Final ID: P1011
Home Blood Pressure Monitoring and Risk of Falls in Older Adults with Hypertension: the AMBROSIA-HOME Cohort Study
Abstract Body: Background: Over-intensification of antihypertensive medication may lead to hypotension and excessive blood pressure (BP) variability and thus increase the risk for falls, a major cause of injury-related hospitalization and death among older adults. Monitoring BP at home may allow for better BP management and avoidance of falls.
Objective: To evaluate the associations of home BP, white coat effect (difference between clinic and home BP), and day-to-day variability of BP with falls.
Methods: The Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Older Adults Home BP Monitoring (HBPM) (AMBROSIA-HOME) study included 541 participants from Kaiser Permanente Southern California aged ≥65 years taking antihypertensive medication. Participants were instructed in proper HBPM technique and asked to take 2 BP readings each morning and each evening for 7 days. We included 499 participants (92.2%) with ≥4 days with 2 morning and 2 evening HBPM readings. For both systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP), the white coat effect was defined as mean clinic BP minus mean BP from HBPM and the standard deviation independent of the mean (SDIM) of morning and evening BP were calculated as measures of day-to-day variability. Participants reported any fall where their body parts hit a surface, including falls that occured on stairs, monthly for 1 year using falls calendars. We used Cox proportional hazards models to estimate hazard ratios of time to first fall across quartiles of each HBPM metric, separately, adjusting for demographic characteristics and chronic conditions.
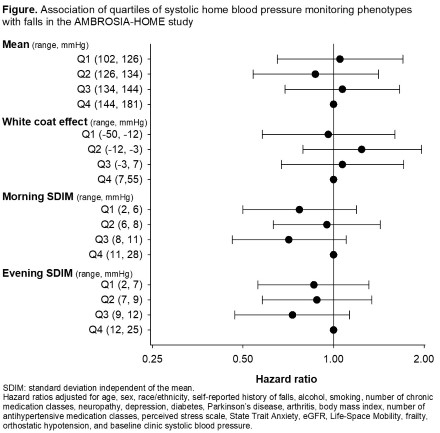
Results: The mean ± SD age of participants was 74.2±6.1 years, and 57.3% were women. The prevalence of prefrailty and frailty were 50.7% and 3.4%, respectively. Participants in the top quartile of mean SBP from HBPM were older, more frequently male, more frequently Black and Hispanic, and had higher prevalence of diabetes, arthritis, and neuropathy than those in the lowest quartile. There were 187 participants who reported falls (376 falls/1,000 person-years). We did not find evidence of associations between mean, white coat effect, or SDIM of SBP (Figure) or DBP from HBPM and falls.
Conclusion: In this population of older US adults with treated hypertension, BP measured using HBPM was not associated with falls.
Objective: To evaluate the associations of home BP, white coat effect (difference between clinic and home BP), and day-to-day variability of BP with falls.
Methods: The Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Older Adults Home BP Monitoring (HBPM) (AMBROSIA-HOME) study included 541 participants from Kaiser Permanente Southern California aged ≥65 years taking antihypertensive medication. Participants were instructed in proper HBPM technique and asked to take 2 BP readings each morning and each evening for 7 days. We included 499 participants (92.2%) with ≥4 days with 2 morning and 2 evening HBPM readings. For both systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP), the white coat effect was defined as mean clinic BP minus mean BP from HBPM and the standard deviation independent of the mean (SDIM) of morning and evening BP were calculated as measures of day-to-day variability. Participants reported any fall where their body parts hit a surface, including falls that occured on stairs, monthly for 1 year using falls calendars. We used Cox proportional hazards models to estimate hazard ratios of time to first fall across quartiles of each HBPM metric, separately, adjusting for demographic characteristics and chronic conditions.
Results: The mean ± SD age of participants was 74.2±6.1 years, and 57.3% were women. The prevalence of prefrailty and frailty were 50.7% and 3.4%, respectively. Participants in the top quartile of mean SBP from HBPM were older, more frequently male, more frequently Black and Hispanic, and had higher prevalence of diabetes, arthritis, and neuropathy than those in the lowest quartile. There were 187 participants who reported falls (376 falls/1,000 person-years). We did not find evidence of associations between mean, white coat effect, or SDIM of SBP (Figure) or DBP from HBPM and falls.
Conclusion: In this population of older US adults with treated hypertension, BP measured using HBPM was not associated with falls.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age and Sex Multiplicatively Moderate the Association of Daily Sedentary Time with Depressive Symptoms in Rural Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases
Kang Junghee, Moser Debra, Cha Geunyeong, Lin Chin-yen, Wu Jia-rong, Okoli Chizimuzo, Latimer Abigail, Lennie Terry, Biddle Martha, Chung Misook
A durable reduction in blood pressure by ultrasound renal denervation: A real-world, single center experienceKing Jordan, Gharib Wissam