Final ID: Su4082
Association of Plasma Cystatin-C with Cancer Risk in Individuals with and without Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Disease: An Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: While previous studies suggested a relationship between circulating Cystatin-C (Cys-C), a cysteine protease inhibitor involved in regulating tissue inflammation and a renal filtration marker, and both cancer and CVD, they often lacked long-term follow-up or did not account for the impact of CVD on the relationship between Cys-C and cancer.
Methods: We included participants from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study followed from visit 2 (1990-1992) through 2015. Plasma Cys-C level was measured by SomaScan. Other renal filtration markers beta-2 microglobulin (B2M) and beta-trace protein (BTP) were used to compare their cancer association with Cys-C. Incident cancer was ascertained by state cancer registry linkage supplemented with medical records. After adjusting for age, sex, race, and study center, adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) of total and site-specific cancers were estimated using Cox proportional hazards regression stratified by baseline chronic kidney disease (CKD) and CVD status.
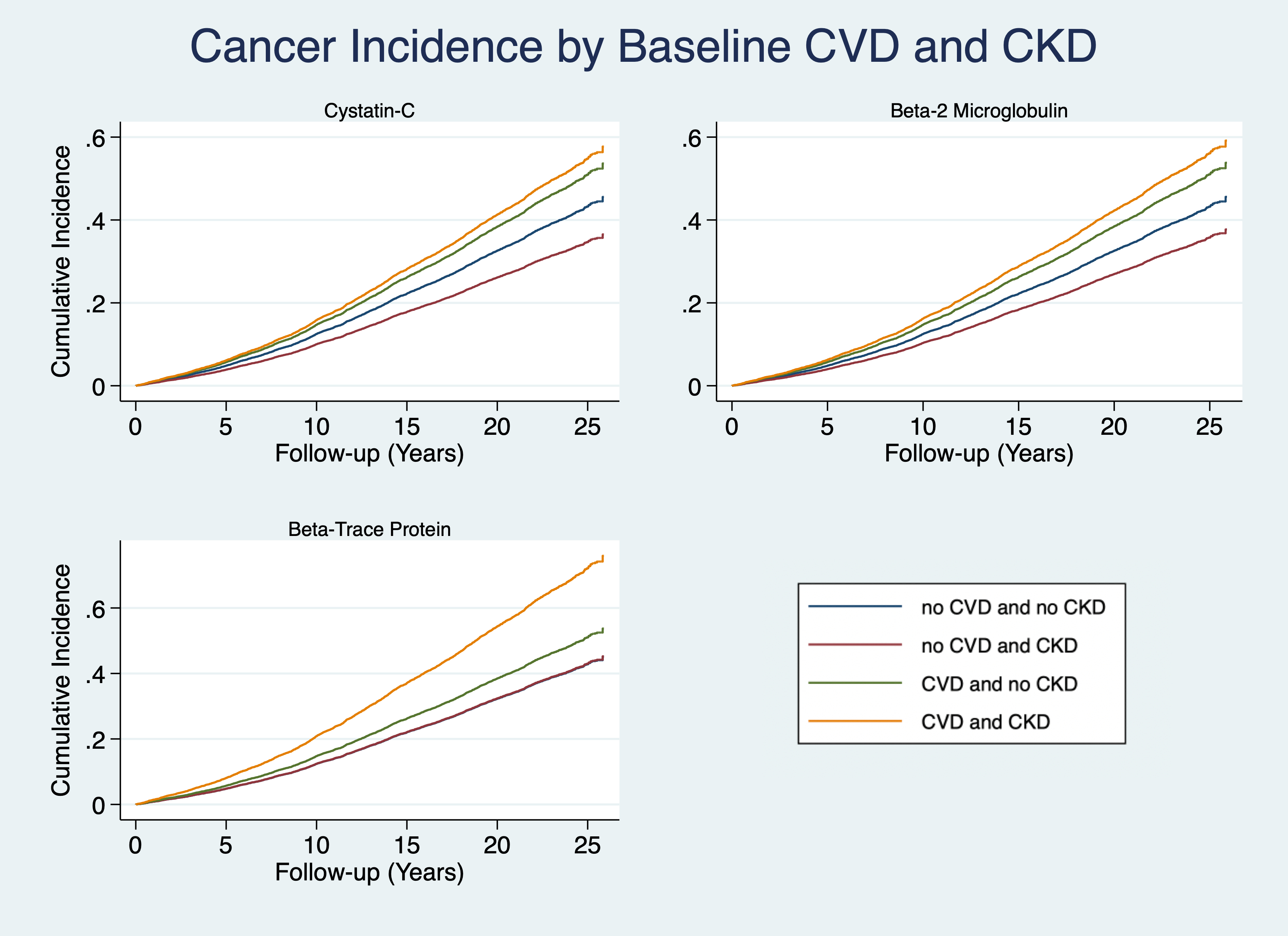
Results: Among 10,869 individuals (median age of 56.9 years, 55% female, 25% Black, 74% White), 3352 incident cancers were ascertained over a median follow-up of 22.9 years. Among 9585 individuals with no history of CKD or CVD, higher Cys-C was significantly associated with a higher risk of total (aHR 1.22, 95%CI 1.02-1.46), bladder, lung, colorectal, and hematologic malignancies. Among 1,050 individuals with CVD, but not CKD, Cys-C level was not associated with total cancer (aHR 1.22, 95%CI 0.74-2.01), but was significantly inversely associated with colorectal (aHR 0.19, 95%CI 0.05-0.76) and positively associated with post-menopausal breast (aHR 4.52, 95%CI 1.05-19.40) cancer risk. In individuals with CKD but not CVD, Cys-C was negatively associated with bladder (HR 0.08, 95%CI 0.0-0.77) and lung (0.23, 95%CI 0.06-0.82) cancers. Lastly, those with both CKD and CVD showed higher hematopoietic and lymphatic cancer with higher Cys-C (HR 4.68, 95%CI 1.32-16.60). Similar patterns were observed for B2M and BTP proteins.
Conclusions: Our study highlights the intricate relationship between various renal filtration markers and cancer risk. It suggests that they may play a significant role in cancer development among the general population and CVD patients but not CKD patients. Further research should explore the biological mechanism underlying these associations with even more CKD cases to refine risk estimates.
Funding: NHLBI, NCI, NPCR
Methods: We included participants from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study followed from visit 2 (1990-1992) through 2015. Plasma Cys-C level was measured by SomaScan. Other renal filtration markers beta-2 microglobulin (B2M) and beta-trace protein (BTP) were used to compare their cancer association with Cys-C. Incident cancer was ascertained by state cancer registry linkage supplemented with medical records. After adjusting for age, sex, race, and study center, adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) of total and site-specific cancers were estimated using Cox proportional hazards regression stratified by baseline chronic kidney disease (CKD) and CVD status.
Results: Among 10,869 individuals (median age of 56.9 years, 55% female, 25% Black, 74% White), 3352 incident cancers were ascertained over a median follow-up of 22.9 years. Among 9585 individuals with no history of CKD or CVD, higher Cys-C was significantly associated with a higher risk of total (aHR 1.22, 95%CI 1.02-1.46), bladder, lung, colorectal, and hematologic malignancies. Among 1,050 individuals with CVD, but not CKD, Cys-C level was not associated with total cancer (aHR 1.22, 95%CI 0.74-2.01), but was significantly inversely associated with colorectal (aHR 0.19, 95%CI 0.05-0.76) and positively associated with post-menopausal breast (aHR 4.52, 95%CI 1.05-19.40) cancer risk. In individuals with CKD but not CVD, Cys-C was negatively associated with bladder (HR 0.08, 95%CI 0.0-0.77) and lung (0.23, 95%CI 0.06-0.82) cancers. Lastly, those with both CKD and CVD showed higher hematopoietic and lymphatic cancer with higher Cys-C (HR 4.68, 95%CI 1.32-16.60). Similar patterns were observed for B2M and BTP proteins.
Conclusions: Our study highlights the intricate relationship between various renal filtration markers and cancer risk. It suggests that they may play a significant role in cancer development among the general population and CVD patients but not CKD patients. Further research should explore the biological mechanism underlying these associations with even more CKD cases to refine risk estimates.
Funding: NHLBI, NCI, NPCR
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute Effects of Isometric Handgrip Exercise on Cardiac Baroreflex Sensitivity in Chronic Kidney Disease
Sabino-carvalho Jeann, Park Jeanie
A Case of Concomitant Wild-Type Transthyretin and Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis Involving Separate OrgansChiu Leonard, Afrough Aimaz, Nadeem Urooba, Jebakumar Deborah, Grodin Justin