Final ID: 33
A Novel Imaging Biomarker to Make Precise Outcome Predictions for Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
Methods: Consecutive patients treated for AIS at certified stroke centers in Houston, TX were included. Patients’ precise functional outcomes at hospital discharge were recorded including decreased level of consciousness, presence of language impairment, visual deficit, arm and leg weakness, need for walking assistance, and gastrostomy placement. The primary outcome for this study was the performance of calculated NWU and clinical variables to predict language impairment at discharge. Baseline characteristics were compared, and then univariate and multivariate logistic regression were used to evaluate the association between clinical variables, imaging data, and the precise neurological outcomes.
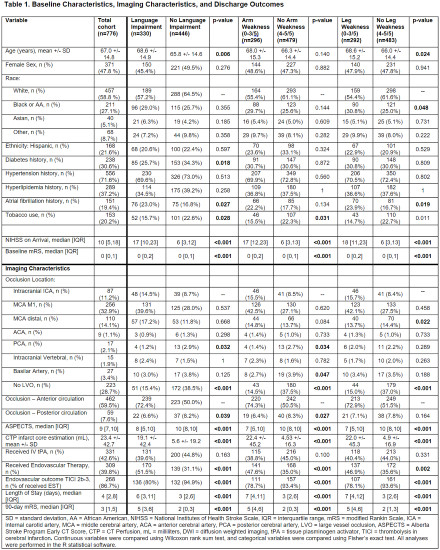
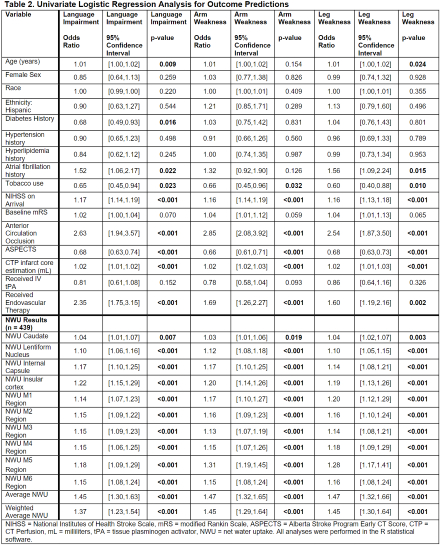
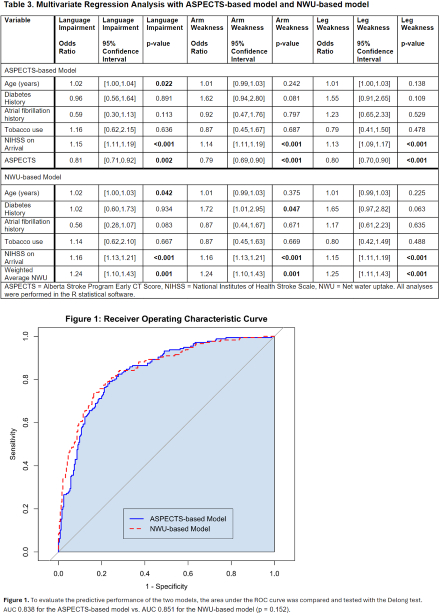
Results: Among 776 patients with AIS, average age was 67.0 +/- 14.8, 47.8% were female, median NIHSS was 10 [5,18], median ASPECTS was 9 [7,10], 42.6% received tPA, and 67.1% had a large vessel occlusion (see Table 1). In univariate logistic regression, higher NWU (OR 1.45, CI 1.30-1.63) and lower ASPECTS (OR 0.68, CI 0.63-0.74) were both significantly associated with higher likelihood of language impairment and other deficits at discharge (see Table 2). Additionally, higher NWU in all ten regions was significantly associated with deficit at discharge. In multivariate logistic regression, certain clinical and imaging variables remained significantly associated as described in Table 3. The ASPECTS and NWU-based regression models were directly compared when predicting language impairment using ROC curve analysis, and areas under the curve were 0.838 vs. 0.851 respectively (p = 0.152 with Delong test, see Figure 1).
Conclusion: The novel NWU biomarker was significantly associated with precise post-AIS outcomes at discharge. When controlling for confounders, NWU was non-inferior to ASPECTS. Moving forward, region-based and overall NWU will need to be studied with long-term patient outcomes. Ultimately, this novel and open-access imaging biomarker could be used in the emergency setting to guide treatment decision-making and patient counseling.
More abstracts on this topic:
Marrero Natalie, Thanassoulis George, Rotter Jerome, Blaha Michael, Whelton Seamus, Jha Kunal, Grant Jelani, Razavi Alexander, Budoff Matthew, Shah Sanjiv, Blumenthal Roger, Post Wendy, Shaw Leslee
A Metabolomic Study of Cardiac Dysfunction in HyperglycemiaYoshida Yilin, Qi Qibin, Cheng Susan, Kaplan Robert, Rodriguez Carlos, Shah Amil, Yu Bing, Nguyen Ngoc Quynh, Moon Eun Hye, Casey Rebholz, Skali Hicham, Arthur Victoria, Echouffo Justin, Ballantyne Christie, Selvin Elizabeth
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.