Final ID: Su2172
Clinical and Hemodynamic Correlates of Supranormal Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) with EF≥65% may have a higher risk for adverse outcomes, however, the exercise, functional status, and hemodynamic correlates of this phenotype in a contemporary cohort is not well defined.
Methods
This single-center study included patients with LVEF ≥50% with clinically indicated invasive right heart catheterization and echocardiogram enrolled in a prospective HFpEF registry at UT Southwestern between 4/2022-5/2024. Participants underwent peak oxygen uptake (VO2) assessment with maximal bicycle test (Lode ergometer), quality of life assessment (Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire [KCCQ]), physical function testing with the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), and 6-minute walk distance (6MWD). Participants were stratified by those with EF ≥ 65% and EF 50%-65%. Multivariable adjusted linear regression models were used to evaluate the association of EF ≥ 65% with peak VO2, quality of life, noninvasive and invasive cardiac filling pressures, and functional outcomes.
Results
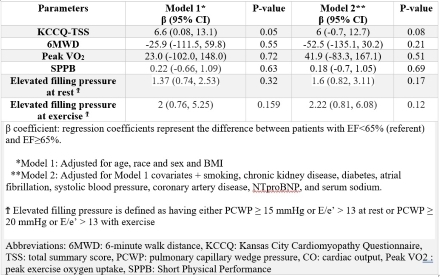
347 participants were included in the study. 112 (32.3%) participants had EF≥65%, and there were no differences in demographics across EF subgroups. Patients with EF≥65% had a higher burden of hypertension (94.6% vs. 86.8%, p = 0.04) and had higher E/e’ (14.0[95% CI 10.9-18.0] vs. 12.7[95% CI 9.5-16.7], p = 0.048) and PCWP with exercise (27[95% CI 20-30] vs 22[95% CI 18-28] mmHg, p=0.04) without differences in resting PCWP or PCWP/cardiac output slope at maximal exercise. After adjustment for age, sex, race, and BMI, EF≥65% was associated with higher KCCQ. However, these findings were attenuated after adjustment for comorbidities (Model 1: β 6.6, p=0.05 vs Model 2: β 6.0, p=0.08). EF≥65% was not associated with functional outcomes, peak exercise capacity, or elevated filling pressures in adjusted models. (Table)
Conclusions
There were no significant differences in quality of life, functional status, exercise capacity, and filling pressures among patients with supranormal and normal ejection fraction. These findings suggest that extra-cardiac mechanisms may be more important contributors to functional status and peak exercise capacity in patients with EF≥65%.
Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) with EF≥65% may have a higher risk for adverse outcomes, however, the exercise, functional status, and hemodynamic correlates of this phenotype in a contemporary cohort is not well defined.
Methods
This single-center study included patients with LVEF ≥50% with clinically indicated invasive right heart catheterization and echocardiogram enrolled in a prospective HFpEF registry at UT Southwestern between 4/2022-5/2024. Participants underwent peak oxygen uptake (VO2) assessment with maximal bicycle test (Lode ergometer), quality of life assessment (Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire [KCCQ]), physical function testing with the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), and 6-minute walk distance (6MWD). Participants were stratified by those with EF ≥ 65% and EF 50%-65%. Multivariable adjusted linear regression models were used to evaluate the association of EF ≥ 65% with peak VO2, quality of life, noninvasive and invasive cardiac filling pressures, and functional outcomes.
Results
347 participants were included in the study. 112 (32.3%) participants had EF≥65%, and there were no differences in demographics across EF subgroups. Patients with EF≥65% had a higher burden of hypertension (94.6% vs. 86.8%, p = 0.04) and had higher E/e’ (14.0[95% CI 10.9-18.0] vs. 12.7[95% CI 9.5-16.7], p = 0.048) and PCWP with exercise (27[95% CI 20-30] vs 22[95% CI 18-28] mmHg, p=0.04) without differences in resting PCWP or PCWP/cardiac output slope at maximal exercise. After adjustment for age, sex, race, and BMI, EF≥65% was associated with higher KCCQ. However, these findings were attenuated after adjustment for comorbidities (Model 1: β 6.6, p=0.05 vs Model 2: β 6.0, p=0.08). EF≥65% was not associated with functional outcomes, peak exercise capacity, or elevated filling pressures in adjusted models. (Table)
Conclusions
There were no significant differences in quality of life, functional status, exercise capacity, and filling pressures among patients with supranormal and normal ejection fraction. These findings suggest that extra-cardiac mechanisms may be more important contributors to functional status and peak exercise capacity in patients with EF≥65%.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age-related Differences in Peak Oxygen Uptake in Patients with Multimorbidity Undergoing Cardiac Rehabilitation
Gomes Pauline, Miller Sophie, Chacin-suarez Audry, Olson Thomas
Association Between Meeting Physical Activity Time-Intensity Guidelines and Calf Muscle Oxygen Saturation in Patients with Symptomatic Peripheral Artery DiseaseGardner Andrew, Montgomery Polly, Wang Ming, Xu Xifei