Final ID: Sa1026
Assessing the Efficacy and Safety of Olezarsen in Lowering Triglyceride Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Elevated fasting serum triglyceride (TG) levels are linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Olezarsen is an inhibitor of apolipoprotein C3 (apo-C3) production with a potential to decrease TG levels and thereby, reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Research Question: Is olezarsen efficacious and safe in reducing the TG levels?
Aim: This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of olezarsen in patients with hypertriglyceridemia.
Methods: A literature search was carried out on Medline, Embase, Google Scholar, Cochrane CENTRAL, Scopus, and clinicaltrials.gov. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs), including adult patients with hypertriglyceridemia and treated with olezarsen, were included. The primary outcome assessed was the mean change in the level of TG, whereas the secondary outcomes were changes in the apo-C3, apo-B48, and non-HDL cholesterol levels at the end of the 6-month follow-up period. Various adverse events were also assessed. Review Manager 5.4 was used to calculate standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) using a random effects model.
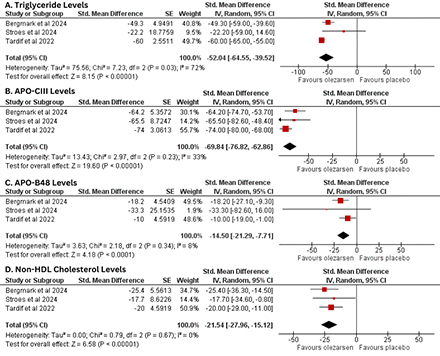
Results: Three RCTs involving 334 patients in total, with 248 receiving olezarsen and 86 receiving placebo, were included. The analysis revealed that at the end of the follow up period, there was a significant change in the levels of TG (SMD -52.04, 95%CI: -64.55 to -39.52; p<0.00001; I2=72%), apo-C3 (SMD -69.84, 95%CI: -76.82 to -62.86; p<0.00001; I2=33%), apo-B48 (SMD -14.50, 95%CI: -21.29 to -7.71; p<0.00001; I2=8%) and non-HDL cholesterol (SMD -21.54, 95%CI: -27.96 to -15.12; p<0.00001; I2=0%). Olezarsen was not associated with any adverse event as demonstrated by the pooled analysis of adverse events. Meta-regression showed that no outcomes were significantly associated with age and BMI as covariates.
Conclusion: A significant reduction was noted in TG, apoC-III, apo-B48, and non-HDLC levels, indicating a significant effect of olezarsen on these parameters. Additionally, olezarsen exhibited no significant side effects, making this medication comparatively safe. More research may be warranted to validate these findings and explore the drug's impact on cardiovascular outcomes.
Research Question: Is olezarsen efficacious and safe in reducing the TG levels?
Aim: This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of olezarsen in patients with hypertriglyceridemia.
Methods: A literature search was carried out on Medline, Embase, Google Scholar, Cochrane CENTRAL, Scopus, and clinicaltrials.gov. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs), including adult patients with hypertriglyceridemia and treated with olezarsen, were included. The primary outcome assessed was the mean change in the level of TG, whereas the secondary outcomes were changes in the apo-C3, apo-B48, and non-HDL cholesterol levels at the end of the 6-month follow-up period. Various adverse events were also assessed. Review Manager 5.4 was used to calculate standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) using a random effects model.
Results: Three RCTs involving 334 patients in total, with 248 receiving olezarsen and 86 receiving placebo, were included. The analysis revealed that at the end of the follow up period, there was a significant change in the levels of TG (SMD -52.04, 95%CI: -64.55 to -39.52; p<0.00001; I2=72%), apo-C3 (SMD -69.84, 95%CI: -76.82 to -62.86; p<0.00001; I2=33%), apo-B48 (SMD -14.50, 95%CI: -21.29 to -7.71; p<0.00001; I2=8%) and non-HDL cholesterol (SMD -21.54, 95%CI: -27.96 to -15.12; p<0.00001; I2=0%). Olezarsen was not associated with any adverse event as demonstrated by the pooled analysis of adverse events. Meta-regression showed that no outcomes were significantly associated with age and BMI as covariates.
Conclusion: A significant reduction was noted in TG, apoC-III, apo-B48, and non-HDLC levels, indicating a significant effect of olezarsen on these parameters. Additionally, olezarsen exhibited no significant side effects, making this medication comparatively safe. More research may be warranted to validate these findings and explore the drug's impact on cardiovascular outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel CRISPR based Epigenetic Silencer Potently, Durably, and Safely Reduces LDLc in Non-Human Primates at Therapeutically Relevant Doses
Duncan-lewis Christopher, Narsineni Lokesh, Karmarkar Maitreyee, Li Yuexuan, Krupa Oleh, Bucher Simon, Sharma Neel, Chang Han, Schulwach Keith, Ripley-phipps Sterling, Tran Vanessa, Fernandes Jason, Goh Natalie, Deiter Fred, Reimer Kirsten, Mrak Anna, Eggers Michelle, Sze Christie, Mirotsou Maria, Oresic Bender Kristina, Bardai Farah, Denny Sarah, Charles Emeric, Khakoo Aarif, Oakes Benjamin, Keller Steven, Alcantara-lee Raniel, Santamaria Carlos, Bale Shyam Sundhar, Kozy Heather, Corbo Lana
A Case of Recurrent Acute Coronary Syndrome and Cardiogenic Shock due to Apolipoprotein A-IV AmyloidosisMuthukkumar Rashmi, Holmes Taylor, Friede Kevin