Final ID: Mo4037
Enhanced Diagnostic Value of High Sensitivity Troponin I After Indexation for Myocardial Mass, Renal Function and Age: the BioHEART-CT Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (CAD) often goes undetected until acute myocardial infarction (AMI). High-sensitivity troponin (hs-cTn) assays, known for diagnosing acute coronary syndrome, are being explored for detecting subclinical CAD. Studies suggest hs-cTn's potential in identifying coronary atherosclerosis, indicating its value in early CAD screening.
Method and Results
This study used the BioHEART-CT cohort (2015-2021) of 2,000 adults undergoing CCTA for known or suspected CAD, excluding those with prior cardiomyopathy, MI, or coronary revascularization. CAD severity was assessed using CACS and Gensini scores. Myocardial mass was estimated via automated segmentation. Hs-cTnI was measured using Abbott ARCHITECT i1000 and Beckman Access 2 assays.
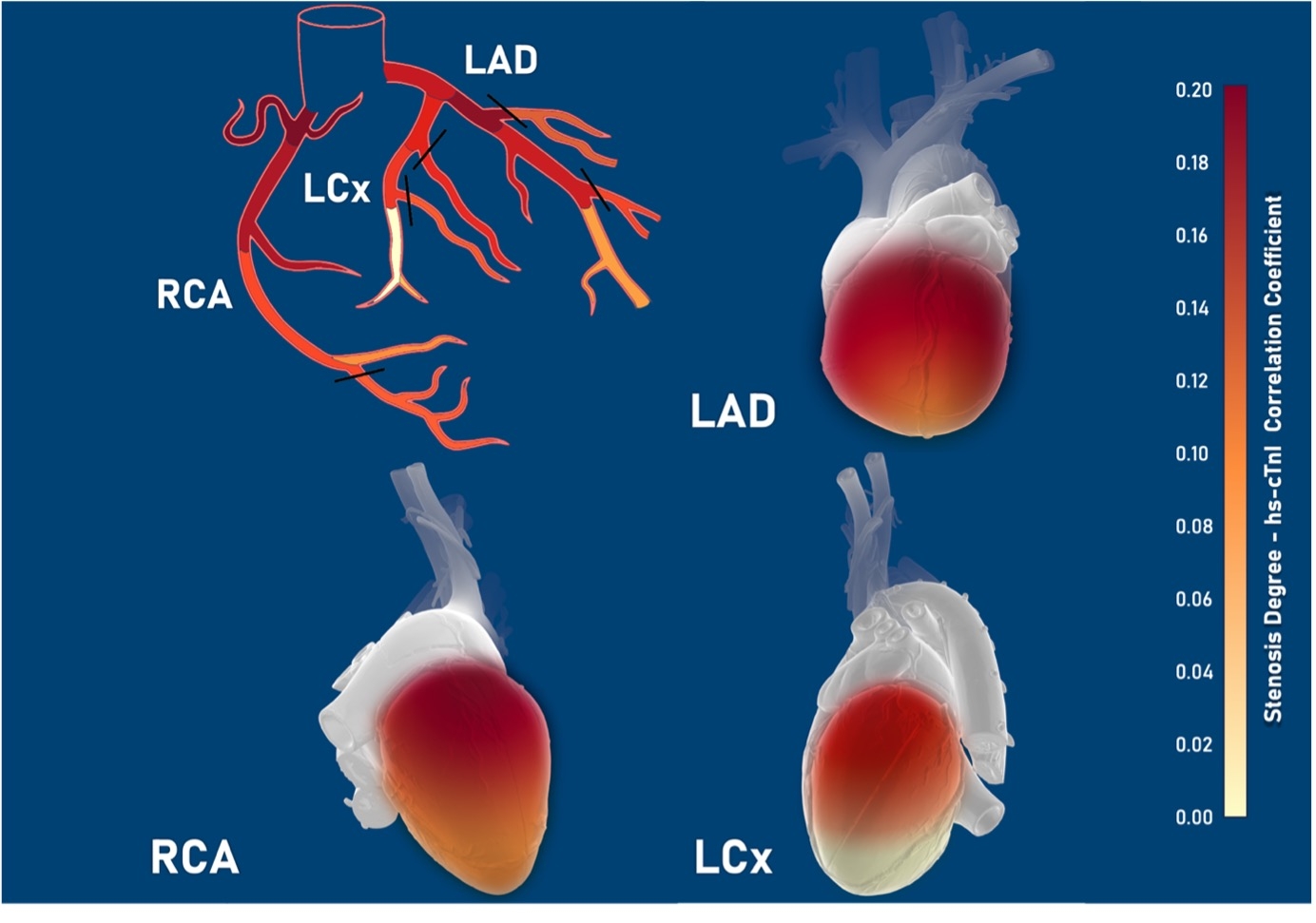
We examined the association between hs-cTnI levels and the extent of myocardial involvement. Hs-cTnI significantly correlated with the total number of coronary artery segments containing detectable plaque (ρs = 0.25; p < 0.001; Figure 1). Additionally, Spearman’s correlation of segment location and stenosis degree with hs-cTnI indicated a stronger association in the proximal segments.
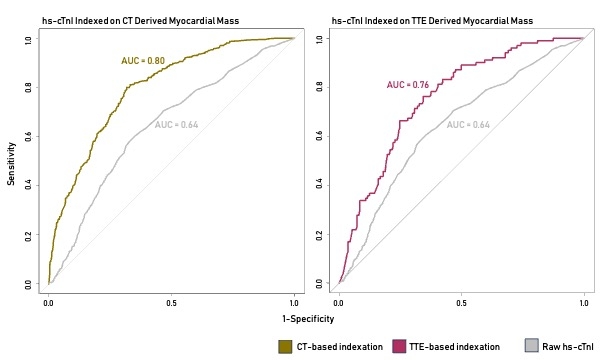
We examined the potential improvement of the association of hs-cTnI with clinically actionable CAD by incorporating myocardial mass (affecting baseline hs-cTnI release) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) into the model. Using PLS with GLM regression, we projected hs-cTnI, age, eGFR, and myocardial mass into a latent feature. This improved detection of clinically actionable CAD, yielding an AUC of 0.79 and 0.80 in the participants without standard CAD risk factors. Using echocardiographic LV mass data (available for 362 patients), the AUC improved to 0.75 overall and 0.76 for SMuRF-less patients (Figure 2).
Conclusion
Baseline serum hs-cTnI may indicate underlying subclinical CAD. The predictive value of troponin can be further enhanced by considering the effect of myocardial mass, renal function, and age.
Atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (CAD) often goes undetected until acute myocardial infarction (AMI). High-sensitivity troponin (hs-cTn) assays, known for diagnosing acute coronary syndrome, are being explored for detecting subclinical CAD. Studies suggest hs-cTn's potential in identifying coronary atherosclerosis, indicating its value in early CAD screening.
Method and Results
This study used the BioHEART-CT cohort (2015-2021) of 2,000 adults undergoing CCTA for known or suspected CAD, excluding those with prior cardiomyopathy, MI, or coronary revascularization. CAD severity was assessed using CACS and Gensini scores. Myocardial mass was estimated via automated segmentation. Hs-cTnI was measured using Abbott ARCHITECT i1000 and Beckman Access 2 assays.
We examined the association between hs-cTnI levels and the extent of myocardial involvement. Hs-cTnI significantly correlated with the total number of coronary artery segments containing detectable plaque (ρs = 0.25; p < 0.001; Figure 1). Additionally, Spearman’s correlation of segment location and stenosis degree with hs-cTnI indicated a stronger association in the proximal segments.
We examined the potential improvement of the association of hs-cTnI with clinically actionable CAD by incorporating myocardial mass (affecting baseline hs-cTnI release) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) into the model. Using PLS with GLM regression, we projected hs-cTnI, age, eGFR, and myocardial mass into a latent feature. This improved detection of clinically actionable CAD, yielding an AUC of 0.79 and 0.80 in the participants without standard CAD risk factors. Using echocardiographic LV mass data (available for 362 patients), the AUC improved to 0.75 overall and 0.76 for SMuRF-less patients (Figure 2).
Conclusion
Baseline serum hs-cTnI may indicate underlying subclinical CAD. The predictive value of troponin can be further enhanced by considering the effect of myocardial mass, renal function, and age.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Critical Illness and Signs of Myocardial Injury
Mueller Joshua, Stepanova Daria, Chidambaram Vignesh, Nakarmi Ukash, Al'aref Subhi
Comparative Associations of High-sensitivity Troponins T and I with Neurocognitive Outcomes in SPRINTLwin Yee May, Zhang Wenxin, Berry Jarett, De Lemos James, Ma Yuan, Ascher Simon