Final ID: Sa1304
Elevated Circulating Mitochondrial DNA Levels After Successful Resuscitation from Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Humans
Abstract Body: Objective: Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has been implicated as a key pro-inflammatory stimulus in post-cardiac arrest syndrome (PCAS), but clinical data evaluating plasma mtDNA concentrations in the early post-resuscitation period are limited. Accordingly, we measured circulating mtDNA in successfully resuscitated out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (sR-OHCA) patients within 6-hours of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) to determine whether elevated mtDNA levels are (1) associated with 30-day survival, (2) influenced by pre-existing ischemic heart disease (IHD) or concomitant myocardial infarction (MI), and (3) driven by selective release of mtDNA within extracellular vesicles (EVs).
Methods: sR-OHCA patients (n=57) from 4 tertiary care centers in Western New York were stratified into 30-day survivor (n=28) and non-survivor (n=29) cohorts. Blood plasma collected within 6-hours of ROSC was subjected to qPCR to quantify circulating mtDNA (CytB) and nuclear DNA (nucDNA; B2M) compared with healthy controls (n=9). Sub-group analysis was performed to evaluate the influence of pre-existing IHD or concomitant MI, and samples were treated with DNase I to quantify EV-encapsulated vs. free floating mtDNA and nucDNA.
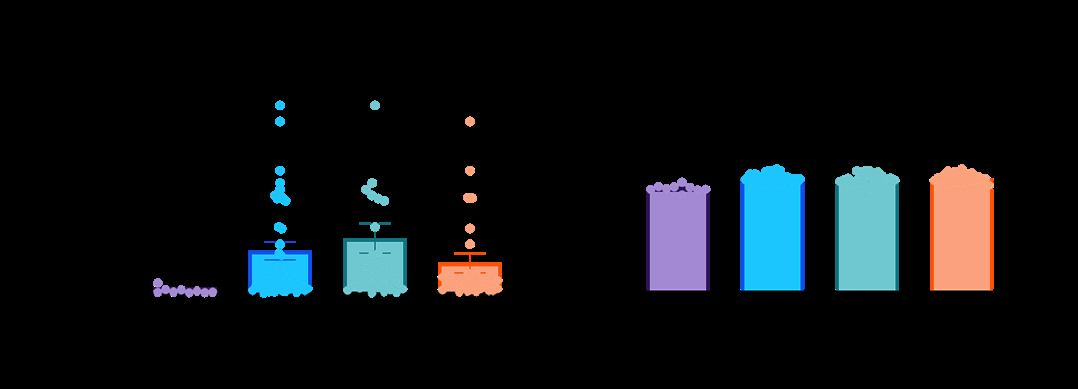
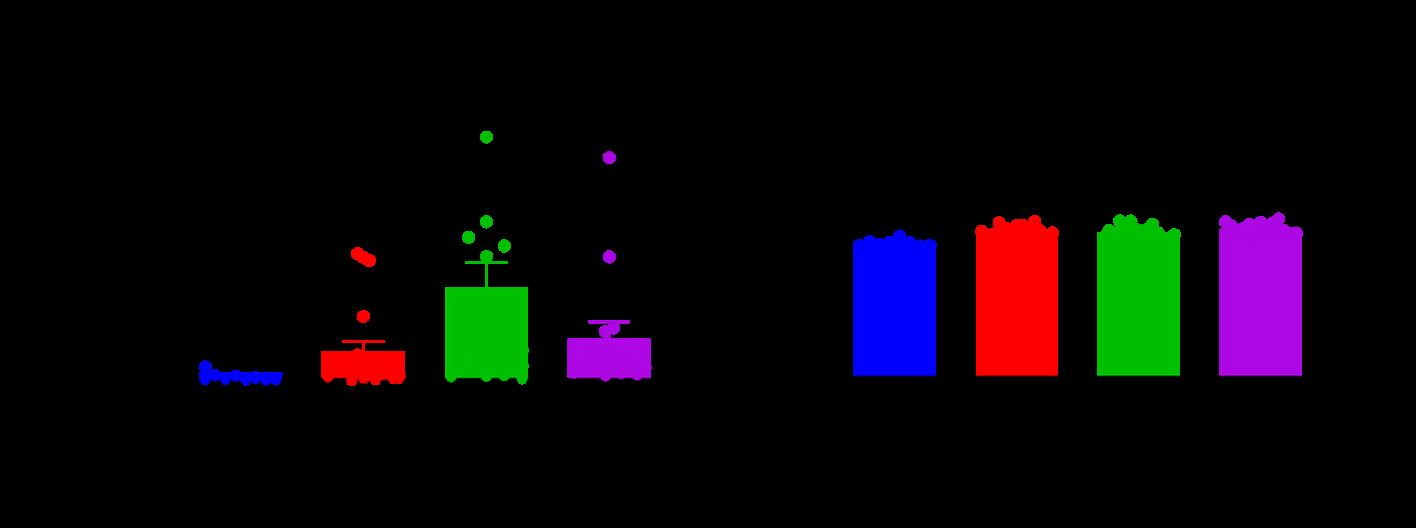
Results: sR-OHCA patients had elevated plasma levels of mtDNA and nucDNA compared to healthy controls (both p<0.01), with a particularly prominent ~14-fold rise in mtDNA that was not different between 30-day survivors and non-survivors (Figure 1). Circulating mtDNA increased regardless of pre-existing IHD or concomitant MI, although patients with IHD exhibited particularly pronounced elevations in mtDNA (Figure 2). Post-ROSC elevations in circulating mtDNA were driven primarily by EV release, as the percentage of EV-encapsulated mtDNA was higher in sR-OHCA samples (79±3%) vs. healthy controls (55±7%, p<0.01).
Conclusion: Human sR-OHCA patients exhibit an early post-ROSC elevation in circulating mtDNA levels independent of pre-existing IHD or concomitant MI that is not associated with 30-day survival. Although these findings argue against the prognostic value of early plasma mtDNA levels in this population, they shed light on mechanisms of post-ROSC mtDNA release and suggest that EV-mediated transfer of mtDNA to immune cells may be a viable target to modulate immune activation in PCAS.
Methods: sR-OHCA patients (n=57) from 4 tertiary care centers in Western New York were stratified into 30-day survivor (n=28) and non-survivor (n=29) cohorts. Blood plasma collected within 6-hours of ROSC was subjected to qPCR to quantify circulating mtDNA (CytB) and nuclear DNA (nucDNA; B2M) compared with healthy controls (n=9). Sub-group analysis was performed to evaluate the influence of pre-existing IHD or concomitant MI, and samples were treated with DNase I to quantify EV-encapsulated vs. free floating mtDNA and nucDNA.
Results: sR-OHCA patients had elevated plasma levels of mtDNA and nucDNA compared to healthy controls (both p<0.01), with a particularly prominent ~14-fold rise in mtDNA that was not different between 30-day survivors and non-survivors (Figure 1). Circulating mtDNA increased regardless of pre-existing IHD or concomitant MI, although patients with IHD exhibited particularly pronounced elevations in mtDNA (Figure 2). Post-ROSC elevations in circulating mtDNA were driven primarily by EV release, as the percentage of EV-encapsulated mtDNA was higher in sR-OHCA samples (79±3%) vs. healthy controls (55±7%, p<0.01).
Conclusion: Human sR-OHCA patients exhibit an early post-ROSC elevation in circulating mtDNA levels independent of pre-existing IHD or concomitant MI that is not associated with 30-day survival. Although these findings argue against the prognostic value of early plasma mtDNA levels in this population, they shed light on mechanisms of post-ROSC mtDNA release and suggest that EV-mediated transfer of mtDNA to immune cells may be a viable target to modulate immune activation in PCAS.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Community-Based Intervention to Improve Cardiovascular Health Understanding in the Dallas-Fort Worth South Asian Community
Deo Parminder, Rohatgi Anand, Sharma Parul, Sathyamoorthy Mohanakrishnan
A New Biomarker of Aging Derived From Electrocardiogram Improves Risk Prediction of Incident Myocardial Infarction and Stroke.Wilsgaard Tom, Rosamond Wayne, Schirmer Henrik, Lindekleiv Haakon, Attia Zachi, Lopez-jimenez Francisco, Leon David, Iakunchykova Olena