Final ID: MP1408
A multi-ethnic foundation model-based artificial intelligence electrocardiogram for detection and prognostication of elevated left ventricular filling pressure
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Left ventricular filling pressure (LVFP) is associated with symptoms and signs of heart failure, can guide therapeutic decision-making, and provides prognostic insights.
Purpose: We aimed to develop an artificial intelligence (AI)-based electrocardiogram (ECG) model to detect increased LVFP and evaluate its prognostic significance through multi-ethnic geographically diverse cohorts.
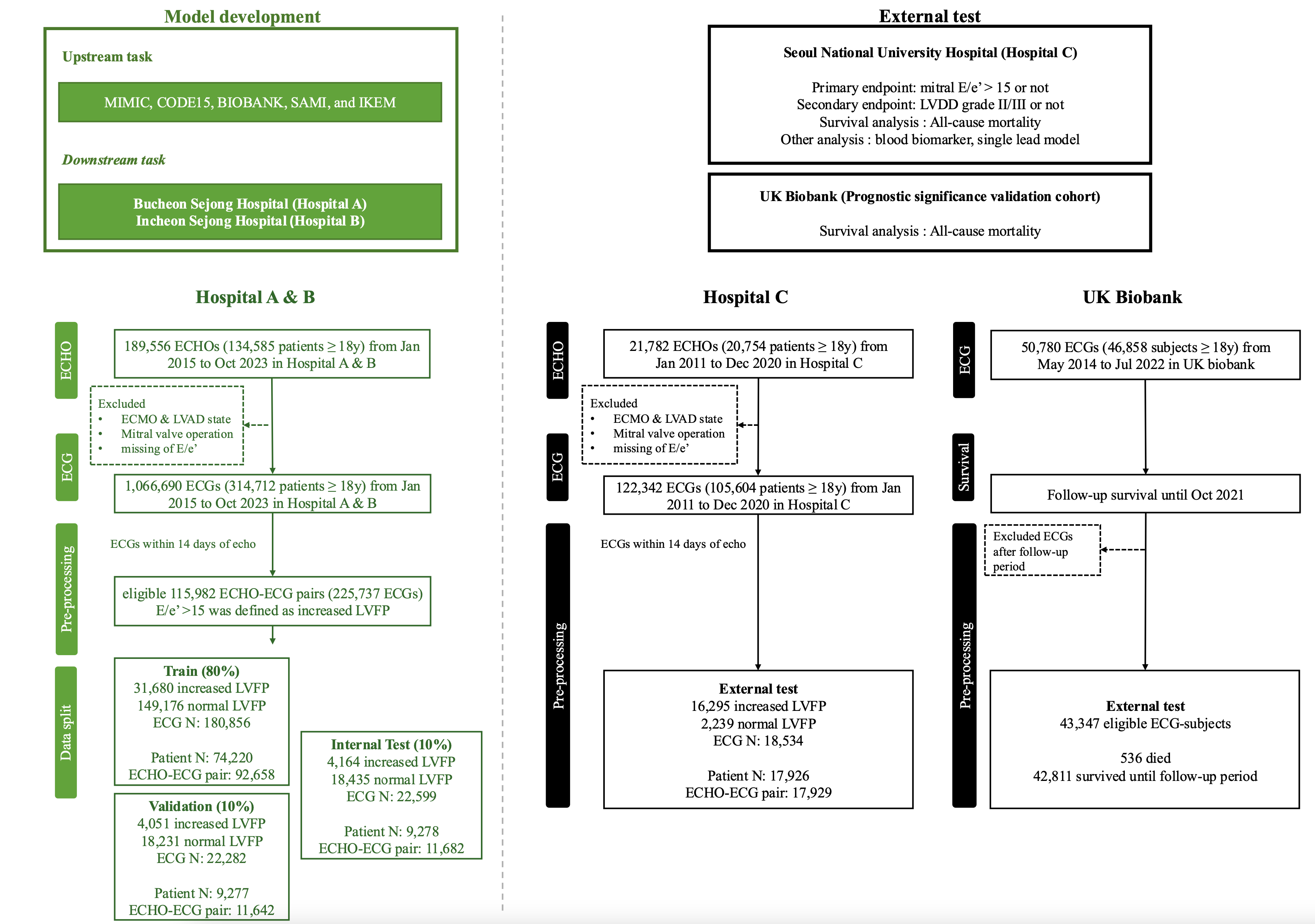
Methods: The septal E/e' value over 15 on Doppler echocardiography was used to define increased LVFP and to guide model training. The AI-ECG model, based on a transformer-enhanced convolutional neural network architecture, was initially pre-trained using a multinational public ECG dataset and subsequently fine-tuned as a binary classifier using a development cohort comprising 225,737 12-lead ECGs and 115,982 echocardiograms from 92,775 unique patients across two tertiary hospitals in Korea. The model performance to discriminate increased LVFP and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction grade (LVDD) II/III were assessed in an internal test cohort (n=9,278) and an independent external test cohort (n=17,926) from a third tertiary Korean hospital. The prognostic significance of the AI-ECG model was validated via survival analyses in these two cohorts and the prognostic significance validation cohort (UK biobank, n=43,347).
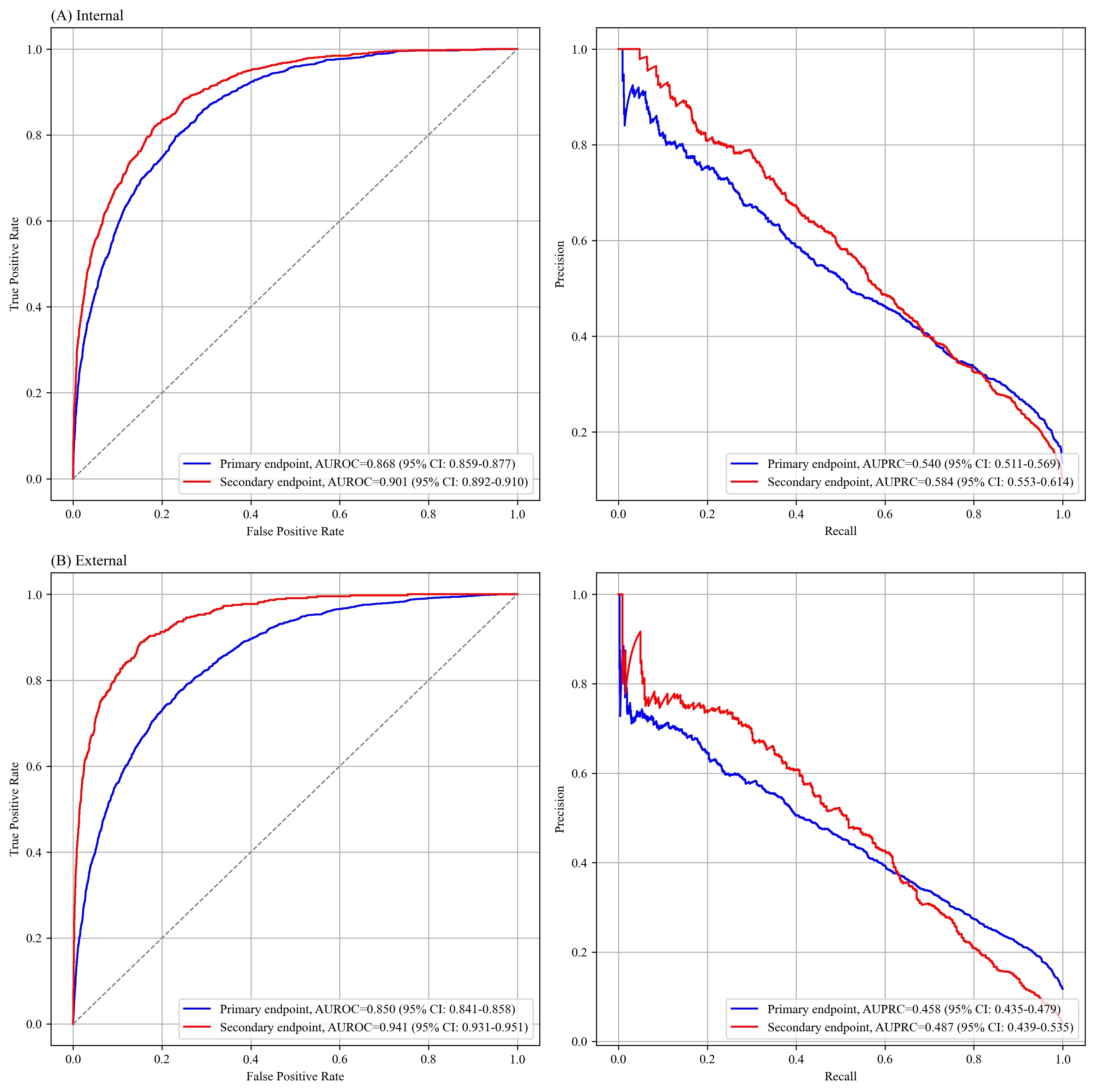
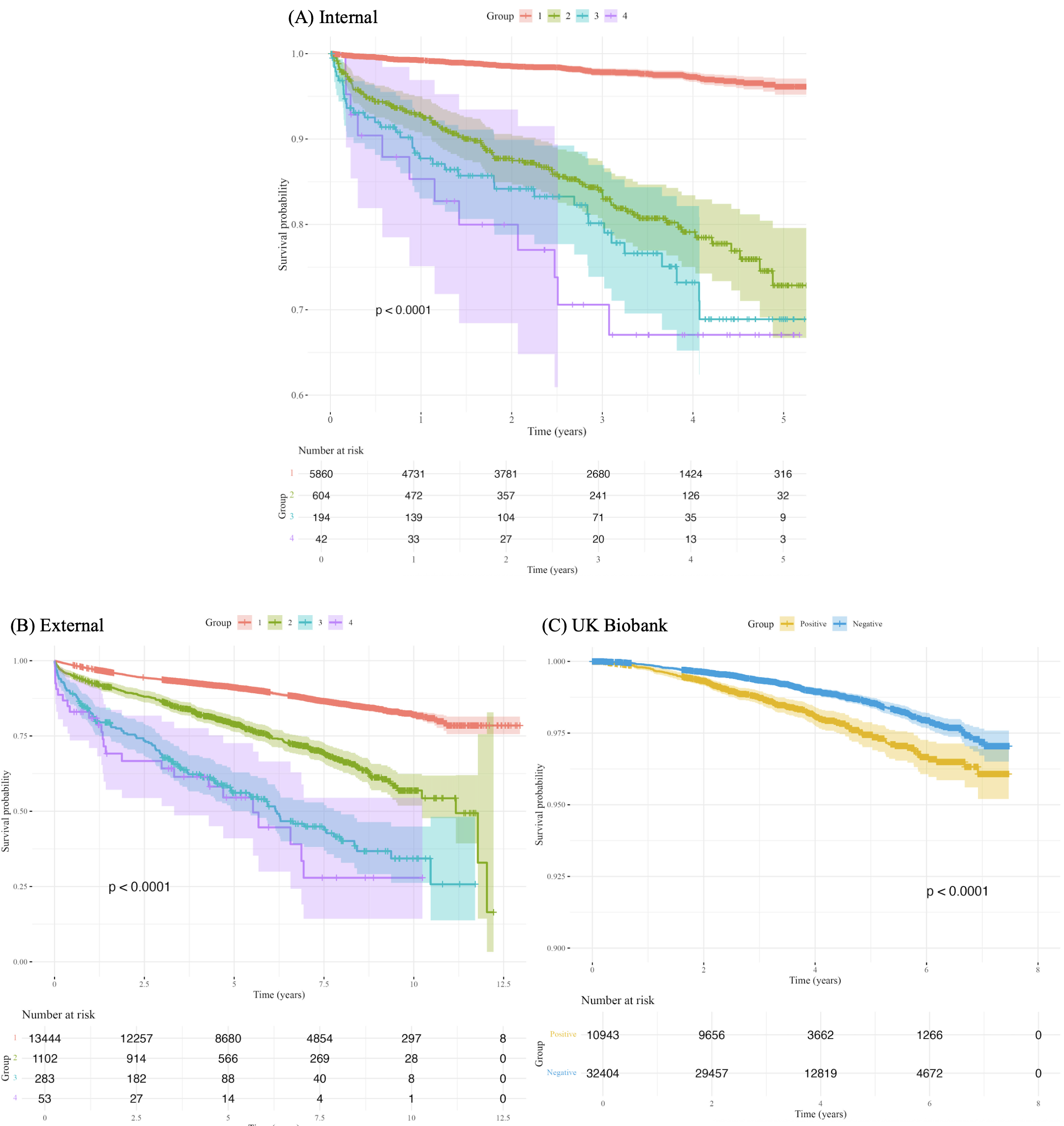
Results: The AI-ECG model detected increased LVFP with area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) of 0.868 (95% confidence interval, 0.859–0.877) and 0.850 (0.841–0.858) in the internal and external test cohort, respectively. For detecting LVDD grade II/III, the model demonstrated an AUROCs of 0.901 (0.892–0.910) and 0.941 (0.931–0.951) in the internal and external test cohort, respectively. The model’s prognostic utility was confirmed across all three cohorts by Kaplan-Meier survival analyses, demonstrating significantly higher mortality in patients with higher AI-ECG scores. In Cox models adjusted for age, sex, and clinical comorbidities, the AI-ECG score remained independently associated with mortality across all cohorts: adjusted hazard ratio 1.31 (95% CI, 1.23–1.38, p<0.001) in the internal test cohort, 1.32 (1.28–1.35, p<0.001) in the external test cohort, and 1.16 (1.07–1.26, p<0.001) in the UK biobank.
Conclusion: We developed a multiethnic foundation model-based, generalizable AI-ECG capable of detecting increased LVFP and prognosticating long-term mortality, with external validation across multiethnic cohorts.
Purpose: We aimed to develop an artificial intelligence (AI)-based electrocardiogram (ECG) model to detect increased LVFP and evaluate its prognostic significance through multi-ethnic geographically diverse cohorts.
Methods: The septal E/e' value over 15 on Doppler echocardiography was used to define increased LVFP and to guide model training. The AI-ECG model, based on a transformer-enhanced convolutional neural network architecture, was initially pre-trained using a multinational public ECG dataset and subsequently fine-tuned as a binary classifier using a development cohort comprising 225,737 12-lead ECGs and 115,982 echocardiograms from 92,775 unique patients across two tertiary hospitals in Korea. The model performance to discriminate increased LVFP and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction grade (LVDD) II/III were assessed in an internal test cohort (n=9,278) and an independent external test cohort (n=17,926) from a third tertiary Korean hospital. The prognostic significance of the AI-ECG model was validated via survival analyses in these two cohorts and the prognostic significance validation cohort (UK biobank, n=43,347).
Results: The AI-ECG model detected increased LVFP with area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) of 0.868 (95% confidence interval, 0.859–0.877) and 0.850 (0.841–0.858) in the internal and external test cohort, respectively. For detecting LVDD grade II/III, the model demonstrated an AUROCs of 0.901 (0.892–0.910) and 0.941 (0.931–0.951) in the internal and external test cohort, respectively. The model’s prognostic utility was confirmed across all three cohorts by Kaplan-Meier survival analyses, demonstrating significantly higher mortality in patients with higher AI-ECG scores. In Cox models adjusted for age, sex, and clinical comorbidities, the AI-ECG score remained independently associated with mortality across all cohorts: adjusted hazard ratio 1.31 (95% CI, 1.23–1.38, p<0.001) in the internal test cohort, 1.32 (1.28–1.35, p<0.001) in the external test cohort, and 1.16 (1.07–1.26, p<0.001) in the UK biobank.
Conclusion: We developed a multiethnic foundation model-based, generalizable AI-ECG capable of detecting increased LVFP and prognosticating long-term mortality, with external validation across multiethnic cohorts.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Steroid-Refractory Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor Induced Myocarditis Responsive to Mycophenolate and Anti-thymocyte globulin
Dabdoub Jorge, Wilson Michael, Gottbrecht Matthew, Salazar Ryan, Shih Jeffrey
Advanced Diagnosis of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with AI-ECG and Differences Based on Race and SubtypeLewontin Myra, Perry Allison, Amos Kaitlyn, Ayers Michael, Kaplan Emily, Bilchick Kenneth, Barber Anita, Bivona Derek, Kramer Christopher, Parrish Anna, Mcclean Karen, Thomas Matthew