Final ID: MDP63
Genome wide association study for residualized apolipoprotein B elucidates its role in coronary artery disease risk
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background Recent studies have shown apolipoprotein B (ApoB), the principle atherogenic lipoproteins, to have greater predictive ability for coronary artery disease (CAD) risk over standard lipid parameters. Moreover, discordantly high ApoB relative to Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC) has repeatedly been associated with increased CAD risk.
Aim Given the strong genetic effects of ApoB and LDLC, we sought to characterize the discordance between ApoB and LDLC by genetics to obtain mechanistic insights into this emerging risk factor.
Method We derived residualized-ApoB regressing ApoB on LDLC in European-like populations (N = 383,500) in the UK Biobank. Using residualized-ApoB as an outcome, we explored clinical associations and conducted genome wide association study (GWAS).
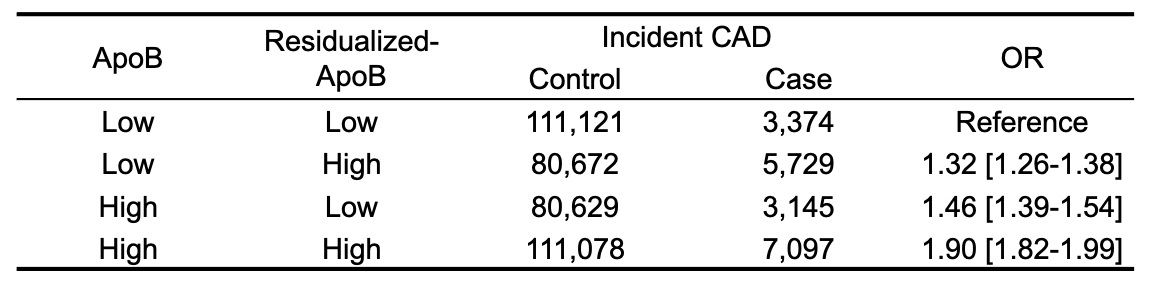
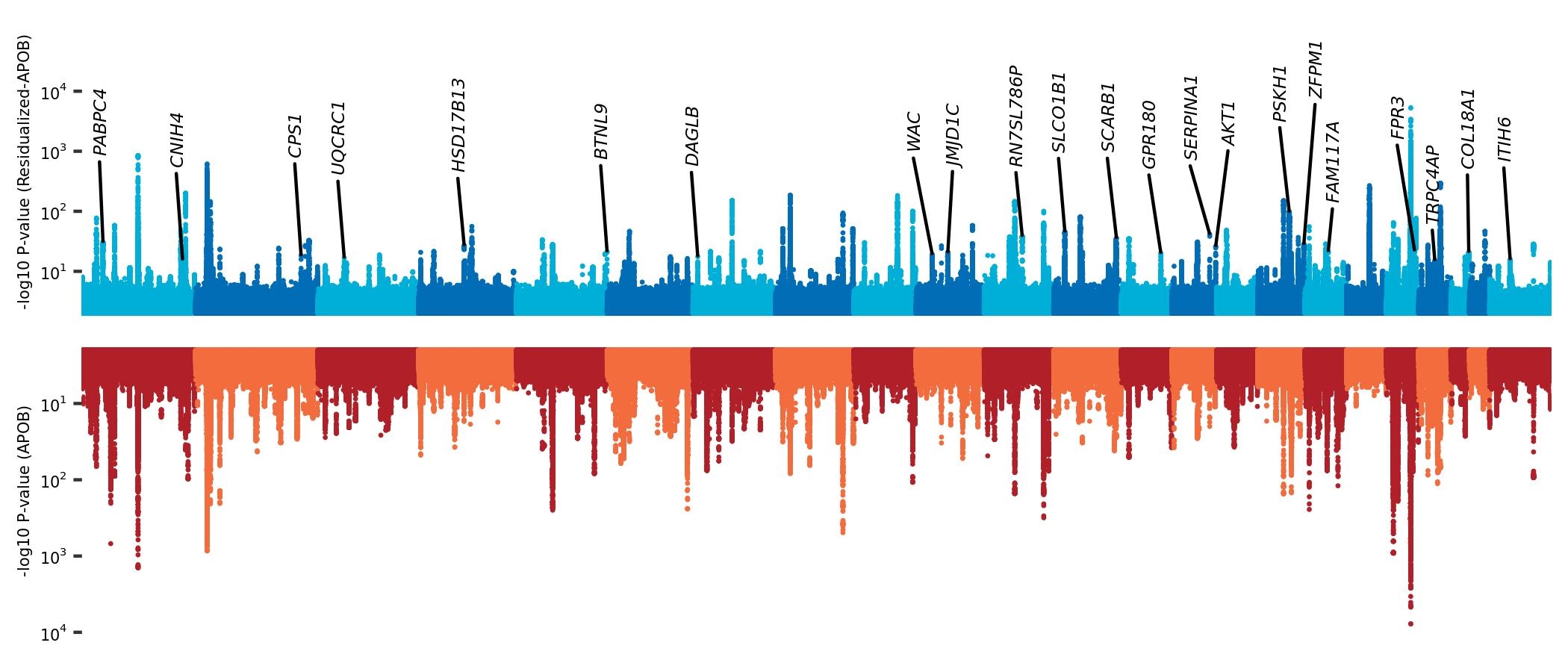
Result Residualized-ApoB only modestly correlated with ApoB and LDLC (Spearman’s rho = 0.248 and -0.0079 respectively). We observed increased residualized-ApoB in males and individuals with lipid lowering therapy. Increased residualized-ApoB was associated with increased risk for CAD [Odds Ratio; 1.25 (95% Confidence interval 1.23-1.27)] independent from LDLC, ApoB, and Triglycerides. By GWAS, we observed significant heritability for residualized-ApoB [h2 = 12.3 (SE 0.012)] and 195 significantly associated genetic loci (P < 5 × 10-8). Only 59 of these lead variants were associated with ApoB or LDLC. We also found different effects in ApoB-related loci. For example, ApoB-increasing alleles at APOB (rs533617) and APOE (rs7412) loci increased residualized-ApoB but ApoB-increasing alleles at ABCG8 (rs4245791) and HAPLN4-TM6SF2 (rs150641967) loci decreased residualized-ApoB.
Conclusions Exploiting genetics, we determined significant heritability of residualized-ApoB which was partially correlated with ApoB/LDLC. We identified distinct effects of genetic variants on residualized-ApoB. Our results provide the clues for further precise understanding of regulatory mechanisms between ApoB and LDLC.
Aim Given the strong genetic effects of ApoB and LDLC, we sought to characterize the discordance between ApoB and LDLC by genetics to obtain mechanistic insights into this emerging risk factor.
Method We derived residualized-ApoB regressing ApoB on LDLC in European-like populations (N = 383,500) in the UK Biobank. Using residualized-ApoB as an outcome, we explored clinical associations and conducted genome wide association study (GWAS).
Result Residualized-ApoB only modestly correlated with ApoB and LDLC (Spearman’s rho = 0.248 and -0.0079 respectively). We observed increased residualized-ApoB in males and individuals with lipid lowering therapy. Increased residualized-ApoB was associated with increased risk for CAD [Odds Ratio; 1.25 (95% Confidence interval 1.23-1.27)] independent from LDLC, ApoB, and Triglycerides. By GWAS, we observed significant heritability for residualized-ApoB [h2 = 12.3 (SE 0.012)] and 195 significantly associated genetic loci (P < 5 × 10-8). Only 59 of these lead variants were associated with ApoB or LDLC. We also found different effects in ApoB-related loci. For example, ApoB-increasing alleles at APOB (rs533617) and APOE (rs7412) loci increased residualized-ApoB but ApoB-increasing alleles at ABCG8 (rs4245791) and HAPLN4-TM6SF2 (rs150641967) loci decreased residualized-ApoB.
Conclusions Exploiting genetics, we determined significant heritability of residualized-ApoB which was partially correlated with ApoB/LDLC. We identified distinct effects of genetic variants on residualized-ApoB. Our results provide the clues for further precise understanding of regulatory mechanisms between ApoB and LDLC.
More abstracts on this topic:
A 10-year longitudinal cohort study of lipid variability, cognitive decline, and dementia in 9846 community-dwelling older adults
Zhou Zhen, Moran Chris, Murray Anne, Zoungas Sophia, Nelson Mark, Talic Stella, Wolfe Rory, Ryan Joanne
Black Patients Have Higher Odds of Discharge with Wearable Cardioverter-DefibrillatorsAntwi Amoabeng Daniel, Sado Ikpemosi, Beutler Bryce, Governor Samuel, Gbadebo T David