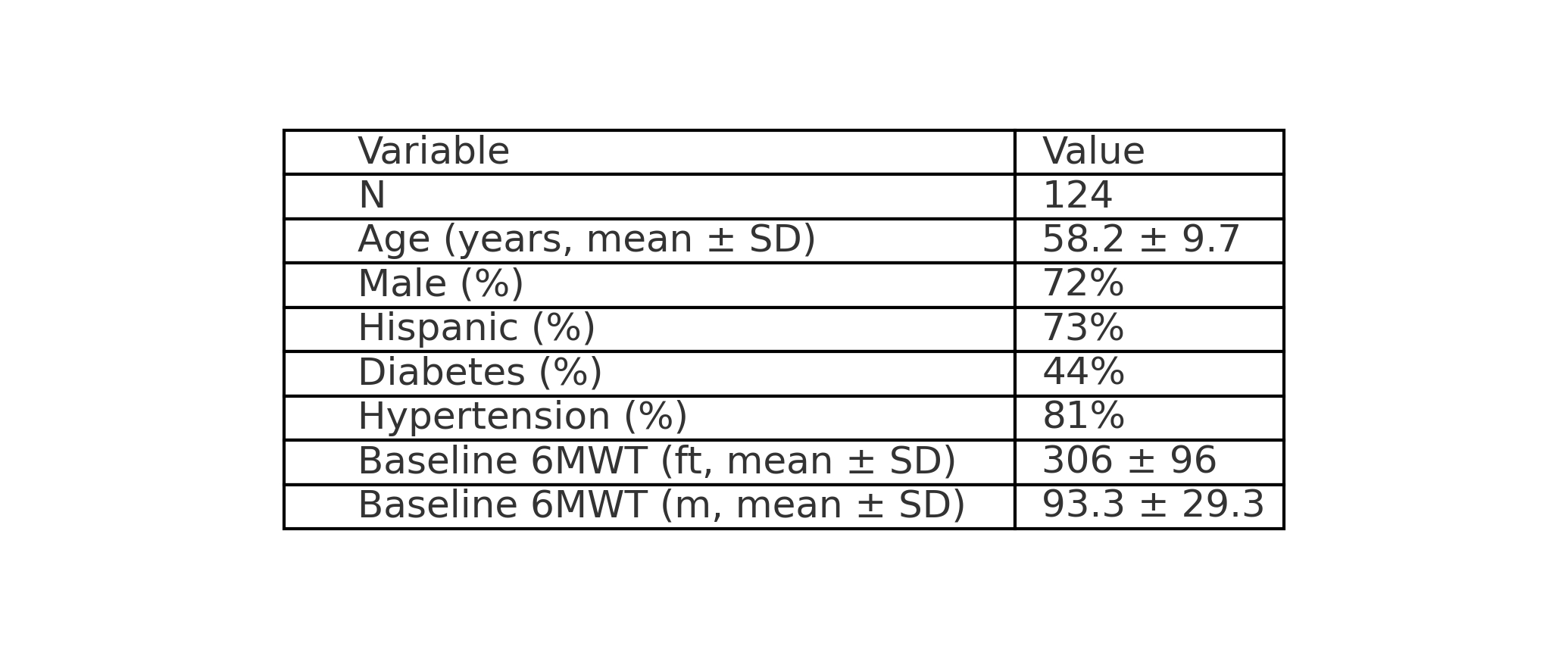
We retrospectively analyzed 128 patients who completed a public health system CR program in 2022 through 2024 with paired 6MWT distances. Demographics included age (mean 58.2±9.7 years), gender (72% male), and ethnicity (73% Hispanic). The primary outcome was change in 6MWT distance. Responders were defined as achieving ≥50 ft or ≥10% improvement. Multivariable linear and logistic regressions assessed predictors of improvement and responder status.
Results:
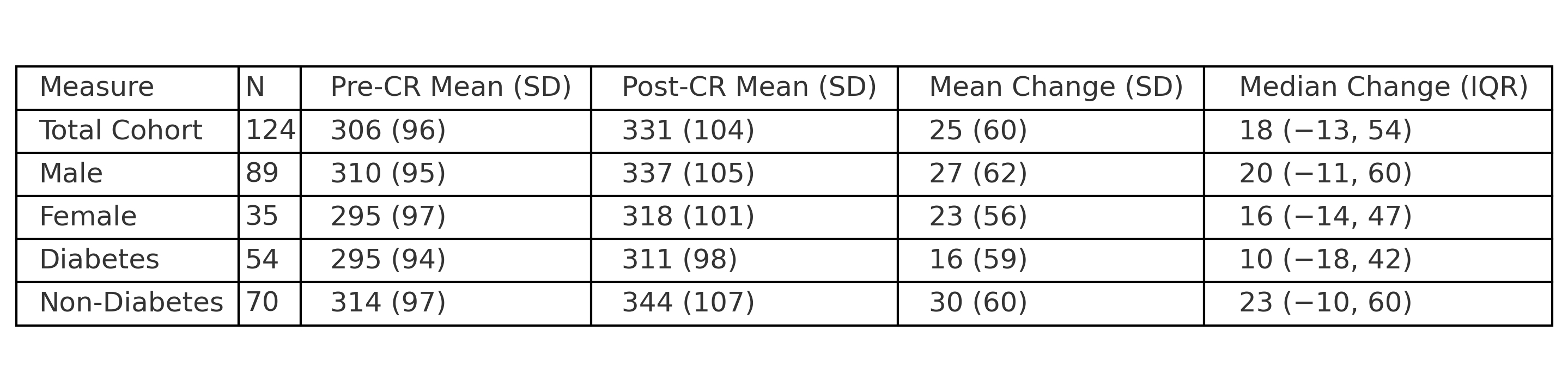
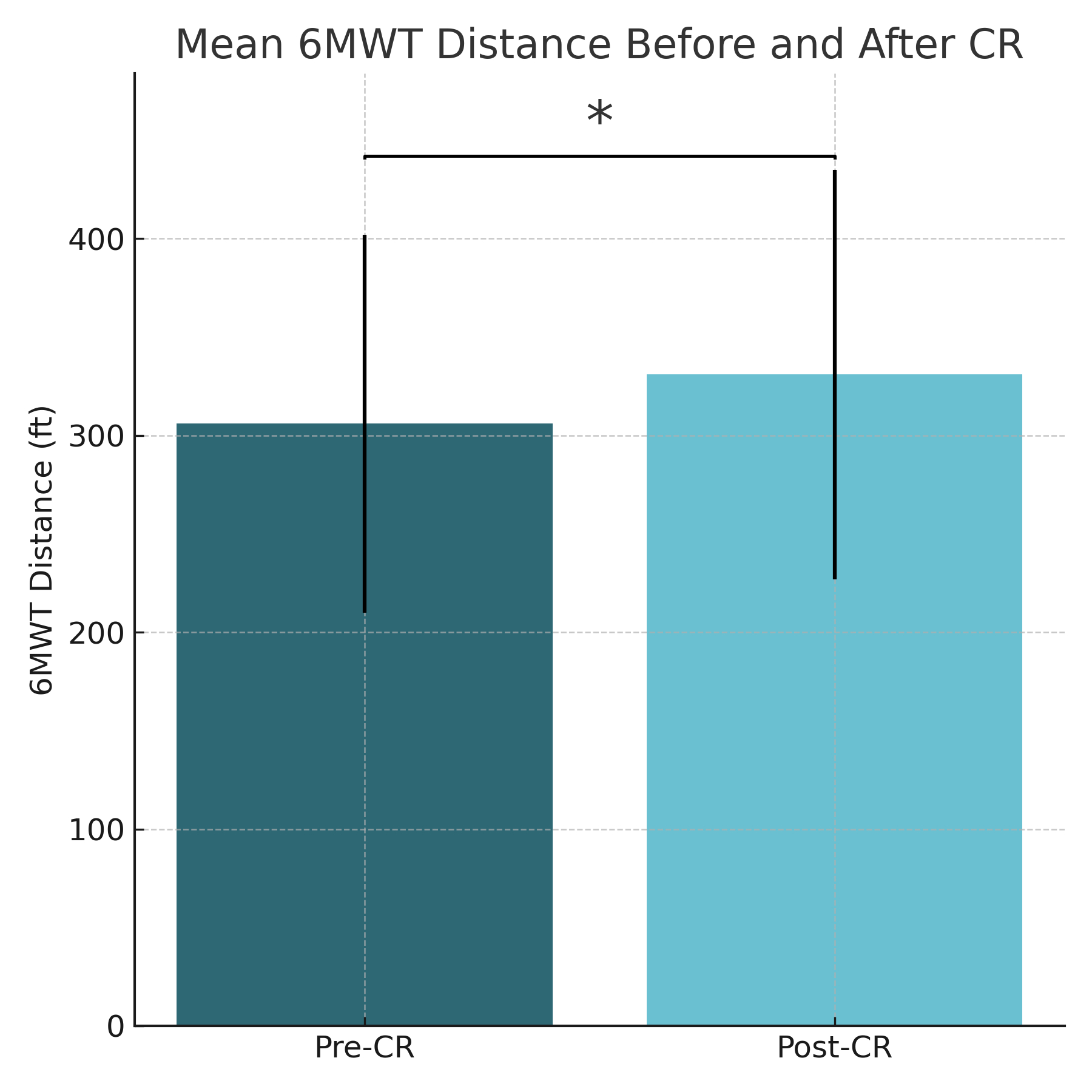
Mean baseline and post-CR 6MWT distances were 1,112±426 ft and 1,322±470 ft, respectively (mean change +210±246 ft, p<0.001). Improvement was significant across all age (<50, 50–60, >60), gender, and major ethnic groups. 78% of participants met the ≥50 ft responder threshold, and 63% met the ≥10% threshold. Male participants had higher responder rates compared to female participants (85% vs 61% for ≥50 ft, p<0.01). In multivariable analysis, male gender independently predicted responder status (OR 4.7, 95% CI 1.8–12.7, p=0.002), while age, baseline function, and ethnicity were not significant predictors.
Conclusions:
In this safety net population patients saw a statistically significant and clinically meaningful increase in their 6MWT distances after undergoing cardiac rehabilitation. Earlier studies of cardiac rehabilitation more commonly used other maximal exercise protocols for endpoints, whereas more recent studies have used the 6MWT as a more practical, submaximal measure of functional capacity, especially for patients with multiple comorbidities. These findings support the implementation and value of CR for improving mobility and functional outcomes in socioeconomically disadvantaged, ethnically diverse populations.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) is recommended for secondary prevention following a range of cardiovascular insults and is proven to improve functional status and mobility in clinical trials. However, the feasibility and impact of CR in socioeconomically disadvantaged and ethnically diverse safety net populations remain understudied. This study evaluates changes in 6-minute walk test (6MWT) distances following CR in a safety-net healthcare system of the Department of Health Services (DHS) for the county of Los Angeles.
Methods:
We retrospectively analyzed 128 patients who completed a public health system CR program in 2022 through 2024 with paired 6MWT distances. Demographics included age (mean 58.2±9.7 years), gender (72% male), and ethnicity (73% Hispanic). The primary outcome was change in 6MWT distance. Responders were defined as achieving ≥50 ft or ≥10% improvement. Multivariable linear and logistic regressions assessed predictors of improvement and responder status.
Results:
Mean baseline and post-CR 6MWT distances were 1,112±426 ft and 1,322±470 ft, respectively (mean change +210±246 ft, p<0.001). Improvement was significant across all age (<50, 50–60, >60), gender, and major ethnic groups. 78% of participants met the ≥50 ft responder threshold, and 63% met the ≥10% threshold. Male participants had higher responder rates compared to female participants (85% vs 61% for ≥50 ft, p<0.01). In multivariable analysis, male gender independently predicted responder status (OR 4.7, 95% CI 1.8–12.7, p=0.002), while age, baseline function, and ethnicity were not significant predictors.
Conclusions:
In this safety net population patients saw a statistically significant and clinically meaningful increase in their 6MWT distances after undergoing cardiac rehabilitation. Earlier studies of cardiac rehabilitation more commonly used other maximal exercise protocols for endpoints, whereas more recent studies have used the 6MWT as a more practical, submaximal measure of functional capacity, especially for patients with multiple comorbidities. These findings support the implementation and value of CR for improving mobility and functional outcomes in socioeconomically disadvantaged, ethnically diverse populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A comparison of outpatient cardiac rehabilitation access between rural and urban counties in Tennessee
Tran Phoebe, Fogelson Benjamin, Sorey Andrew, Heidel Robert, Baljepally Raj
Cardiac Rehabilitation In a Safety Net Population - Effects on Hypertension ManagementBurke Morgan, Gan Arnold, Jinno Stephanie, Ge Brandon, Haq Ubayd, Balasubramanian Satish, Chen Grace, Gordon Samuel