Final ID: Su506
A Comparison of Synchronized Versus Unsynchronized Mechanical Chest Compressions in a Swine Model
Abstract Body: Background: The proportion of cardiac arrest presenting with pulseless electrical activity (PEA), which includes pseudo-PEA, is increasing and survival remains dismal. We hypothesized that mechanical chest compressions synchronized to native cardiac contractions improve coronary perfusion pressure (CPP) during resuscitation of pseudo-PEA.
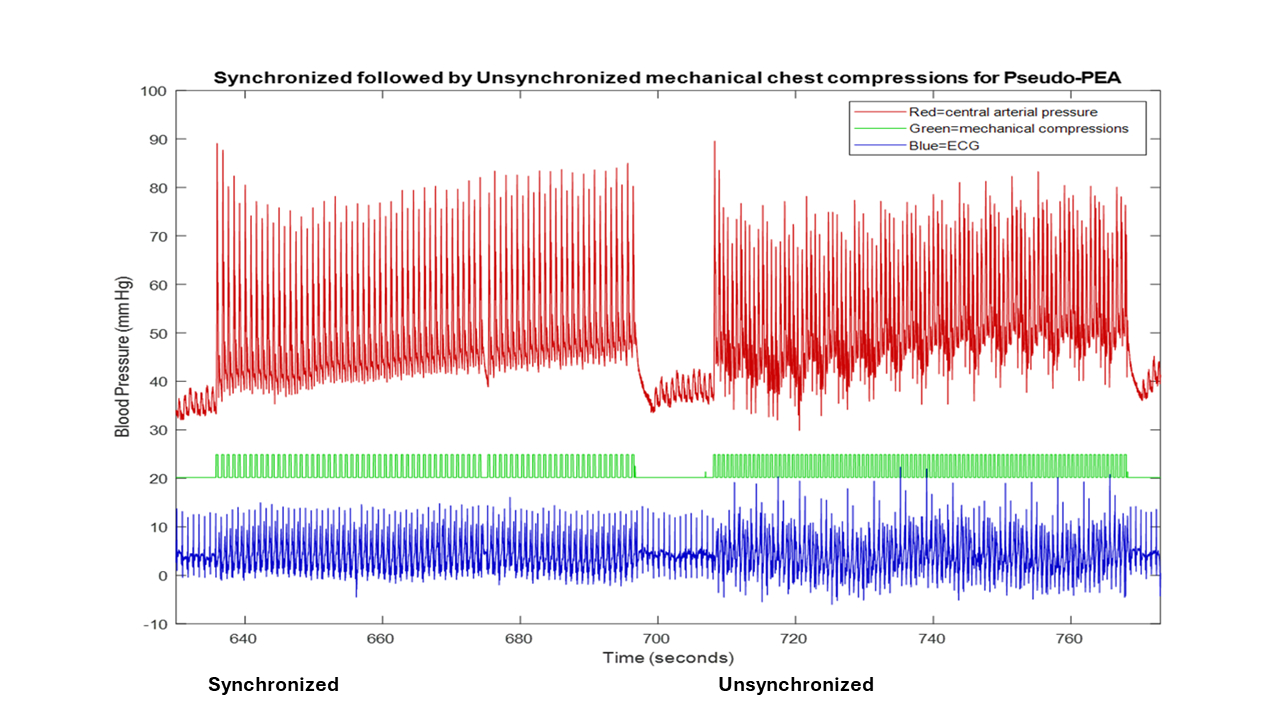
Methods: We developed a model of pseudo-PEA by infusing high dose esmolol intravenously into anaesthetized, intubated, and central arterial and venous catheterized swine to a goal of 45 mm Hg mean arterial blood pressure (MAP). We then provided alternating synchronized and unsynchronized chest compressions for 52 seconds preceded by 8 second breaks consecutively four times. We repeated the protocol two to three times with one minute breaks after each four minute block. Synchronized compressions were provided 1:1 with native contractions during systole and unsynchronized compressions were provided at 100 beats per minute (BPM). We measured average CPP, MAP, and heartrate (HR) for 5 beats immediately preceding the onset of chest compressions and for 30 seconds 10 seconds after the onset of compressions. We computed the difference in continuous CPP during compressions compared to the immediately preceding baseline for each interval. We developed a mixed linear model with outcome variable average CPP during compressions minus baseline, fixed variable compression type, and random variable animal.
Results: We included four animals. Mean baseline HR was 78.9 BPM, MAP 55.2, and CPP 44.0. Chest compressions increased CPP from baseline an average 4.0 mm Hg when unsynchronized and 6.4 mm Hg synchronized. The adjusted difference was 2.5 mm Hg (95% CI 0.3 – 4.6).
Conclusions: Synchronized chest compressions significantly increased CPP 2.5 mm Hg (62%) more than unsynchronized chest compressions despite a lower compression rate in a medication-induced swine model of pseudo-PEA. Further refinement and application to patients suffering pseudo-PEA cardiac arrest appear warranted.
Methods: We developed a model of pseudo-PEA by infusing high dose esmolol intravenously into anaesthetized, intubated, and central arterial and venous catheterized swine to a goal of 45 mm Hg mean arterial blood pressure (MAP). We then provided alternating synchronized and unsynchronized chest compressions for 52 seconds preceded by 8 second breaks consecutively four times. We repeated the protocol two to three times with one minute breaks after each four minute block. Synchronized compressions were provided 1:1 with native contractions during systole and unsynchronized compressions were provided at 100 beats per minute (BPM). We measured average CPP, MAP, and heartrate (HR) for 5 beats immediately preceding the onset of chest compressions and for 30 seconds 10 seconds after the onset of compressions. We computed the difference in continuous CPP during compressions compared to the immediately preceding baseline for each interval. We developed a mixed linear model with outcome variable average CPP during compressions minus baseline, fixed variable compression type, and random variable animal.
Results: We included four animals. Mean baseline HR was 78.9 BPM, MAP 55.2, and CPP 44.0. Chest compressions increased CPP from baseline an average 4.0 mm Hg when unsynchronized and 6.4 mm Hg synchronized. The adjusted difference was 2.5 mm Hg (95% CI 0.3 – 4.6).
Conclusions: Synchronized chest compressions significantly increased CPP 2.5 mm Hg (62%) more than unsynchronized chest compressions despite a lower compression rate in a medication-induced swine model of pseudo-PEA. Further refinement and application to patients suffering pseudo-PEA cardiac arrest appear warranted.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association Between Area of Maximal Compression During CPR Determined by Transesophageal Echocardiography, ETCO2, and Return of Spontaneous Circulation: An International Multicenter Study
Teran Felipe, Doynow Daniel, De Villa Eleonora, Woo Michael, Thavanathan Rajiv, Burns Katharine, Prager Ross, Arntfield Robert, Myslik Frank, Robinson Evan, Haines Lawrence, Owyang Clark, Buchanan Brian, Jafry Zan, Sands Nathaniel, Kaviyarasu Aarthi, Abella Benjamin, Wray Trenton, Lessard Justine, Bedard Michel William, Hipskind John, Salinas Pedro, Dieiev Vladyslav, Nogueira Jonathan
A First-In-Human Phase 1 Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacodynamics of REGN7544, a Novel Natriuretic Peptide Receptor 1–Blocking Monoclonal AntibodyAhmed Mohsin, Morton Lori, Olenchock Benjamin, Herman Gary, Wynne Chris, Marin Ethan, Tuckwell Katie, Xu Meng, Cheng Xiping, Redington Emily, Koyani Bharatkumar, Mateo Katrina, Thakur Mazhar, Devalaraja-narashimha Kishor