Final ID: Sa2068
Clinical outcomes associated with utilization of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in heart failure patients in the United States
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Current evidence recommends glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) utilization in type 2 diabetes or obesity with cardiovascular diseases. However, GLP-1 RA utility in improving HF outcomes has been variable across studies. We sought to investigate the current practice in prescribing GLP1-RA in a large database and assess their impact on heart failure hospitalization and all-cause mortality.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective study using the TriNetX database from January 2023 through April 2024 including adults with heart failure, and either type II diabetes or obesity. Patients were excluded if they had diabetes mellitus type 1, multiple endocrine neoplasia [MEN] type IIA, malignant neoplasms of thyroid gland, or presence of ketoacidosis. Patients were divided into two groups based on the utilization of GLP1-RA. Clinical characteristics, demographics and medications use were compared using appropriate statistics. Propensity score matching (PSM) (1:1, SD<0.1) balanced the baseline characteristics. Cox regression and Kaplan–Meier survival curves evaluated clinical outcomes of heart failure hospitalization and 1 year all-cause mortality.
Results
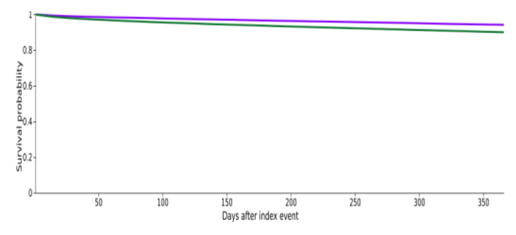
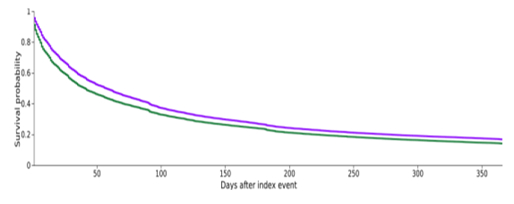
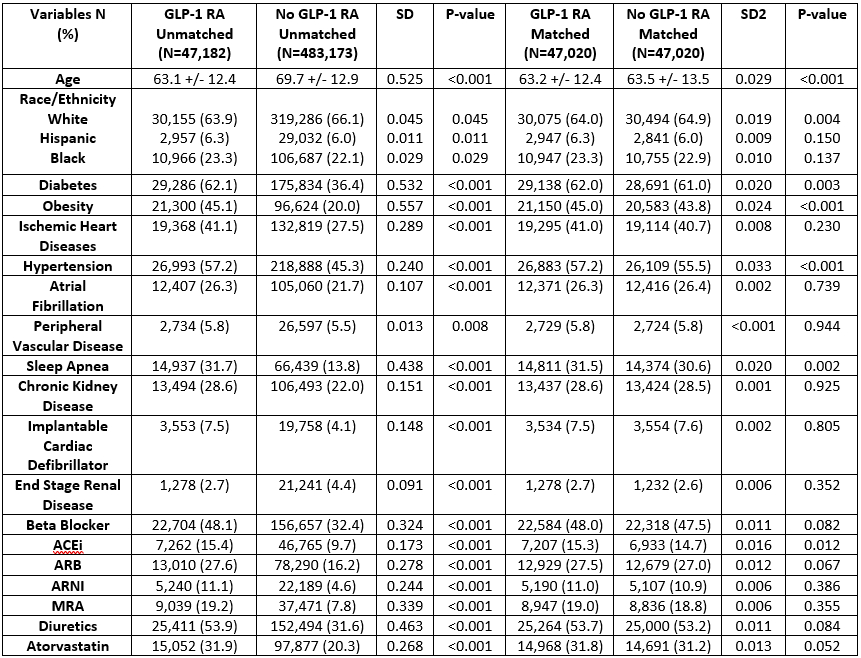
Out of 530,355 heart failure patients, 47,179 (8.8%) were prescribed GLP-1 RA. Mean age in GLP-1 RA group was 63 ±12 years and 46.7% were female. The GLP1-RA group patients were younger, had significantly higher proportions of type II diabetes, obesity, obstructive sleep apnea, ischemic heart disease, chronic kidney disease, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and more likely to receive guideline directed medical therapy. Using propensity score matching, 47,020 patients on GLP-1 RA were matched with 47,020 patients in the control group. GLP1-RA utilization was significantly associated with lower 1 year all-cause mortality [HR 0.56 (0.53-0.59)], heart failure hospitalization [HR 0.86 (0.85-0.87)] and the composite outcome of all-cause mortality and heart failure hospitalization [ 0.85 (0.84-0.87)].
Conclusion
Our study showed that utilizing GLP-1 RA in heart failure patients with either type II DM or obesity was associated with lower all-cause mortality and heart failure hospitalization at 1 year follow up.
Background
Current evidence recommends glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) utilization in type 2 diabetes or obesity with cardiovascular diseases. However, GLP-1 RA utility in improving HF outcomes has been variable across studies. We sought to investigate the current practice in prescribing GLP1-RA in a large database and assess their impact on heart failure hospitalization and all-cause mortality.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective study using the TriNetX database from January 2023 through April 2024 including adults with heart failure, and either type II diabetes or obesity. Patients were excluded if they had diabetes mellitus type 1, multiple endocrine neoplasia [MEN] type IIA, malignant neoplasms of thyroid gland, or presence of ketoacidosis. Patients were divided into two groups based on the utilization of GLP1-RA. Clinical characteristics, demographics and medications use were compared using appropriate statistics. Propensity score matching (PSM) (1:1, SD<0.1) balanced the baseline characteristics. Cox regression and Kaplan–Meier survival curves evaluated clinical outcomes of heart failure hospitalization and 1 year all-cause mortality.
Results
Out of 530,355 heart failure patients, 47,179 (8.8%) were prescribed GLP-1 RA. Mean age in GLP-1 RA group was 63 ±12 years and 46.7% were female. The GLP1-RA group patients were younger, had significantly higher proportions of type II diabetes, obesity, obstructive sleep apnea, ischemic heart disease, chronic kidney disease, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and more likely to receive guideline directed medical therapy. Using propensity score matching, 47,020 patients on GLP-1 RA were matched with 47,020 patients in the control group. GLP1-RA utilization was significantly associated with lower 1 year all-cause mortality [HR 0.56 (0.53-0.59)], heart failure hospitalization [HR 0.86 (0.85-0.87)] and the composite outcome of all-cause mortality and heart failure hospitalization [ 0.85 (0.84-0.87)].
Conclusion
Our study showed that utilizing GLP-1 RA in heart failure patients with either type II DM or obesity was associated with lower all-cause mortality and heart failure hospitalization at 1 year follow up.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Contemporary Machine Learning-Based Risk Stratification for Mortality and Hospitalization in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Using Multimodal Real-World Data
Fudim Marat, Weerts Jerremy, Patel Manesh, Balu Suresh, Hintze Bradley, Torres Francisco, Micsinai Balan Mariann, Rigolli Marzia, Kessler Paul, Touzot Maxime, Lund Lars, Van Empel Vanessa, Pradhan Aruna, Butler Javed, Zehnder Tobias, Sauty Benoit, Esposito Christian, Balazard Félix, Mayer Imke, Hallal Mohammad, Loiseau Nicolas
Application of PLGA-PEG-PLGA Thermosensitive Hydrogel Loaded with Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes and Ginsenoside Rb3 in the Treatment of Acute Myocardial InfarctionXiang Kun, Zheng Zilong, Li Yichen, Tang Weijie, Chen Wangping, Yang Jinfu, Fan Chengming