Final ID: P1036
ABO Blood Type, Plasma Proteomic Profile, and Risk of Chronic Disease
Abstract Body: Background: ABO blood type has been related to cardiometabolic diseases, but the underlying mechanism is not well-understood.
Hypothesis: O blood group has lower risks of cardiometabolic diseases, and a cardiometabolic favorable plasma proteomic profile compared to non-O blood group.
Methods: In ~500,000 participants from the UK Biobank, we examined associations of ABO blood type (O [43%] vs. non-O blood group) with 37 non-cancer diseases both cross-sectionally and prospectively. In a subsample with plasma proteomics data (n = 44,562), we examined whether O-type-related proteins mediate the associations between O blood type and diseases.
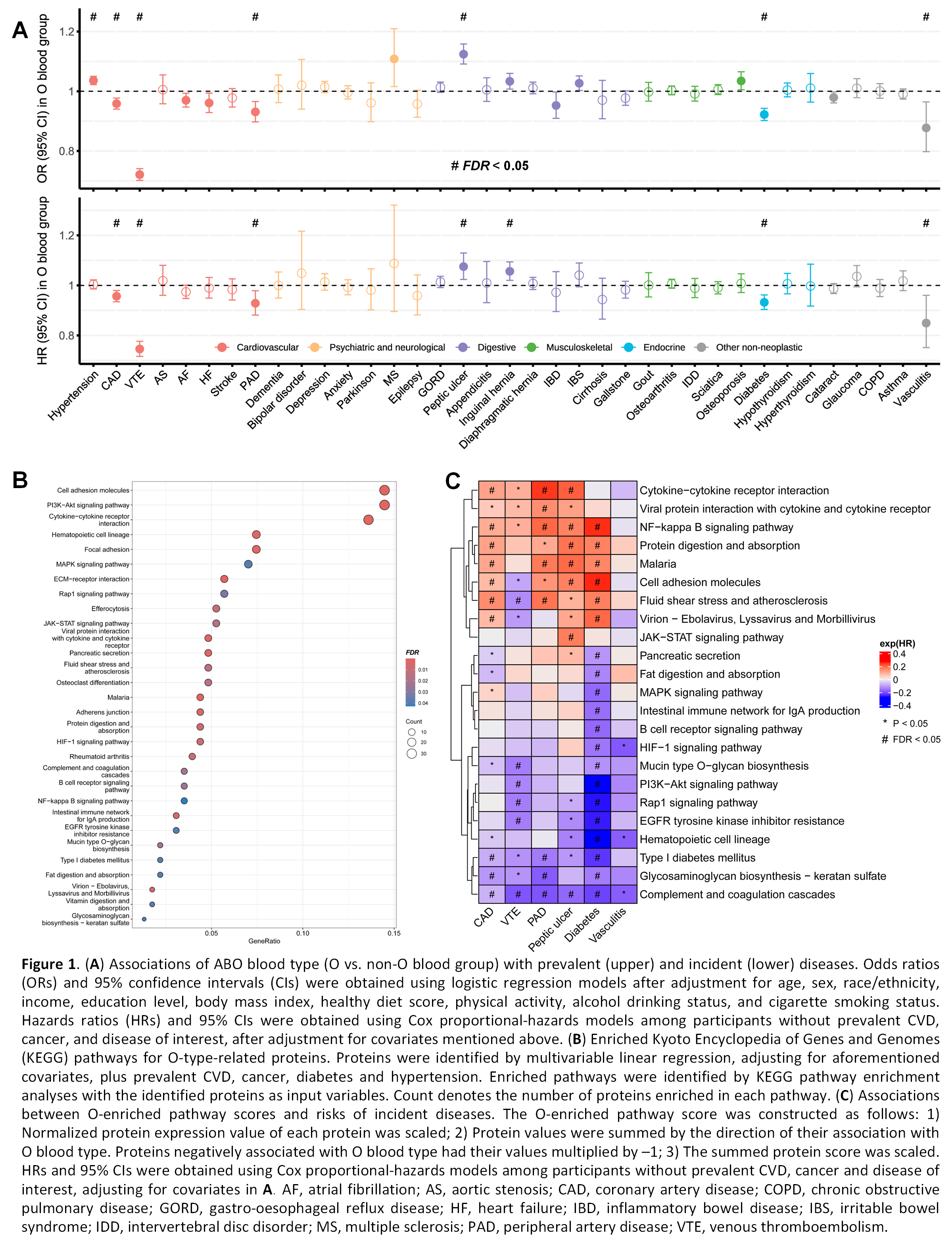
Results: O blood type was associated with six diseases in both cross-sectional and prospective analyses (FDR < 0.05). Compared to non-O blood group, O blood group had lower risks of venous thromboembolism (VTE; HR = 0.75 [95% CI: 0.72–0.78]), peripheral artery disease (0.93 [0.88–0.98]), coronary artery disease (CAD; 0.96 [0.93–0.98]), diabetes (0.93 [0.90–0.96]) and vasculitis (0.85 [0.75–0.96]), and a higher risk of peptic ulcer (1.08 [1.02–1.13]; Figure 1A). Out of 2911 proteins, 198 and 184 proteins were positively and negatively associated with O blood type, respectively; and these proteins were enriched in 30 KEGG pathways (Figure 1B). By constructing O-enriched protein pathway scores, we found that 13 and 6 scores were negatively associated with risks of diabetes and VTE, respectively, and seven scores were positively associated with risk of peptic ulcer (Figure 1C; FDR < 0.05). Further mediation analyses revealed that certain protein pathways such as mucin O-glycan or glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis potentially mediated the negative associations of O blood type with VTE, diabetes, and CAD, while infection-related pathways potentially mediated the positive association between O blood type and peptic ulcer.
Conclusions: O blood type is associated with lower risks of multiple cardiometabolic diseases. Circulating proteins may potentially link O blood type and these diseases.
Hypothesis: O blood group has lower risks of cardiometabolic diseases, and a cardiometabolic favorable plasma proteomic profile compared to non-O blood group.
Methods: In ~500,000 participants from the UK Biobank, we examined associations of ABO blood type (O [43%] vs. non-O blood group) with 37 non-cancer diseases both cross-sectionally and prospectively. In a subsample with plasma proteomics data (n = 44,562), we examined whether O-type-related proteins mediate the associations between O blood type and diseases.
Results: O blood type was associated with six diseases in both cross-sectional and prospective analyses (FDR < 0.05). Compared to non-O blood group, O blood group had lower risks of venous thromboembolism (VTE; HR = 0.75 [95% CI: 0.72–0.78]), peripheral artery disease (0.93 [0.88–0.98]), coronary artery disease (CAD; 0.96 [0.93–0.98]), diabetes (0.93 [0.90–0.96]) and vasculitis (0.85 [0.75–0.96]), and a higher risk of peptic ulcer (1.08 [1.02–1.13]; Figure 1A). Out of 2911 proteins, 198 and 184 proteins were positively and negatively associated with O blood type, respectively; and these proteins were enriched in 30 KEGG pathways (Figure 1B). By constructing O-enriched protein pathway scores, we found that 13 and 6 scores were negatively associated with risks of diabetes and VTE, respectively, and seven scores were positively associated with risk of peptic ulcer (Figure 1C; FDR < 0.05). Further mediation analyses revealed that certain protein pathways such as mucin O-glycan or glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis potentially mediated the negative associations of O blood type with VTE, diabetes, and CAD, while infection-related pathways potentially mediated the positive association between O blood type and peptic ulcer.
Conclusions: O blood type is associated with lower risks of multiple cardiometabolic diseases. Circulating proteins may potentially link O blood type and these diseases.
More abstracts on this topic:
A community-engaged approach to culturally tailoring a dietary intervention to improve cardiometabolic health among Black adults with obesity in Los Angeles County
Adeyemo Mopelola, Thorpe Roland
A phenomapping-informed machine learning tool estimates individualized cardiometabolic effects from Tirzepatide and generalizes to a new population.Thangaraj Phyllis, Oikonomou Evangelos, Khera Rohan