Final ID: MDP19
Enhanced Subclinical CAD Risk Prediction Using Lp(a): the BioHEART-CT Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) is now recognised as a key cardiovascular risk factor. Genetically determined and stable throughout adulthood, Lp(a) increases thrombotic risk and promotes atherosclerosis. Doubling Lp(a) levels raises cardiovascular disease risk by 22%. We aimed to evaluate the potential of Lp(a) to predict subclinical coronary artery disease in a well-characterised CCTA cohort, where early plaque detection may guide personalised treatment.
Method and Results
1,718 participants from the BioHEART-CT cohort were included in this analysis, who presented for a CCTA for suspected CAD without a prior history of myocardial injury or revascularisation between 2015 and 2021. CAD burden was assessed using coronary artery calcium scores and Gensini scores. Lp(a) levels were measured using ELISA.
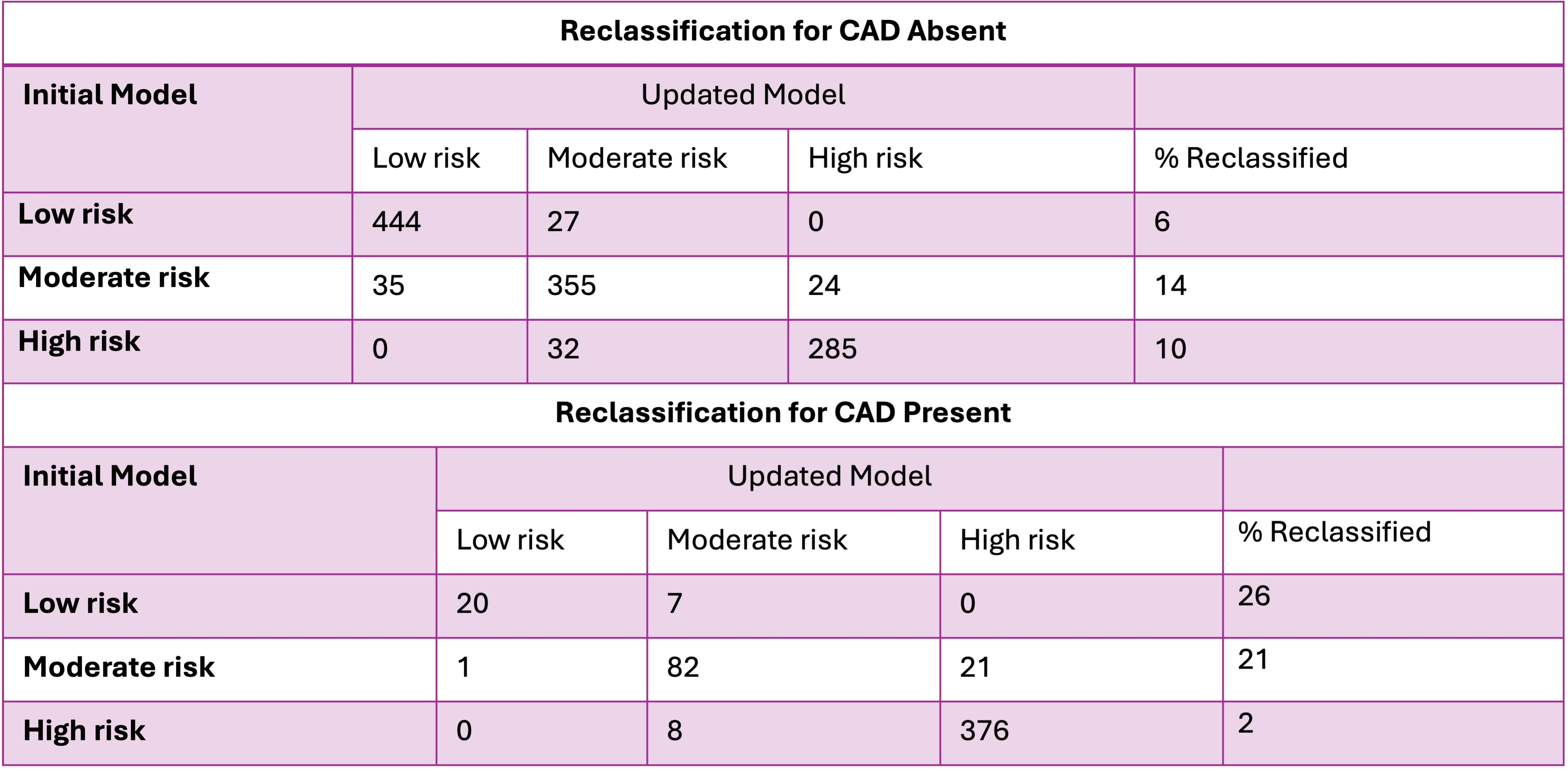
We evaluated the ability of Lp(a) to reclassify patients into correct CAD risk prediction categories: <10% low risk, 10-30% moderate risk, and >30% high risk. Logistic regression, adjusting for age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and smoking status, revealed a net reclassification index (NRI) of 16% (p=0.001) and an integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) of 0.0046 (p=0.03), indicating accurate reclassification of one in 20 patients. In clinically actionable CAD (calcium score ≥100) cases, 26% were correctly reclassified from low to intermediate risk, 21% from intermediate to high risk, and only 2% were incorrectly reclassified . For non-clinically actionable CAD, 10% shifted from high to intermediate risk, 5% from intermediate to low risk, while 14% and 6% were misclassified into higher and intermediate-risk groups, respectively.
Conclusion
Consideration of Lp(a) can potentially triage patients otherwise considered low risk for imaging to identify and treat atherosclerosis. It serves as an important screening biomarker with the potential to serve as an important non-invasive tool to identify vulnerable CAD patients who are currently underdiagnosed, such as patients without standard modifiable cardiovascular risk factors (SMuRFs).
Lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) is now recognised as a key cardiovascular risk factor. Genetically determined and stable throughout adulthood, Lp(a) increases thrombotic risk and promotes atherosclerosis. Doubling Lp(a) levels raises cardiovascular disease risk by 22%. We aimed to evaluate the potential of Lp(a) to predict subclinical coronary artery disease in a well-characterised CCTA cohort, where early plaque detection may guide personalised treatment.
Method and Results
1,718 participants from the BioHEART-CT cohort were included in this analysis, who presented for a CCTA for suspected CAD without a prior history of myocardial injury or revascularisation between 2015 and 2021. CAD burden was assessed using coronary artery calcium scores and Gensini scores. Lp(a) levels were measured using ELISA.
We evaluated the ability of Lp(a) to reclassify patients into correct CAD risk prediction categories: <10% low risk, 10-30% moderate risk, and >30% high risk. Logistic regression, adjusting for age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and smoking status, revealed a net reclassification index (NRI) of 16% (p=0.001) and an integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) of 0.0046 (p=0.03), indicating accurate reclassification of one in 20 patients. In clinically actionable CAD (calcium score ≥100) cases, 26% were correctly reclassified from low to intermediate risk, 21% from intermediate to high risk, and only 2% were incorrectly reclassified . For non-clinically actionable CAD, 10% shifted from high to intermediate risk, 5% from intermediate to low risk, while 14% and 6% were misclassified into higher and intermediate-risk groups, respectively.
Conclusion
Consideration of Lp(a) can potentially triage patients otherwise considered low risk for imaging to identify and treat atherosclerosis. It serves as an important screening biomarker with the potential to serve as an important non-invasive tool to identify vulnerable CAD patients who are currently underdiagnosed, such as patients without standard modifiable cardiovascular risk factors (SMuRFs).
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Signature of Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Aging Defines Elevated Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
Perera Sudheesha, Biswas Dhruva, Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Coppi Andreas, Khera Rohan
Association of Elevated Serum Lipoprotein(a) with New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Study of 108930 PatientsKamel Moaz, Arsanjani Reza, Awad Kamal, Mahmoud Ahmed K., Farina Juan, Scalia Isabel, Pereyra Milagros, Abbas Mohammed Tiseer, Baba Nima, Ayoub Chadi