Final ID: P1067
Impact of Health Literacy, Numeracy, and Social Determinants on Readmission and Outpatient Adherence in Heart Failure Patients at an Urban Safety-Net Hospital
Abstract Body: Background and Aims: Low health literacy and numeracy are associated with increased mortality and rehospitalization in heart failure (HF) patients. However, their combined effect on long-term readmission rates and outpatient visit-adherence remains unclear, particularly in underserved populations. This study aimed to evaluate the association of health literacy and numeracy with 3-month post-discharge readmission rates and outpatient visits in a large, urban, safety-net county hospital.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, observational cohort study of 169 English or Spanish-speaking patients hospitalized with HF in Dallas, TX, from 11/2022 to 06/2023. Patients were stratified into two groups based on validated health literacy (SAHL-E) and numeracy (NUMi) scores: (1) Low Numeracy or Literacy (LNL) and (2) High Numeracy and Literacy (HNL). The primary outcome was a composite rate of emergency department (ED) visits and hospital re-admission rate at 3-months post-discharge, expressed per 100 patient-months. Clinic attendance at 3 months was a secondary outcome. We used univariate analyses and multivariate linear regressions adjusted for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and Charlson comorbidity score.
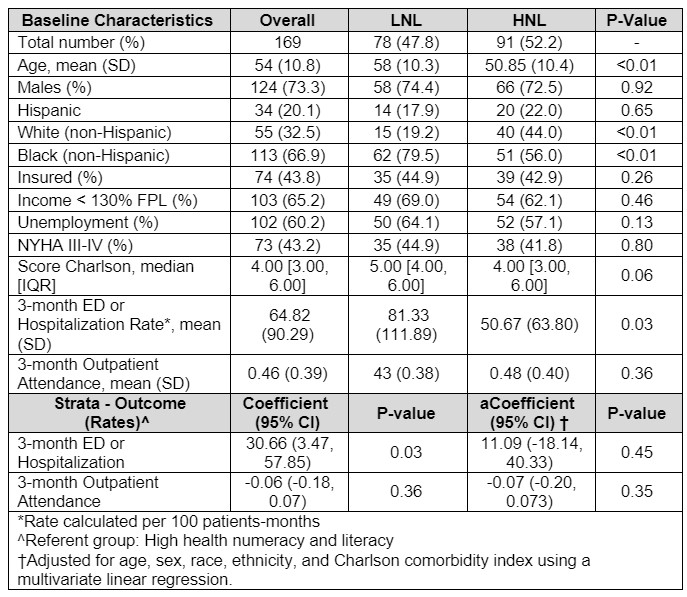
Results: Among participants (mean age 54 years; 73.3% male, 66.9 % Black, 20.1 % Hispanic), 47.8% were in the LNL group and 52.2% in the HNL group. In univariate analyses, the LNL group showed a significantly higher composite ED/hospitalization rate at 3 months (81.33 vs 50.67 per 100 patient-months; β = 30.66, 95% CI: 3.47 to 57.85, P = 0.03). No significant difference was observed in 3-month clinic attendance (43% vs 48%, P = 0.36). After adjustment, both associations were not statistically significant (adjusted β = 11.09, 95% CI: -18.14 to 40.33, P = 0.45 for ED/hospitalization rate).
Conclusions: Low numeracy or literacy was associated with worse clinical outcomes at 3 months in univariate analyses. However, these associations were not significant after adjustment, suggesting that broader social determinants of health may play a more substantial role in healthcare outcomes among underserved patients with HF.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, observational cohort study of 169 English or Spanish-speaking patients hospitalized with HF in Dallas, TX, from 11/2022 to 06/2023. Patients were stratified into two groups based on validated health literacy (SAHL-E) and numeracy (NUMi) scores: (1) Low Numeracy or Literacy (LNL) and (2) High Numeracy and Literacy (HNL). The primary outcome was a composite rate of emergency department (ED) visits and hospital re-admission rate at 3-months post-discharge, expressed per 100 patient-months. Clinic attendance at 3 months was a secondary outcome. We used univariate analyses and multivariate linear regressions adjusted for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and Charlson comorbidity score.
Results: Among participants (mean age 54 years; 73.3% male, 66.9 % Black, 20.1 % Hispanic), 47.8% were in the LNL group and 52.2% in the HNL group. In univariate analyses, the LNL group showed a significantly higher composite ED/hospitalization rate at 3 months (81.33 vs 50.67 per 100 patient-months; β = 30.66, 95% CI: 3.47 to 57.85, P = 0.03). No significant difference was observed in 3-month clinic attendance (43% vs 48%, P = 0.36). After adjustment, both associations were not statistically significant (adjusted β = 11.09, 95% CI: -18.14 to 40.33, P = 0.45 for ED/hospitalization rate).
Conclusions: Low numeracy or literacy was associated with worse clinical outcomes at 3 months in univariate analyses. However, these associations were not significant after adjustment, suggesting that broader social determinants of health may play a more substantial role in healthcare outcomes among underserved patients with HF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Characteristics and Association of Cannabis Use on Cardiovascular Outcomes in patients hospitalized with Atrial Fibrillation: An NRD Propensity Matched Analysis
Brar Ajit, Ravi Soumiya, Chirumamilla Yashitha, Garg Ayushi, Omer Mohammed, Maharjan Nikky, Maini Shriya, Zreik Ali
A Multi-centre, Randomized, Controlled Study of External CounterPulsation for Patients with Recent Atherosclerotic Stroke (SPA)Xiong Li, Chen Xiangyan, Leung Howan, Zhu Lixia, Leung Thomas, Wong Lawrence