Final ID: LBP10
Cellular retention of growth arrest specific protein 6 (GAS6) accelerates calcification of aortic valves
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): BACKGROUND: Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) resulting in aortic stenosis affects 2% of individuals over the age of 65; however, aortic valve (AV) calcification lacks needed pharmacological interventions.
AIMS: To identify novel disease drivers and characterize their role in the pathophysiology of CAVD using mass-spectrometry proteomics. We identified GAS6, a secreted γ-carboxylated vitamin K-dependent protein currently undescribed in heart valves, as a prominent protein in the calcification of human AVs.
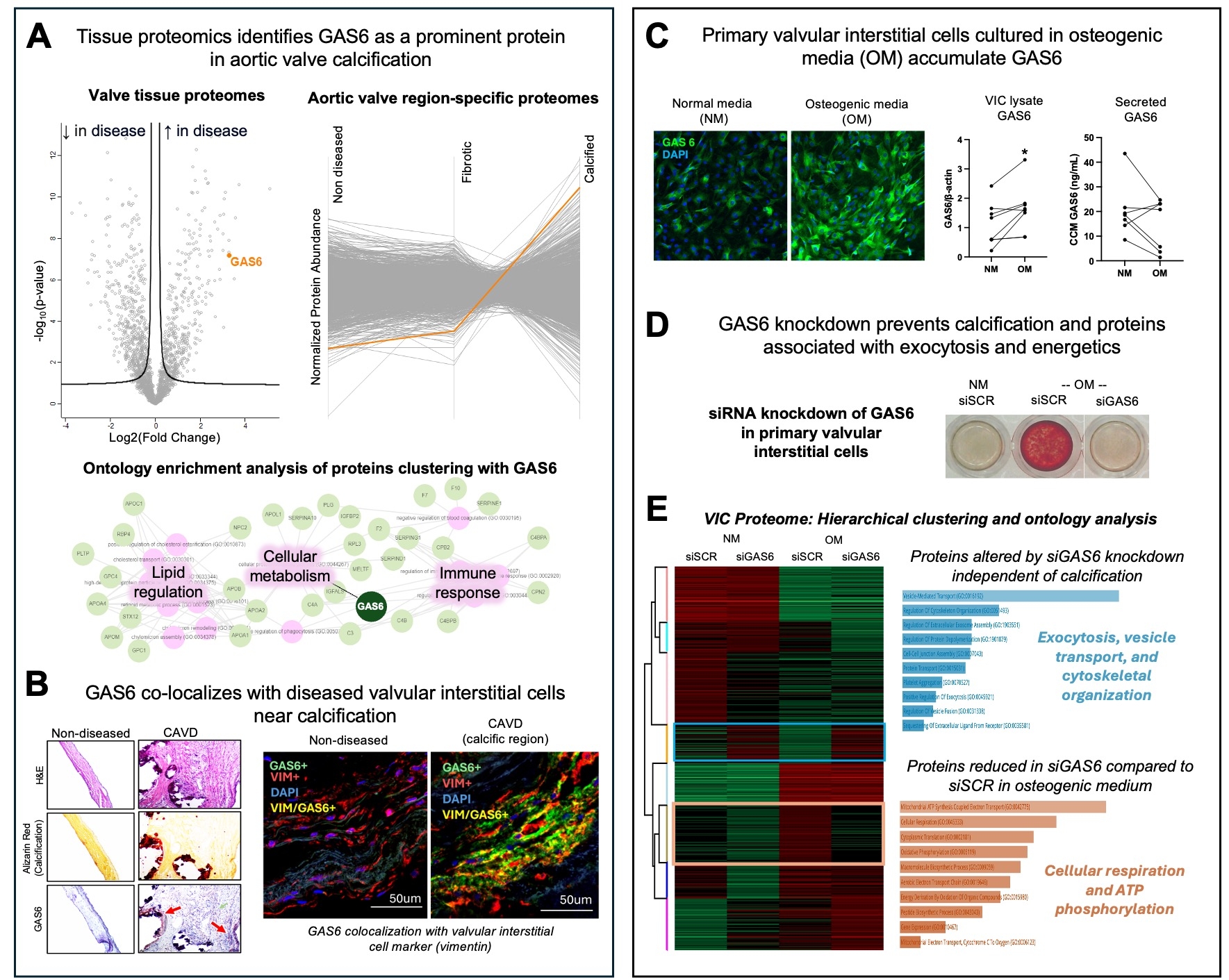
METHODS AND RESULTS: Human AV specimens collected from surgical replacements at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, underwent whole AV and cellular label-free mass-spectrometry proteomics, histopathology, and valvular interstitial cell (VIC) isolation. The calcified AV tissue proteome (N=18, 2319 proteins) was differentially enriched in GAS6 compared to non-diseased AV (log2FC=3.8, p=1.1e-6) (A). Remining of region-specific proteomes of AVs displayed that GAS6 shifts from one of the least abundant identified proteins in non-diseased regions (99th percentile) to one of the most abundant proteins (1st percentile) in calcified regions. Proteins with trajectories that clustered with GAS6 (FDR<0.05) were preferentially associated with perturbed cellular metabolism Gene Ontology pathways (OR-ranked). Immunohistochemistry and co-immunofluorescence identified vimentin+ VICs as a source of GAS6 in calcified AV regions (B). In primary VIC culture, GAS6 protein expression increased following 14 days in osteogenic medium (p<0.05); however, secretion of GAS6 into cell culture media did not change, suggesting intracellular accumulation (C). Knockdown of GAS6 using siRNA attenuated in vitro calcification deposition induced by osteogenic media detected by Alizarin Red staining (N=9/12 donors; D). Independent of calcification, silencing of GAS6 in VICs modulated proteins associated with exocytosis and vesicular pathways, and in osteogenic medium siGAS6 modulated proteins associated with cellular energetics and metabolism aligning with human tissue-enrichment analysis (E).
CONCLUSIONS: These findings support GAS6 as a novel protein of pathological significance in CAVD. A previously unrecognized role of cellular GAS6, rather than its known secretory functions, may modulate vesicular release and alter cellular metabolism and energetics pathways in vivo and in vitro. GAS6 may have important implications for future pharmacotherapy in CAVD.
AIMS: To identify novel disease drivers and characterize their role in the pathophysiology of CAVD using mass-spectrometry proteomics. We identified GAS6, a secreted γ-carboxylated vitamin K-dependent protein currently undescribed in heart valves, as a prominent protein in the calcification of human AVs.
METHODS AND RESULTS: Human AV specimens collected from surgical replacements at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, underwent whole AV and cellular label-free mass-spectrometry proteomics, histopathology, and valvular interstitial cell (VIC) isolation. The calcified AV tissue proteome (N=18, 2319 proteins) was differentially enriched in GAS6 compared to non-diseased AV (log2FC=3.8, p=1.1e-6) (A). Remining of region-specific proteomes of AVs displayed that GAS6 shifts from one of the least abundant identified proteins in non-diseased regions (99th percentile) to one of the most abundant proteins (1st percentile) in calcified regions. Proteins with trajectories that clustered with GAS6 (FDR<0.05) were preferentially associated with perturbed cellular metabolism Gene Ontology pathways (OR-ranked). Immunohistochemistry and co-immunofluorescence identified vimentin+ VICs as a source of GAS6 in calcified AV regions (B). In primary VIC culture, GAS6 protein expression increased following 14 days in osteogenic medium (p<0.05); however, secretion of GAS6 into cell culture media did not change, suggesting intracellular accumulation (C). Knockdown of GAS6 using siRNA attenuated in vitro calcification deposition induced by osteogenic media detected by Alizarin Red staining (N=9/12 donors; D). Independent of calcification, silencing of GAS6 in VICs modulated proteins associated with exocytosis and vesicular pathways, and in osteogenic medium siGAS6 modulated proteins associated with cellular energetics and metabolism aligning with human tissue-enrichment analysis (E).
CONCLUSIONS: These findings support GAS6 as a novel protein of pathological significance in CAVD. A previously unrecognized role of cellular GAS6, rather than its known secretory functions, may modulate vesicular release and alter cellular metabolism and energetics pathways in vivo and in vitro. GAS6 may have important implications for future pharmacotherapy in CAVD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comparative Effectiveness of Cardiac Rehabilitation After Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement – A Target Trial Emulation
Rr Decker Sergio, Rosa Regis, Yeh Robert, Sperling Laurence, Fonarow Gregg, Keteyian Steven, Beatty Alexis, Dahabreh Issa, Kazi Dhruv, Essa Mohammed, Song Yang, Liang Lichen, Inoue Kosuke, Mcconeghy Kevin, Wu Wen-chih, Varghese Merilyn, Thompson Mike
“Atrialized” Minimally Invasive Transcatheter Mitral Valve-In-MAC Replacement to Prevent Outflow Tract ObstructionSteafo Lark, Smielewski Mitchell, Madanat Luai, Bloomingdale Richard, Jabri Ahmad, Gallagher Michael, Birk Vishal, Abbas Amr, Young John, Suri Rakesh