Final ID: TP277
Hispanic Ethnicity and Diabetes are Associated with High On-Treatment Platelet Reactivity
Abstract Body: Introduction: Clopidogrel (Plavix) is an antiplatelet medication that requires conversion to an active drug through metabolic pathways in the liver using the CYP2C19 enzyme. The objective of this study is to assess the prevalence rate of high on-treatment platelet reactivity (HTPR, poor metabolizers) and evaluate rates of HTPR by principal diagnosis, demographics, and clinical characteristics.
Methods: This retrospective observational cohort study included 586 patients admitted to a comprehensive stroke center in the USA from 1/1/2022 – 1/1/2024 with a P2Y12 enzyme activity assay. Patients were excluded from the analysis if they were non-compliant on-treatment (n=3) or were clopidogrel naïve and did not receive a timely loading dose > 6 hours before the assay or 3 daily standard doses prior to the assay (n=211). Platelet inhibition assay results were expressed as P2Y12 platelet reaction units (PRUs); >194 PRUs were considered HTPR (poor metabolizers), while <194 PRUs were adequate metabolizers. Chi-square tests were used to compare HTPR by principal diagnosis, demographics (age, sex, race, comorbidities), laboratory findings, and AIS stroke subtype (TOAST classification).
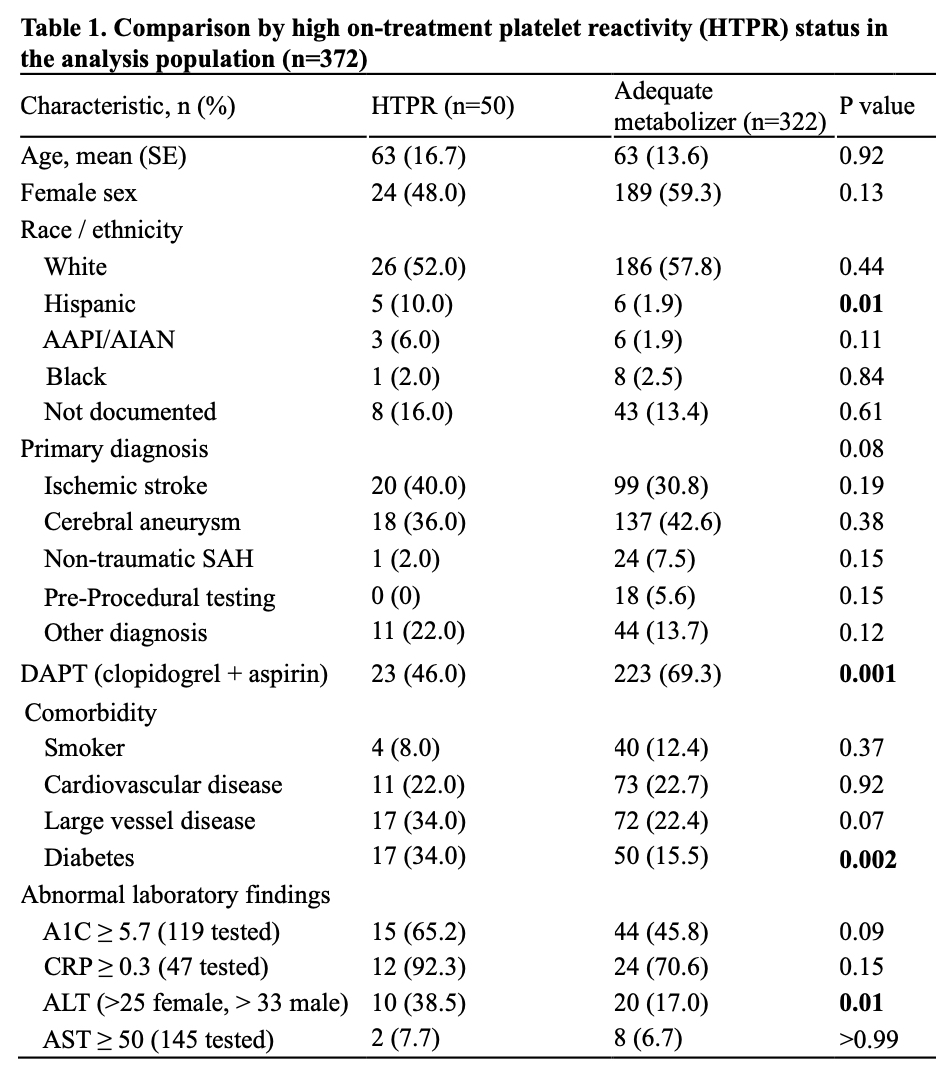
Results: The analysis population included 372 (63%) patients; most patients (n=284, 76%) were chronic clopidogrel users while 88 patients received therapeutic clopidogrel in-hospital. The most common principal diagnoses were cerebral aneurysm (42%) and AIS (32%). HTPR was identified in 50 patients (13%), Table 1. Compared to adequate responders, patients with HTPR were more likely to be Hispanic (10% vs. 2%, p=0.01), to have diabetes (34% vs. 16%, p<0.001), to have elevated alanine transaminase (ALT; 39% vs. 17%, p=0.01), and less likely to be on dual antiplatelet therapy (46% vs. 69%, p=0.01); there were no differences in age, sex, other examined comorbidities, and other abnormal lab findings (A1C, CRP, AST), or by principal diagnosis, p=0.08. Diabetes was more common in Hispanic patients; however, diabetes was significantly associated with HTPR independent of ethnicity. In the subset of patients with AIS (n=119), similar trends were identified.
Conclusion: Providers should be aware that patients with diabetes and those of Hispanic ethnicity are at higher risk for HTPR. These findings support greater use of personalized medicine, especially when prescribing medications with known discrepant activity.
Methods: This retrospective observational cohort study included 586 patients admitted to a comprehensive stroke center in the USA from 1/1/2022 – 1/1/2024 with a P2Y12 enzyme activity assay. Patients were excluded from the analysis if they were non-compliant on-treatment (n=3) or were clopidogrel naïve and did not receive a timely loading dose > 6 hours before the assay or 3 daily standard doses prior to the assay (n=211). Platelet inhibition assay results were expressed as P2Y12 platelet reaction units (PRUs); >194 PRUs were considered HTPR (poor metabolizers), while <194 PRUs were adequate metabolizers. Chi-square tests were used to compare HTPR by principal diagnosis, demographics (age, sex, race, comorbidities), laboratory findings, and AIS stroke subtype (TOAST classification).
Results: The analysis population included 372 (63%) patients; most patients (n=284, 76%) were chronic clopidogrel users while 88 patients received therapeutic clopidogrel in-hospital. The most common principal diagnoses were cerebral aneurysm (42%) and AIS (32%). HTPR was identified in 50 patients (13%), Table 1. Compared to adequate responders, patients with HTPR were more likely to be Hispanic (10% vs. 2%, p=0.01), to have diabetes (34% vs. 16%, p<0.001), to have elevated alanine transaminase (ALT; 39% vs. 17%, p=0.01), and less likely to be on dual antiplatelet therapy (46% vs. 69%, p=0.01); there were no differences in age, sex, other examined comorbidities, and other abnormal lab findings (A1C, CRP, AST), or by principal diagnosis, p=0.08. Diabetes was more common in Hispanic patients; however, diabetes was significantly associated with HTPR independent of ethnicity. In the subset of patients with AIS (n=119), similar trends were identified.
Conclusion: Providers should be aware that patients with diabetes and those of Hispanic ethnicity are at higher risk for HTPR. These findings support greater use of personalized medicine, especially when prescribing medications with known discrepant activity.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cardiovascular and Bleeding Outcomes of Proton-Pump Inhibitor and Clopidogrel Co-therapy after Percutaneous Intervention: A Meta-Analysis
Haider Mobeen, Hamza Mohammad, Singh Sahib, Mir Junaid, Javed Nismat, Khalid Yousra, Sattar Yasar, Subramaniam Parameshwari Subanandhini, Sengodan Prasanna
From Treatment to Trigger: A Case of Atomoxetine-Induced Brugada PatternAbdelsalam Mahmoud, Elsayed Omar, Ezaldin Shady, Ahmed Maram, Gharib Elie
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)