Final ID: Su3140
Identification of Acute Air Pollution Induced Altered Metabolomic Pathways that May Lead to CAD and AMI: the BioHEART-CT Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Outdoor air pollution, a persistent threat since the Industrial Revolution, continues to pose a global challenge with severe implications for public health. Despite advancements, air quality issues —particularly particulate matter —are associated with diseases like coronary artery disease (CAD) and stroke. The unknown pathophysiology that links air pollution to cardiovascular diseases is a pressing issue that demands immediate attention. Understanding these mechanisms is critical for effective prevention and treatment.
Methods:
The BioHEART-CT Discovery cohort included 1,002 adults referred for elective CTCA (2015-2020). Blood (20-30 ml) was collected at the time of CTCA, processed, stored at -80°C, and analysed using Agilent 1260 LC and QTRAP 5500 MS. Maximum daily PM2.5 was measured using home postcodes and publicly available land-based monitors. After normalisation, PCA and PLS-DA were employed to reduce dimensionality and identify significant variables, followed by pathway analysis of significant metabolites using metabolite set enrichment analysis.
Results:
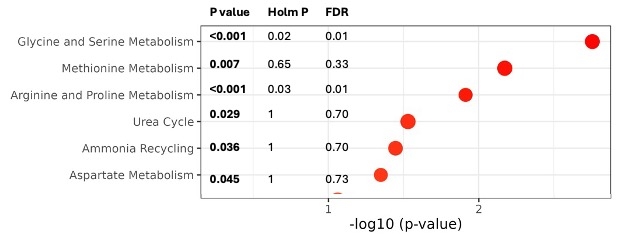
Using the threshold of PM2.5 ≥12 μg/m3 to categorise patients into high vs low-exposure, low-exposure subjects formed a distinct cluster from high-exposure subjects. PLS-DA clustering with ten-fold cross-validation identified key metabolites with high VIP scores: transHYP, betaine, and alanine. Metabolite set enrichment analysis revealed significant pathways: Glycine, Serine, and Threonine metabolism, and Arginine and Proline metabolism (p<0.001, FDR <0.05) (Figure 1).
Conclusion:
Our study's most significant finding—the enriched metabolic set of glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism, along with arginine and proline metabolism—has been implicated in the development of CAD in previous studies. These findings can potentially inform preventive and treatment strategies, making a real difference in the lives of those affected by air pollution-related cardiovascular diseases.
Outdoor air pollution, a persistent threat since the Industrial Revolution, continues to pose a global challenge with severe implications for public health. Despite advancements, air quality issues —particularly particulate matter —are associated with diseases like coronary artery disease (CAD) and stroke. The unknown pathophysiology that links air pollution to cardiovascular diseases is a pressing issue that demands immediate attention. Understanding these mechanisms is critical for effective prevention and treatment.
Methods:
The BioHEART-CT Discovery cohort included 1,002 adults referred for elective CTCA (2015-2020). Blood (20-30 ml) was collected at the time of CTCA, processed, stored at -80°C, and analysed using Agilent 1260 LC and QTRAP 5500 MS. Maximum daily PM2.5 was measured using home postcodes and publicly available land-based monitors. After normalisation, PCA and PLS-DA were employed to reduce dimensionality and identify significant variables, followed by pathway analysis of significant metabolites using metabolite set enrichment analysis.
Results:
Using the threshold of PM2.5 ≥12 μg/m3 to categorise patients into high vs low-exposure, low-exposure subjects formed a distinct cluster from high-exposure subjects. PLS-DA clustering with ten-fold cross-validation identified key metabolites with high VIP scores: transHYP, betaine, and alanine. Metabolite set enrichment analysis revealed significant pathways: Glycine, Serine, and Threonine metabolism, and Arginine and Proline metabolism (p<0.001, FDR <0.05) (Figure 1).
Conclusion:
Our study's most significant finding—the enriched metabolic set of glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism, along with arginine and proline metabolism—has been implicated in the development of CAD in previous studies. These findings can potentially inform preventive and treatment strategies, making a real difference in the lives of those affected by air pollution-related cardiovascular diseases.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adverse Cardiovascular Health Impacts Associated with Fossil-fuel-related Source-specific Particulate Matter Particles
Yu Wuyue, Thurston George
A Novel RNA Interference Agent RN0191 Lowering Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9, Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Other Lipid Biomarkers in Healthy Volunteers with Elevated LDL Cholesterol: A Randomized, Single-blind, Placebo-controlled, Phase 1 TrialWang Fangfang, Li Haiyan, Zeng Jie, Shi Yibin, Li Hongmei