Final ID: Sa3109
Cardiovascular Adverse Events in BTKi-Treated Patients: A Propensity-Matched Study of Ibrutinib and Acalabrutinib
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKis) have transformed the management of B-cell malignancies but have varying cardiovascular toxicity profiles. We evaluated and compared the incidence of cardiovascular adverse events between ibrutinib and acalabrutinib in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Methods
We performed a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX database, including adults treated with ibrutinib (n=6,114) or acalabrutinib (n=4,663). Patients receiving both therapies within five years were excluded. The index event was initiation of ibrutinib or acalabrutinib therapy, with a 680 day follow up for cardiovascular outcomes. Propensity score matching was performed 1:1 across the overall population and within each disease subgroup. The primary outcome was the incidence of six adverse cardiovascular events (CVAEs): cardiac rhythm disorders, cerebrovascular disease, revascularization procedures, heart failure, ischemic heart disease, and inflammatory conditions (pericarditis, myocarditis). Hazard ratios (HRs) were derived from Cox regression, and Kaplan-Meier methods assessed event-free survival.
Results
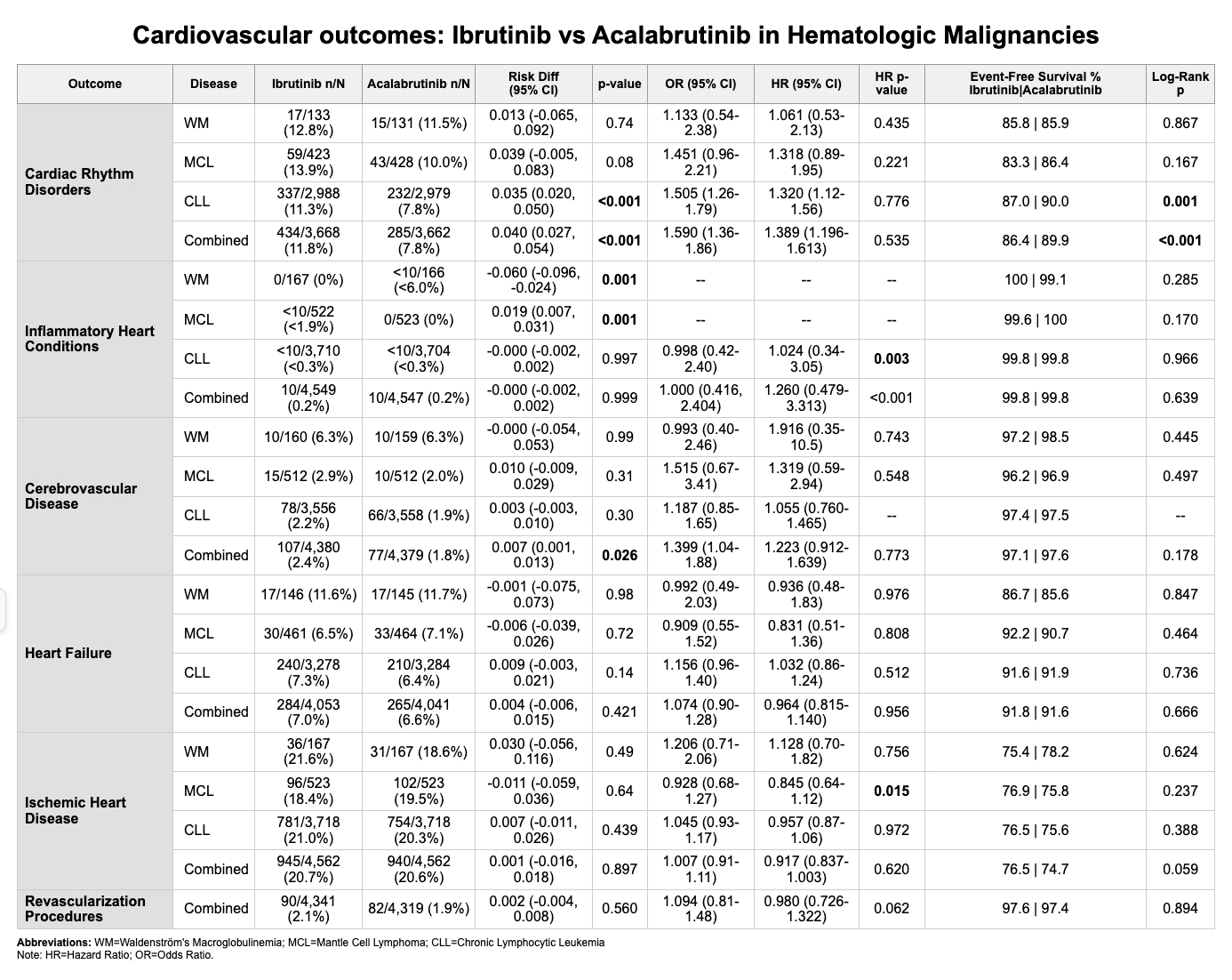
After matching, 4,562 patients remained in each group. Baseline cardiovascular comorbidities and medication use were balanced. Ibrutinib was associated with significantly higher rates of cardiac rhythm disorders (11.8% vs 7.8%; HR 1.39, 95% CI 1.20–1.61; p<0.001), primarily driven by the CLL subgroup (11.3% vs 7.8%; HR 1.32, p=0.001). Cerebrovascular events were also higher with ibrutinib overall (2.4% vs 1.8%; OR 1.40, 95% CI 1.04–1.88; p=0.026), though not statistically significant in subgroup analyses. No significant differences were observed in cardiac revascularization procedures (2.1% vs 1.9%, p=0.560; HR 0.980, 95% CI: 0.726-1.322), heart failure (7.0% vs 6.6%, p=0.421; HR 0.964, 95% CI: 0.815-1.140), ischemic heart disease (20.7% vs 20.6%, p=0.897; HR 0.917, 95% CI: 0.837-1.003), or inflammatory heart conditions (0.2% vs 0.2%, p=0.999; HR 1.260, 95% CI: 0.479-3.313).
Conclusions
In this large, real-world analysis of patients with B-cell malignancies, ibrutinib was associated with significantly higher rates of cardiac rhythm disorders and cerebrovascular events compared to acalabrutinib, particularly in CLL patients. These real-world findings may support the use of acalabrutinib compared to ibrutinib in patients with elevated cardiovascular risk.
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKis) have transformed the management of B-cell malignancies but have varying cardiovascular toxicity profiles. We evaluated and compared the incidence of cardiovascular adverse events between ibrutinib and acalabrutinib in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Methods
We performed a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX database, including adults treated with ibrutinib (n=6,114) or acalabrutinib (n=4,663). Patients receiving both therapies within five years were excluded. The index event was initiation of ibrutinib or acalabrutinib therapy, with a 680 day follow up for cardiovascular outcomes. Propensity score matching was performed 1:1 across the overall population and within each disease subgroup. The primary outcome was the incidence of six adverse cardiovascular events (CVAEs): cardiac rhythm disorders, cerebrovascular disease, revascularization procedures, heart failure, ischemic heart disease, and inflammatory conditions (pericarditis, myocarditis). Hazard ratios (HRs) were derived from Cox regression, and Kaplan-Meier methods assessed event-free survival.
Results
After matching, 4,562 patients remained in each group. Baseline cardiovascular comorbidities and medication use were balanced. Ibrutinib was associated with significantly higher rates of cardiac rhythm disorders (11.8% vs 7.8%; HR 1.39, 95% CI 1.20–1.61; p<0.001), primarily driven by the CLL subgroup (11.3% vs 7.8%; HR 1.32, p=0.001). Cerebrovascular events were also higher with ibrutinib overall (2.4% vs 1.8%; OR 1.40, 95% CI 1.04–1.88; p=0.026), though not statistically significant in subgroup analyses. No significant differences were observed in cardiac revascularization procedures (2.1% vs 1.9%, p=0.560; HR 0.980, 95% CI: 0.726-1.322), heart failure (7.0% vs 6.6%, p=0.421; HR 0.964, 95% CI: 0.815-1.140), ischemic heart disease (20.7% vs 20.6%, p=0.897; HR 0.917, 95% CI: 0.837-1.003), or inflammatory heart conditions (0.2% vs 0.2%, p=0.999; HR 1.260, 95% CI: 0.479-3.313).
Conclusions
In this large, real-world analysis of patients with B-cell malignancies, ibrutinib was associated with significantly higher rates of cardiac rhythm disorders and cerebrovascular events compared to acalabrutinib, particularly in CLL patients. These real-world findings may support the use of acalabrutinib compared to ibrutinib in patients with elevated cardiovascular risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case Series of Papillary Fibroelastomas on the Coumadin ridge
Aboukhatwa Omar, Akiki Elias, Kurmann Reto, Larson Kathryn, Keeney Michael, Bois Melanie, Klarich Kyle
A Blood(y) Pressure Crisis: Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage as a Rare Manifestation of Severely Uncontrolled HypertensionNandyal Shreyas, Amdetsion Gedion Yilma, Varma Revati, Kohli Saksham, Hammo Hasan