Final ID: FR525
Hypertensive Disease as a Contributor to Mortality in Mental and Behavioral Disorders: Insights from CDC WONDER database
Abstract Body: Background:
Mental and behavioral disorders contribute substantially to global disease burden, though they are less commonly the direct cause of death. The role of coexisting conditions, particularly hypertensive disease(HD), in shaping mortality outcomes among individuals with primary psychiatric diagnoses remains underexplored.
Methods:
Using CDC WONDER Multiple Cause of Death data (1999–2020), we identified deaths with underlying cause coded as MBDs and evaluated HD as a contributing cause. Annualized percentage change (APC) was calculated using log-linear regression. Subgroup analyses were performed by age, race, and urbanization level.
Results:
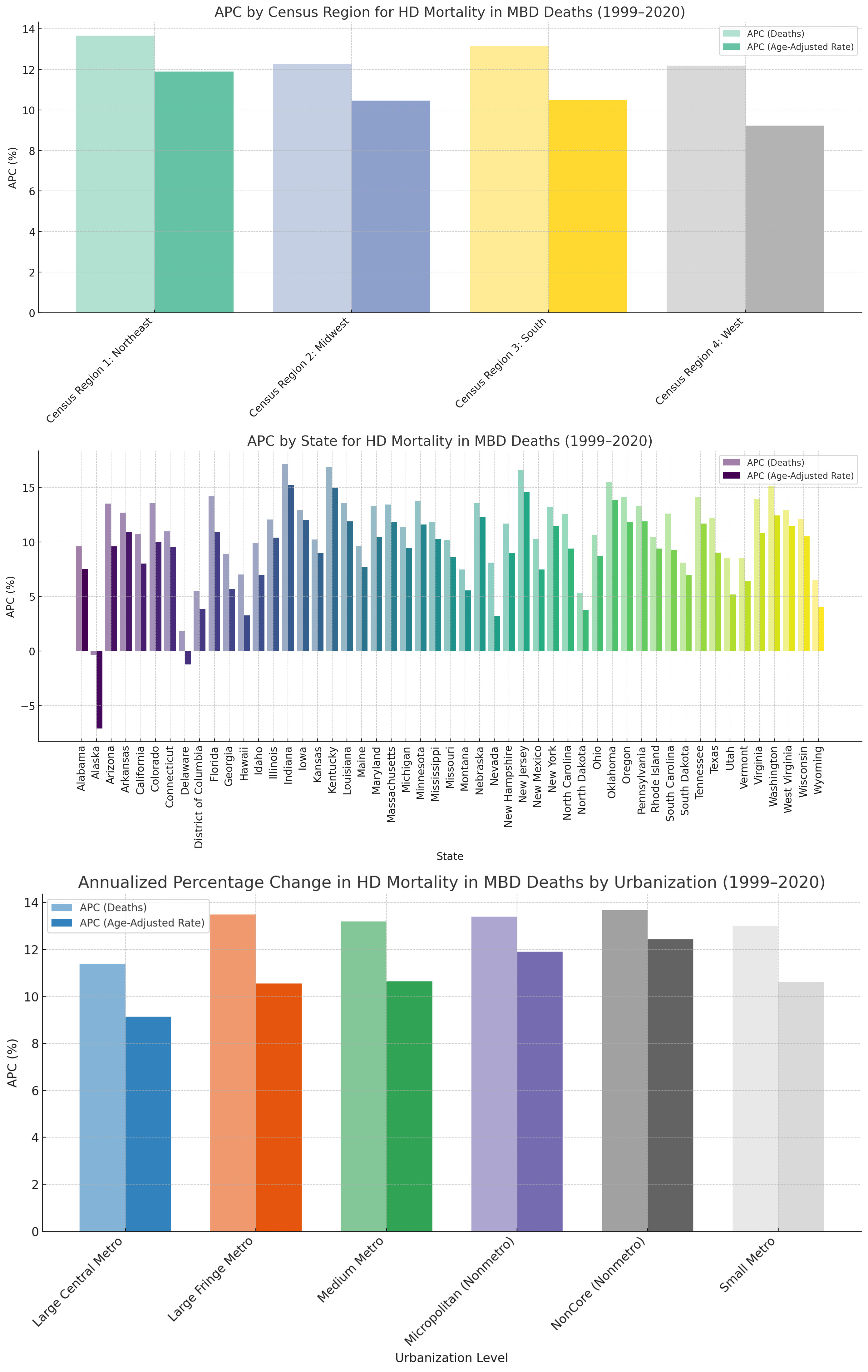
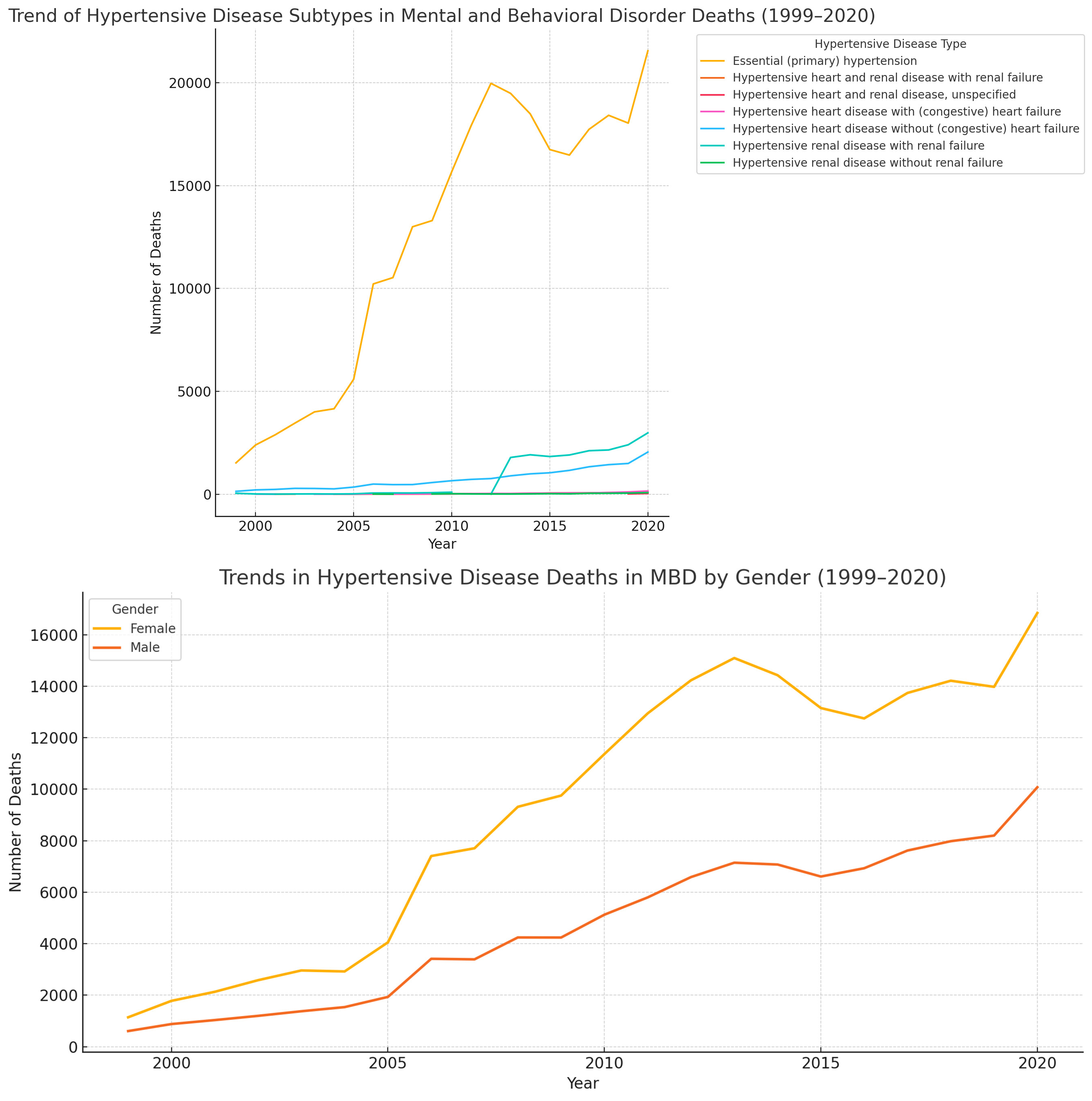
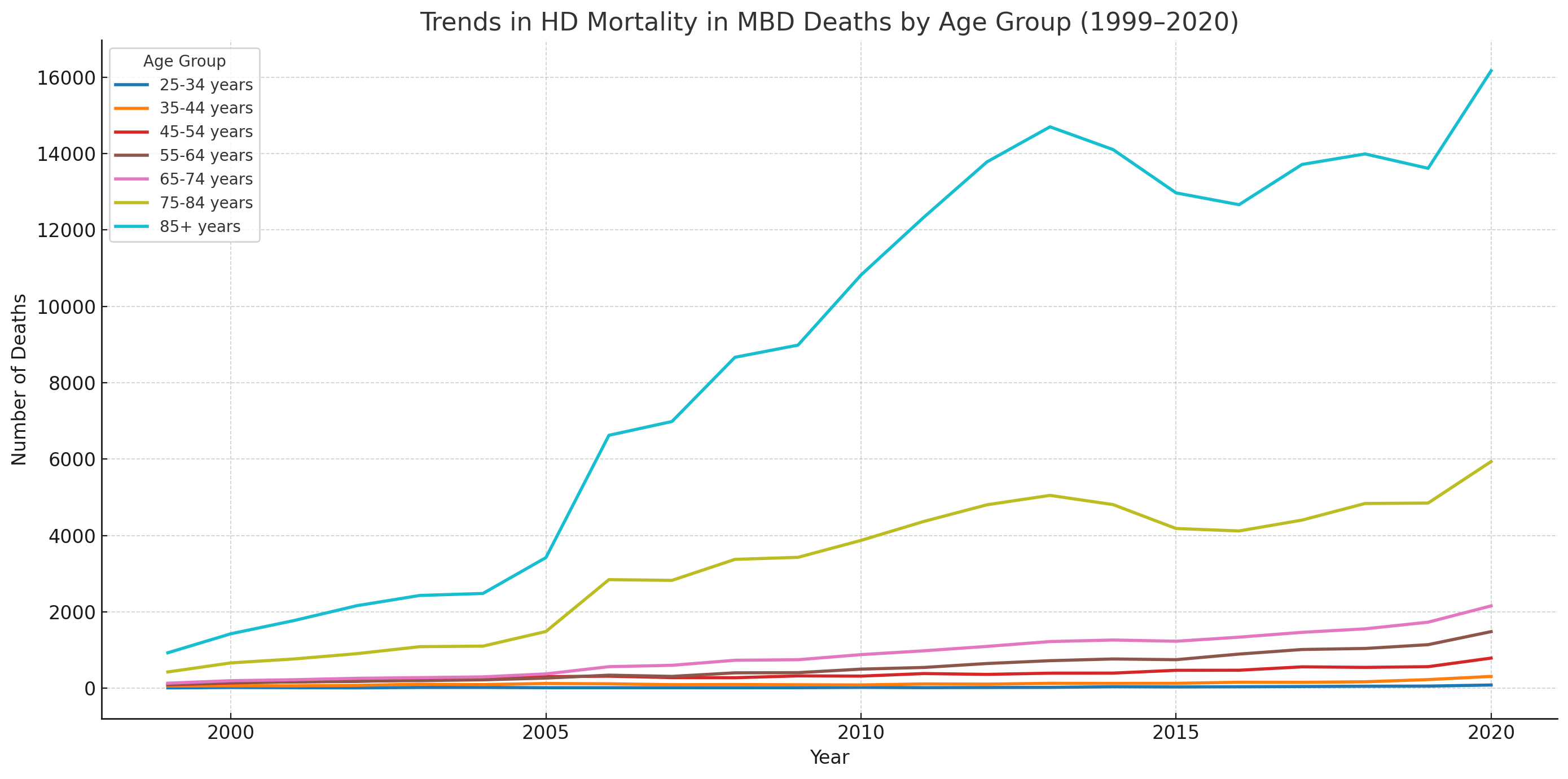
Between 1999-2020, deaths due to HD in MBDs surged from 1,749 to 26,922, reflecting an annualized increase of +12.82%; concurrently, the age-adjusted mortality rate rose from 0.6 (95% UI: 0.6–0.7) to 6.5 (6.5–6.7) per 100,000, with an APC of +10.53%. From 1999-2020, among deaths attributed to mental and behavioral disorders (MBDs), hypertensive renal disease with renal failure showed the highest annualized increase (+33.34%), followed by hypertensive heart disease with heart failure (+14.59%), essential hypertension (+12.16%), hypertensive renal disease without failure (+12.35%), and hypertensive heart disease without heart failure (+11.73%). Hispanic or Latino individuals observed higher increased in APC compared to non-hispanic ((APC: +17.08% vs +8.85%). In terms of race, deaths rose highest among Asian or Pacific Islanders (APC: +18.41%), followed by American Indian or Alaska Natives (+14.81%), Whites (+12.87%), and Black or African Americans (+11.72%). From 1999-2020, HD deaths in MBDs rose more sharply among males (APC: +13.37%) than females (+12.53%), with the steepest increases observed in older adults aged 85+ years (+13.76%), 65–74 years (+12.93%), and 55–64 years (+12.18%).
Conclusion:
These findings highlight a concerning rise in HD–related mortality among individuals with mental and behavioral disorders, with the greatest increases seen among Hispanic communities, Asian or Pacific Islanders, American Indian or Alaska Natives, older adults, and men. Moving forward, integrated care models that unify cardiovascular and mental health services are essential to addressing these compounded risks and reducing preventable mortality in high-risk populations.
Mental and behavioral disorders contribute substantially to global disease burden, though they are less commonly the direct cause of death. The role of coexisting conditions, particularly hypertensive disease(HD), in shaping mortality outcomes among individuals with primary psychiatric diagnoses remains underexplored.
Methods:
Using CDC WONDER Multiple Cause of Death data (1999–2020), we identified deaths with underlying cause coded as MBDs and evaluated HD as a contributing cause. Annualized percentage change (APC) was calculated using log-linear regression. Subgroup analyses were performed by age, race, and urbanization level.
Results:
Between 1999-2020, deaths due to HD in MBDs surged from 1,749 to 26,922, reflecting an annualized increase of +12.82%; concurrently, the age-adjusted mortality rate rose from 0.6 (95% UI: 0.6–0.7) to 6.5 (6.5–6.7) per 100,000, with an APC of +10.53%. From 1999-2020, among deaths attributed to mental and behavioral disorders (MBDs), hypertensive renal disease with renal failure showed the highest annualized increase (+33.34%), followed by hypertensive heart disease with heart failure (+14.59%), essential hypertension (+12.16%), hypertensive renal disease without failure (+12.35%), and hypertensive heart disease without heart failure (+11.73%). Hispanic or Latino individuals observed higher increased in APC compared to non-hispanic ((APC: +17.08% vs +8.85%). In terms of race, deaths rose highest among Asian or Pacific Islanders (APC: +18.41%), followed by American Indian or Alaska Natives (+14.81%), Whites (+12.87%), and Black or African Americans (+11.72%). From 1999-2020, HD deaths in MBDs rose more sharply among males (APC: +13.37%) than females (+12.53%), with the steepest increases observed in older adults aged 85+ years (+13.76%), 65–74 years (+12.93%), and 55–64 years (+12.18%).
Conclusion:
These findings highlight a concerning rise in HD–related mortality among individuals with mental and behavioral disorders, with the greatest increases seen among Hispanic communities, Asian or Pacific Islanders, American Indian or Alaska Natives, older adults, and men. Moving forward, integrated care models that unify cardiovascular and mental health services are essential to addressing these compounded risks and reducing preventable mortality in high-risk populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
COVID-19-Related Changes in Dalily Life, Concerns, and Their Associations with Sleep Disturbances
Cho Sung-il, Kim Young-mee
Association between Chronotype and Psychological Health in South Korean AdolescentsSeo Jinhee, Cho Sung-il, Won Sung-ho