Final ID: P2048
Comparison of Incident Cardiovascular Diseases Between Asian American, Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islanders in Hawaii vs. Northern California: The PANACHE Study
Abstract Body: Introduction: Hawaii (HI) and California (CA) are home to the largest and fast-growing Asian American, Native Hawaiian, and other Pacific Islander (AANHPI) populations in the U.S., yet our understanding about the influence of factors related to geographic location on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risks within the AANHPI population is limited. We compared incident CVD rates for eight AANHPI subgroups between HI and California CA.
Methods: We identified AANHPI members of Kaiser Permanente Hawaii and Northern California aged ≥30 years with no prior CVD from 2012-2022. Outcomes included incident acute myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, heart failure (HF) and atrial fibrillation (AF) using validated diagnosis codes in electronic health records. Cox proportional hazards models stratified by AANHPI subgroup were performed to evaluate the association between geographic region (CA vs. HI) and each CVD outcome, after patient-level adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, census tract-level education and income, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease stage, depression, alcohol use, and smoking status.
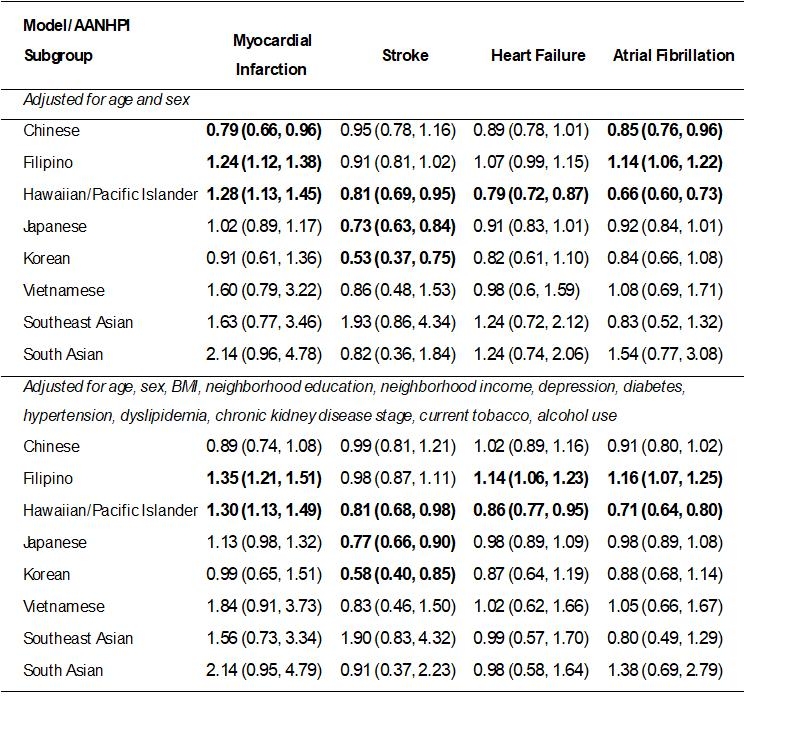
Results: Among 677,563 AANHPI adults with no prior CVD, mean age was 47±14 years, with higher proportion of women at both sites (53.0% HI, 58.8% CA), and a mean BMI of 28.2 in HI and 25.8 in CA. In stratified multivariable models that adjusted for demographic and CVD risk factors, rates of incident MI, stroke, HF and AF varied between CA and HI depending on the CVD outcome and AANHPI subgroup. Among Filipino adults, those living in CA had a higher adjusted rate of MI (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.35, 1.21-1.51), HF (aHR 1.14, 1.06-1.23) and AF (aHR 1.16, 1.07-1.25) than those living in HI. Among Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander adults, those living in CA had a higher adjusted rate of MI (aHR 1.30, 1.13-1.49) but a lower adjusted rate of stroke (aHR 0.81, 0.68-0.98), HF (aHR 0.86, 0.77-0.95) and AF (aHR 0.71, 0.64-0.80) than those living in HI. In addition, the adjusted rate of stroke was lower for Japanese (aHR 0.77, 0.66-0.90) and Korean (aHR 0.58, 0.40-0.85) adults in CA.
Conclusions: We observed varying rates of incident CVD events across AANHPI subgroups between HI and CA that were not explained by measured sociodemographic and clinical risk factors. Further investigation into environmental, structural, and behavioral risk factors that may contribute to the observed CVD outcome variation within AANHPI subgroups is needed.
Methods: We identified AANHPI members of Kaiser Permanente Hawaii and Northern California aged ≥30 years with no prior CVD from 2012-2022. Outcomes included incident acute myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, heart failure (HF) and atrial fibrillation (AF) using validated diagnosis codes in electronic health records. Cox proportional hazards models stratified by AANHPI subgroup were performed to evaluate the association between geographic region (CA vs. HI) and each CVD outcome, after patient-level adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, census tract-level education and income, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease stage, depression, alcohol use, and smoking status.
Results: Among 677,563 AANHPI adults with no prior CVD, mean age was 47±14 years, with higher proportion of women at both sites (53.0% HI, 58.8% CA), and a mean BMI of 28.2 in HI and 25.8 in CA. In stratified multivariable models that adjusted for demographic and CVD risk factors, rates of incident MI, stroke, HF and AF varied between CA and HI depending on the CVD outcome and AANHPI subgroup. Among Filipino adults, those living in CA had a higher adjusted rate of MI (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.35, 1.21-1.51), HF (aHR 1.14, 1.06-1.23) and AF (aHR 1.16, 1.07-1.25) than those living in HI. Among Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander adults, those living in CA had a higher adjusted rate of MI (aHR 1.30, 1.13-1.49) but a lower adjusted rate of stroke (aHR 0.81, 0.68-0.98), HF (aHR 0.86, 0.77-0.95) and AF (aHR 0.71, 0.64-0.80) than those living in HI. In addition, the adjusted rate of stroke was lower for Japanese (aHR 0.77, 0.66-0.90) and Korean (aHR 0.58, 0.40-0.85) adults in CA.
Conclusions: We observed varying rates of incident CVD events across AANHPI subgroups between HI and CA that were not explained by measured sociodemographic and clinical risk factors. Further investigation into environmental, structural, and behavioral risk factors that may contribute to the observed CVD outcome variation within AANHPI subgroups is needed.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adiposity and Cardiac Function in South Asian Americans: Findings from the MASALA Study
Kanaya Alka, Nelson Lauren, Running Allison, Lin Feng, Kandula Namratha, Gadgil Meghana, Win Sithu, Shah Sanjiv
A Novel Cardioprotective Mechanism in Myocardial Reperfusion Injury: Dual Neutrophil Modulation and ROS/HOCl Scavenging by an Atypical ChemokineZwissler Leon, Bernhagen Juergen, Cabrera-fuentes Hector Alejandro, Hernandez Resendiz Sauri, Yap En Ping, Schindler Lisa, Zhang Zhishen, Dickerhof Nina, Hampton Mark, Liehn Elisa, Hausenloy Derek