Final ID: MP1269
A Novel ECG Time-Frequency Eyeball Method for Robust Detection of Myocardial Infarction from Single-Channel ECG: A Preclinical Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Myocardial infarction (MI) alters the heart’s electrophysiology, often seen as ST-segment deviation, T-wave inversion, or QRS distortion in electrocardiogram (ECG). While these features support diagnosis, they may miss early or subtle waveform changes in single-channel ECGs during ischemic injury. Capturing such changes could enhance MI detection, particularly in non-classical presentations. Here, we propose a new analytical approach that reveals advanced ECG morphology changes, to capture MI-related signatures not easily detectable by standard interpretation.
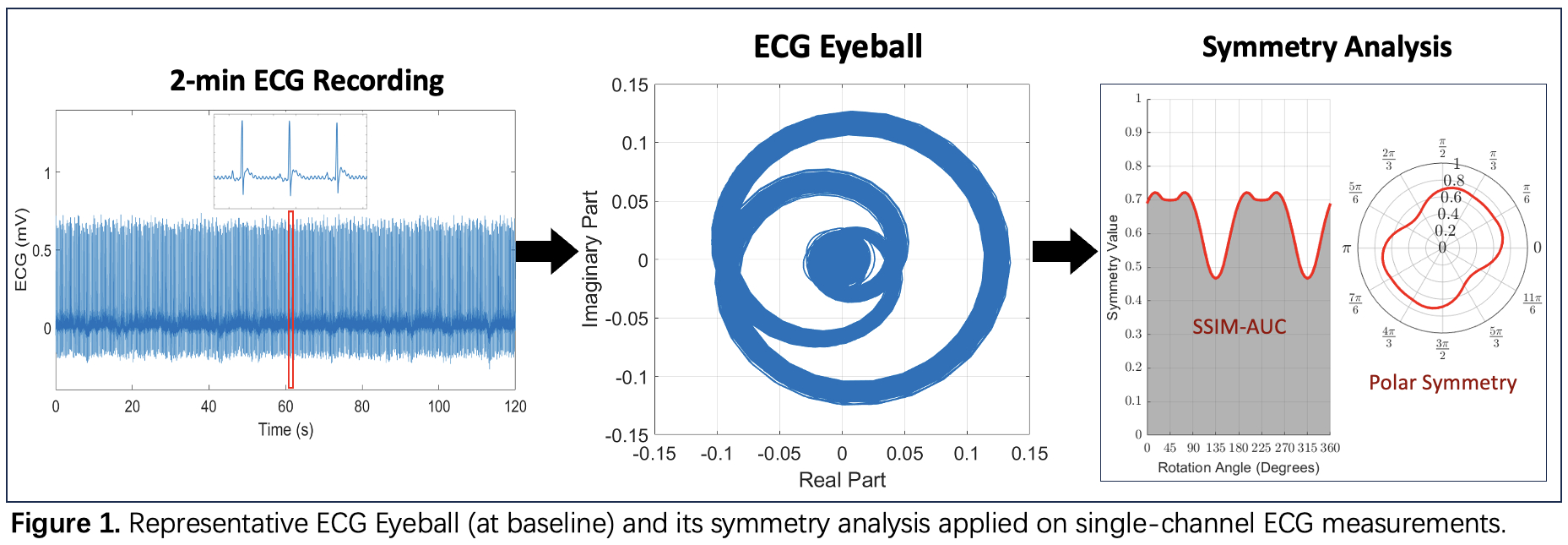
Methods: Acute MI was induced in SD rats (n=13; Male; ~300g) via 30 minutes of proximal left coronary artery occlusion, followed by 3 hours of reperfusion. Necrosis was confirmed post-surgery via triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining. ECG signals were continuously recorded via subcutaneous needle electrodes. The ECG time-frequency eyeball method involves: (1) empirical mode decomposition to extract intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) from ECG signal; (2) the Hilbert Transform to derive analytic signal of each IMF; (3) rotational mapping of the analytic signals onto the complex plane, where they exhibited a distinct eyeball-shaped pattern for IMF1 (ECG eyeball, Fig1). To quantify ECG dynamic changes, we performed symmetry analysis on the ECG eyeballs using the Structural Similarity Index Measurement (SSIM). Specifically, each eyeball was mirrored across incrementally rotated axes, and SSIM was calculated between the original and mirrored images at each angle. The normalized area under the SSIM curve over all rotation angles (SSIM-AUC) was used as a global symmetry metric (Fig1). SSIM-AUC was computed at three time points: baseline, pre-reperfusion (MI with occluded coronary), and 3 hours post-reperfusion (early recovery after MI). 2-minute ECG recordings were used at each time point for computing the eyeballs.
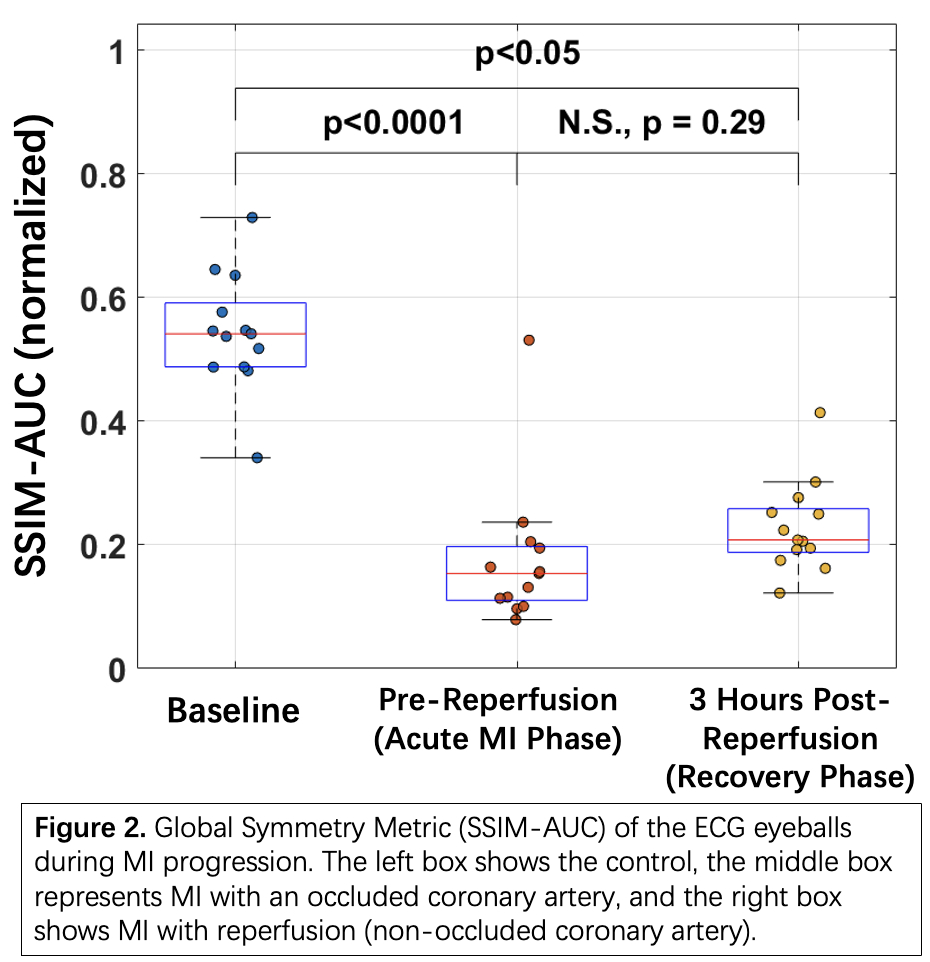
Results: SSIM-AUC significantly decreased after MI (P<0.05), from baseline to both pre-reperfusion and post-reperfusion (Fig2). A modest post-reperfusion increase vs. pre-reperfusion was observed but not significant.
Conclusion: We introduced a time-frequency-based analytics approach (ECG Eyeball) that maps multi-minute ECG data into a single interpretable pattern. Symmetry analysis of the ECG eyeball effectively captured MI-induced electrical changes. This method offers new directions for leveraging single-channel ECG data in noninvasive and interpretable tools for MI detection.
Methods: Acute MI was induced in SD rats (n=13; Male; ~300g) via 30 minutes of proximal left coronary artery occlusion, followed by 3 hours of reperfusion. Necrosis was confirmed post-surgery via triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining. ECG signals were continuously recorded via subcutaneous needle electrodes. The ECG time-frequency eyeball method involves: (1) empirical mode decomposition to extract intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) from ECG signal; (2) the Hilbert Transform to derive analytic signal of each IMF; (3) rotational mapping of the analytic signals onto the complex plane, where they exhibited a distinct eyeball-shaped pattern for IMF1 (ECG eyeball, Fig1). To quantify ECG dynamic changes, we performed symmetry analysis on the ECG eyeballs using the Structural Similarity Index Measurement (SSIM). Specifically, each eyeball was mirrored across incrementally rotated axes, and SSIM was calculated between the original and mirrored images at each angle. The normalized area under the SSIM curve over all rotation angles (SSIM-AUC) was used as a global symmetry metric (Fig1). SSIM-AUC was computed at three time points: baseline, pre-reperfusion (MI with occluded coronary), and 3 hours post-reperfusion (early recovery after MI). 2-minute ECG recordings were used at each time point for computing the eyeballs.
Results: SSIM-AUC significantly decreased after MI (P<0.05), from baseline to both pre-reperfusion and post-reperfusion (Fig2). A modest post-reperfusion increase vs. pre-reperfusion was observed but not significant.
Conclusion: We introduced a time-frequency-based analytics approach (ECG Eyeball) that maps multi-minute ECG data into a single interpretable pattern. Symmetry analysis of the ECG eyeball effectively captured MI-induced electrical changes. This method offers new directions for leveraging single-channel ECG data in noninvasive and interpretable tools for MI detection.
More abstracts on this topic:
Absence of standard modifiable risk factors (SMuRF-less) among 5002 Middle Eastern patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: (Interim analysis from the Jo-SMuRF Study)
Aldalal'ah Mo'men, Hammoudeh Ayman, Hamza Ibrahem, Alqudah Mohammad, Khasawneh Hasan, Alomari Sawsan, Alomari Ahmad, H. Assaf Sarah, Zaqqa Ayah, Khatatbeh Moawiah
A New Analytical Approach for Noninvasive Reconstruction of the Entire Left Ventricular Pressure Waveform in Myocardial Ischemia and InfarctionBilgi Coskun, Li Jiajun, Alavi Rashid, Dai Wangde, Matthews Ray, Kloner Robert, Pahlevan Niema