Final ID: P1170
Lifestyle interventions for prevention of cardiovascular disease among mothers of young children: a scoping review
Abstract Body: Background: The prevalence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors is high and rising among younger women. Mothers of young children often exhibit poorer diets and lower physical activity levels than mothers of older children and women without children. CVD risk remains elevated well past the 1-year postpartum period for those with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Yet, little is known about interventions for CVD prevention among this group.
Objective: To review and synthesize the available literature on lifestyle interventions for CVD prevention among mothers of young children (≤5 years) and highlight gaps to inform future research.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL, and EMBASE for peer-reviewed English-language articles published 2009-2023 on lifestyle interventions for CVD prevention in mothers with children 1-5 years. The rationale for this age range was because the care needs for this age group are distinct from those of infants but require a higher degree of hands-on caregiving compared to older children. The review was conducted following PRISMA-ScR guidelines, with articles screened by two independent reviewers, with a third reviewer available to resolve conflicts.
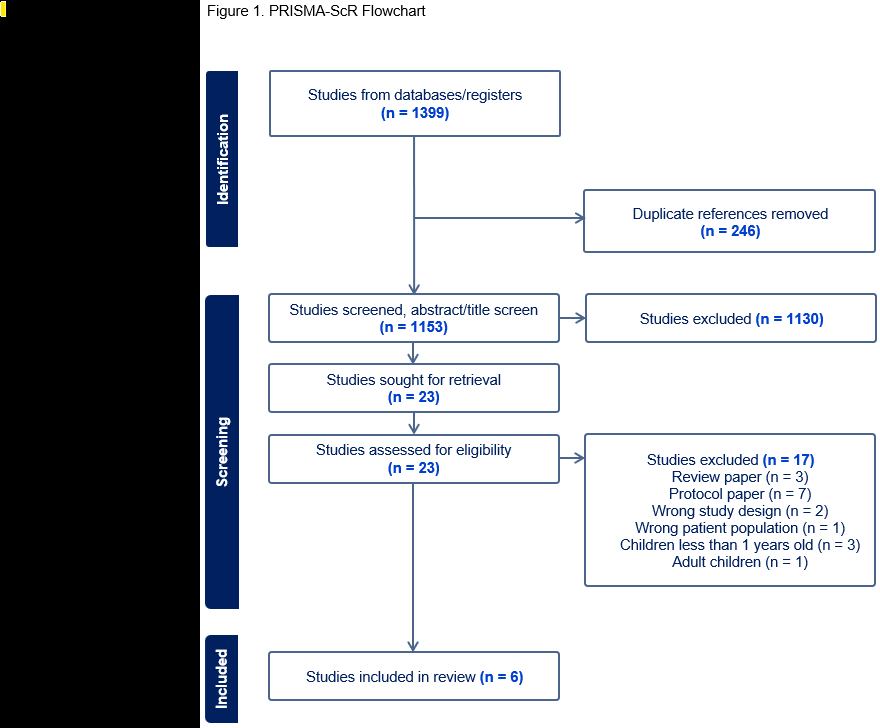
Results: Of 1,405 studies, none exclusively recruited mothers with children 1-5 years. Six studies were eligible because reported mean child age was ≤5 years (Figure 1). Total sample size across studies was 1,614. Five were randomized controlled trials testing in-person (n=3) or digital (n=2) lifestyle interventions. Interventions included workshops with physical activity sessions (n=1), in-person physical/mental health education (n=3), video-based physical/mental health education with peer support groups (n=1), and a smartphone app (n=1). No interventions focused on sleep or tobacco use (Life’s Essential 8 components), or addressed social determinants, which are major drivers of health. Study follow-up ranged from 6-18 months. Outcome measures included self-reported diet, physical activity, perceived stress, and quality of life, and objective assessments of blood pressure, glucose, lipid levels, and weight. Five of 6 studies reported positive results at their primary time points.
Conclusions: Effective strategies to improve CVD risk in mothers of young children have the potential to prevent CV events in later life. Our results highlight a significant gap in the literature on such interventions, underscoring the need for targeted research for this population.
Objective: To review and synthesize the available literature on lifestyle interventions for CVD prevention among mothers of young children (≤5 years) and highlight gaps to inform future research.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL, and EMBASE for peer-reviewed English-language articles published 2009-2023 on lifestyle interventions for CVD prevention in mothers with children 1-5 years. The rationale for this age range was because the care needs for this age group are distinct from those of infants but require a higher degree of hands-on caregiving compared to older children. The review was conducted following PRISMA-ScR guidelines, with articles screened by two independent reviewers, with a third reviewer available to resolve conflicts.
Results: Of 1,405 studies, none exclusively recruited mothers with children 1-5 years. Six studies were eligible because reported mean child age was ≤5 years (Figure 1). Total sample size across studies was 1,614. Five were randomized controlled trials testing in-person (n=3) or digital (n=2) lifestyle interventions. Interventions included workshops with physical activity sessions (n=1), in-person physical/mental health education (n=3), video-based physical/mental health education with peer support groups (n=1), and a smartphone app (n=1). No interventions focused on sleep or tobacco use (Life’s Essential 8 components), or addressed social determinants, which are major drivers of health. Study follow-up ranged from 6-18 months. Outcome measures included self-reported diet, physical activity, perceived stress, and quality of life, and objective assessments of blood pressure, glucose, lipid levels, and weight. Five of 6 studies reported positive results at their primary time points.
Conclusions: Effective strategies to improve CVD risk in mothers of young children have the potential to prevent CV events in later life. Our results highlight a significant gap in the literature on such interventions, underscoring the need for targeted research for this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Predictors of School Non-Engagement in School Aged Children and Adolescents Born with Heart Disease
Hodgson Sarah, Peterson Jennifer
Association of neighborhood environment chracteristics and suboptimal cardiovascular health based on Life’s Essential 8 among young adults in Puerto RicoPerez Cynthia, Tucker Katherine, Kiefe Catarina, Person Sharina, Torres Polaris, Boneu Claudia, Sanchez Miredys, Rodriguez Jose, Rosal Milagros