Final ID: 109
Characteristics and Temporal Usage Patterns of Omron Home Blood Pressure Device Users in the United States
Abstract Body: Background Patients increasingly monitor blood pressure (BP) at home using consumer devices, but little is known about active users and their behaviors. Blood pressure device companies such as Omron collects user data via Omron mobile application that pair with home blood pressure (HBP) devices, representing a unique opportunity to characterize self-monitoring trends and behaviors.
Objective To characterize the demographic and behavioral characteristics, clinical conditions, and temporal usage patterns of Omron HBP users.
Methods De-identified data of US Omron HBP device and compatible mobile application users were obtained from Omron Healthcare, Inc. (Hoffman Estates, IL). We performed a descriptive analysis of users’ self-reported demographic characteristics, behaviors, and medical conditions. Additionally, we examined patterns of HBP device usage over time.
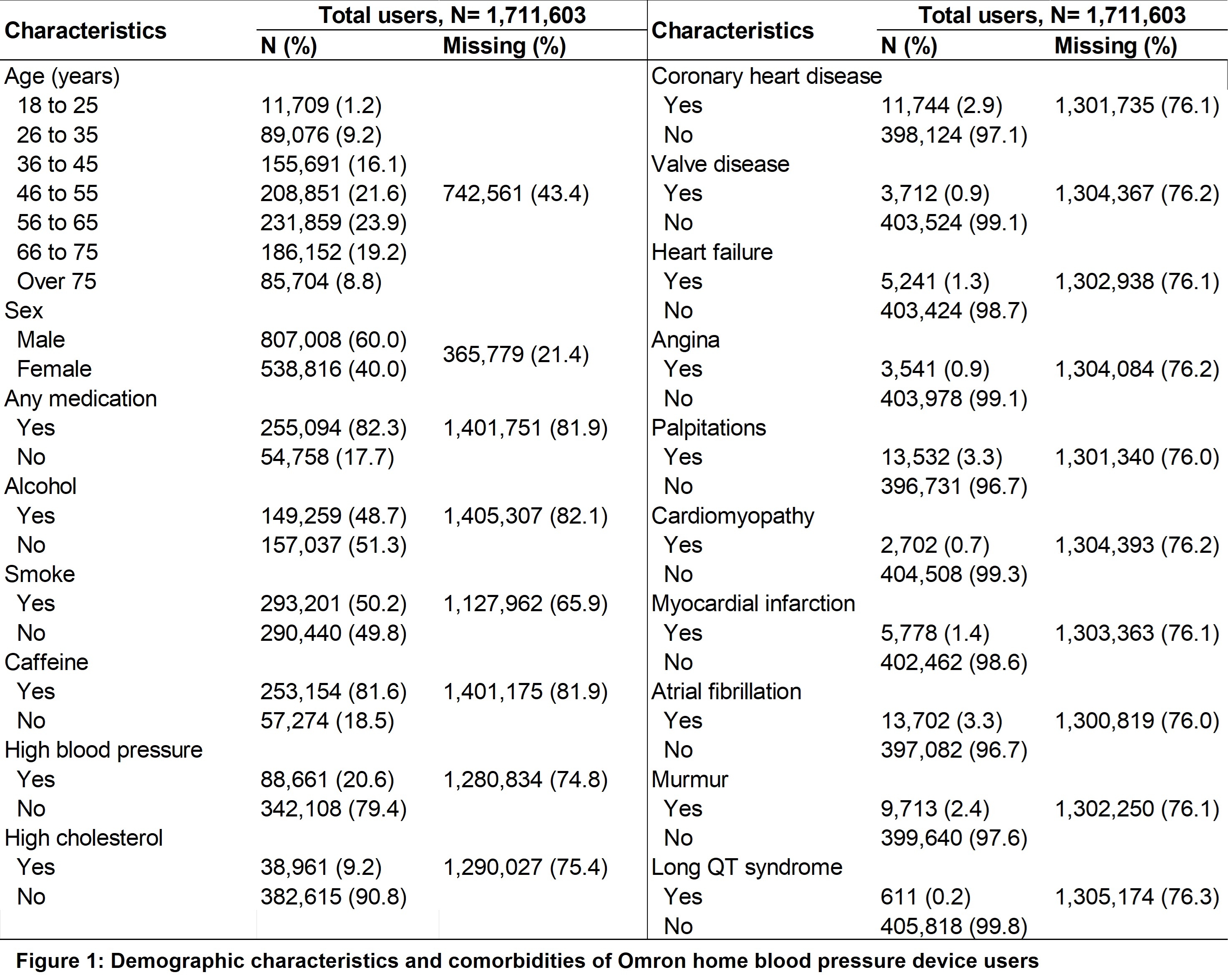
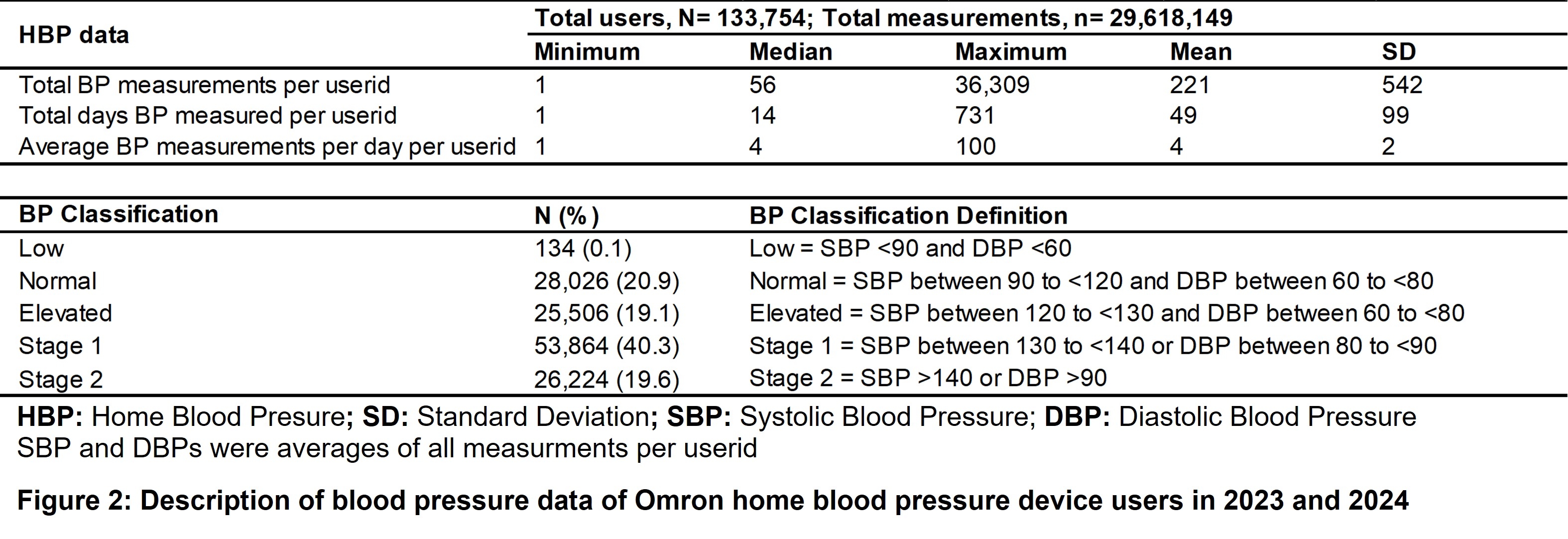
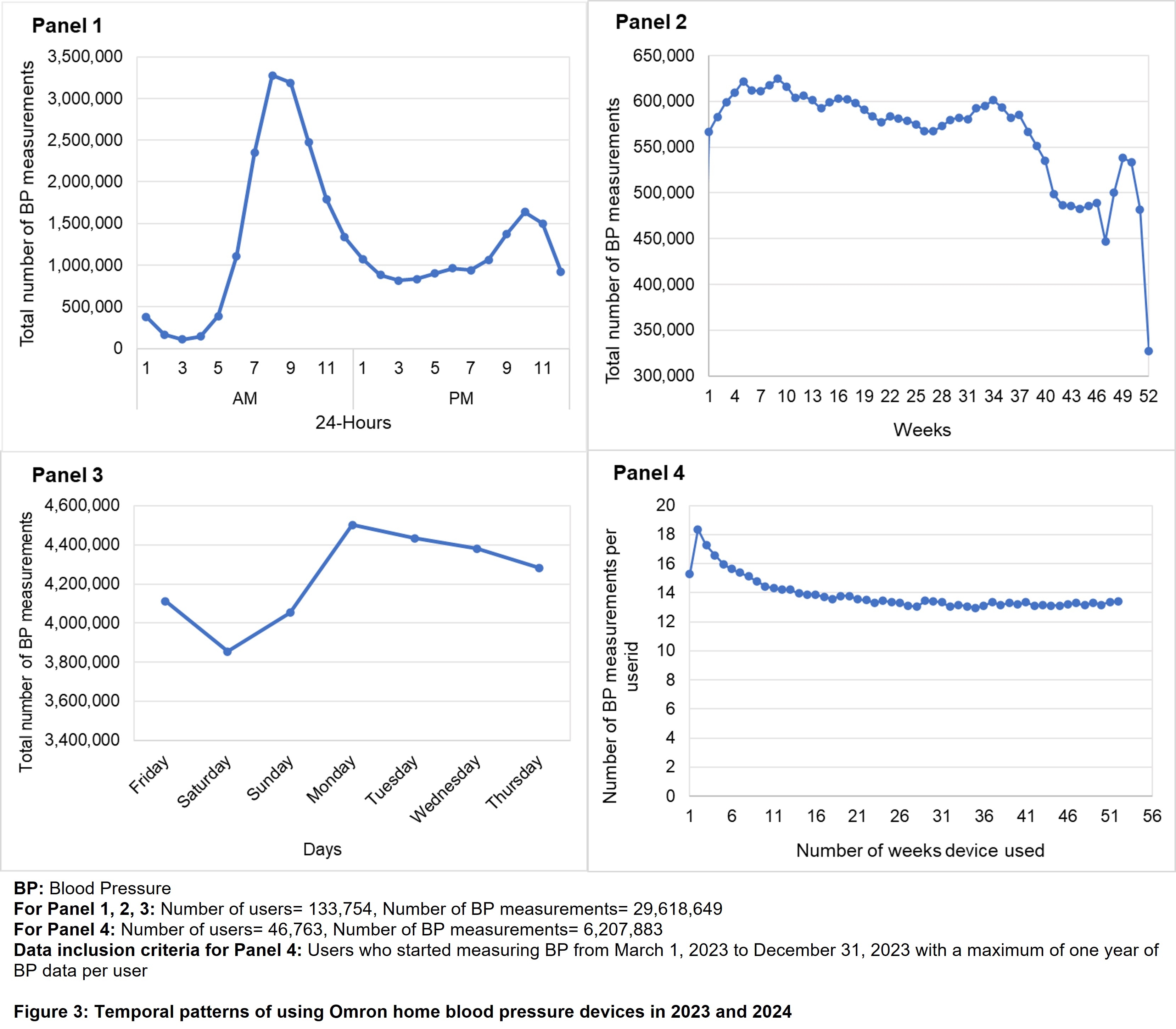
Results Of 1,711,603 Omron HBP device and compatible mobile application users, proportion of missing data for demographic and clinical characteristics ranged from 21.4% to 81.9%. Among users who provided information, 28.0% were over 65 years old and 60.0% were male. The majority of users (>80.0%) reported medication and caffeine use. Around half of them reported smoking or drinking alcohol. More than 20% reported having high BP, while 9.2% had high cholesterol. Users reported various cardiovascular symptoms and diseases (e.g., palpitations, coronary heart disease) with prevalence ranging from 0.2% to 3.3% (Figure 1). Among the 133,754 Omron HBP users in 2023 and 2024, device usage duration ranged from 1 to 731 days, with the number of BP measurements per user ranging from 1 to 36,309. Half of the users used their devices a total of ≤14 days and measured BP ≤56 times; 60% of users had stage 1 or 2 hypertension (Figure 2). The majority of BP readings were taken in the morning between 7 and 10 AM, and at night between 9 and 11 PM. A sharp decline in BP measurements was observed from weeks 36 to 48 of the calendar year. Users measured BP more during weekdays compared to the weekend. Users measured BP more frequently at the beginning of device registration and use gradually declined over time (Figure 3, Panels 1, 2, 3, and 4).
Conclusion Given the wide variation in HBP device usage, Omron’s cloud-based data is an unparalleled source of HBP data to further explore patterns and barriers in monitoring BP at home. The findings could inform interventions to improve long-term engagement with HBP devices in the US.
Objective To characterize the demographic and behavioral characteristics, clinical conditions, and temporal usage patterns of Omron HBP users.
Methods De-identified data of US Omron HBP device and compatible mobile application users were obtained from Omron Healthcare, Inc. (Hoffman Estates, IL). We performed a descriptive analysis of users’ self-reported demographic characteristics, behaviors, and medical conditions. Additionally, we examined patterns of HBP device usage over time.
Results Of 1,711,603 Omron HBP device and compatible mobile application users, proportion of missing data for demographic and clinical characteristics ranged from 21.4% to 81.9%. Among users who provided information, 28.0% were over 65 years old and 60.0% were male. The majority of users (>80.0%) reported medication and caffeine use. Around half of them reported smoking or drinking alcohol. More than 20% reported having high BP, while 9.2% had high cholesterol. Users reported various cardiovascular symptoms and diseases (e.g., palpitations, coronary heart disease) with prevalence ranging from 0.2% to 3.3% (Figure 1). Among the 133,754 Omron HBP users in 2023 and 2024, device usage duration ranged from 1 to 731 days, with the number of BP measurements per user ranging from 1 to 36,309. Half of the users used their devices a total of ≤14 days and measured BP ≤56 times; 60% of users had stage 1 or 2 hypertension (Figure 2). The majority of BP readings were taken in the morning between 7 and 10 AM, and at night between 9 and 11 PM. A sharp decline in BP measurements was observed from weeks 36 to 48 of the calendar year. Users measured BP more during weekdays compared to the weekend. Users measured BP more frequently at the beginning of device registration and use gradually declined over time (Figure 3, Panels 1, 2, 3, and 4).
Conclusion Given the wide variation in HBP device usage, Omron’s cloud-based data is an unparalleled source of HBP data to further explore patterns and barriers in monitoring BP at home. The findings could inform interventions to improve long-term engagement with HBP devices in the US.
More abstracts on this topic:
Lifestyle interventions for prevention of cardiovascular disease among mothers of young children: a scoping review
Liu Olivia, Sareen Sinia, Zhu Jiachen, Spruill Tanya, Arabadjian Milla
AI-Driven Gait Classification for Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Detection Using Machine Learning and Nonlinear Gait DynamicsMohammadzadeh Gonabadi Arash, Fallahtafti Farahnaz, Pipinos Iraklis, Burnfield Judith, Myers Sara