Final ID: P1023
Temporal Changes in High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation in African Americans: The Jackson Heart Study
Abstract Body: Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Inflammation plays an important role in AF pathogenesis. The relationship between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), a key biomarker of chronic inflammation, and incident AF in African Americans (AAs), remains unclear. This study aimed to examine the association between baseline and serial hs-CRP levels and incident AF in AAs in the Jackson Heart Study (JHS).
Methods: Participants of the JHS with hs-CRP assessment and without previous AF at baseline were included in the study. hs-CRP measurement at Visit 1 (baseline) and Visit 2 were used. Elevated hs-CRP was defined as 3 mg/L per guidelines. Incident AF was defined as having 12 lead electrocardiogram evidence at a subsequent follow up, or a documented diagnosis code at the time of hospital discharge from 2000 to 2016. Cox proportional hazards models were used to evaluate the association between baseline hs-CRP as a continuous variable and AF risk (t0=Visit 1), and the risk of AF in those with elevated hs-CRP at Visit 1 or 2, compared to those who had never had elevated hs-CRP (t0=Visit 2).
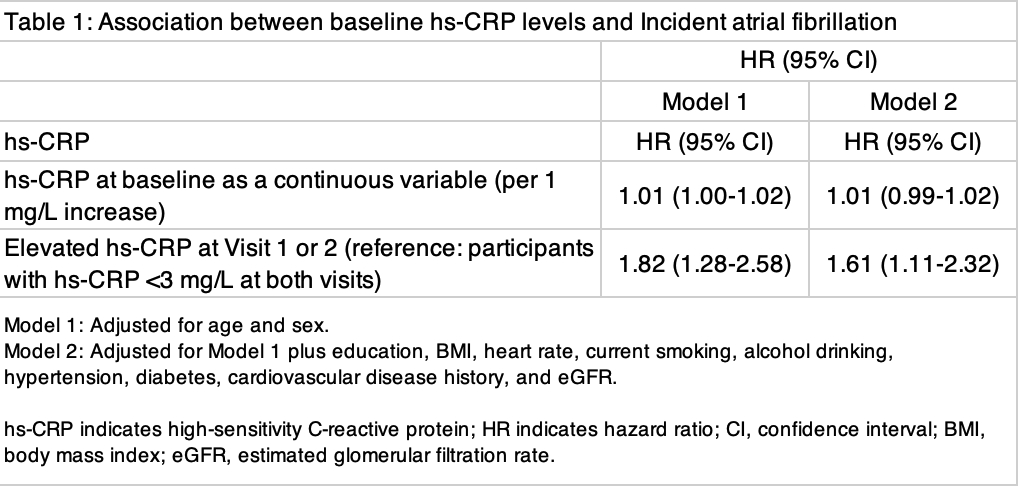
Results: Of the 4,169 participants followed for a median of 13.7 years, 351 participants developed AF (6.7 cases per 1,000 person-years). 1,089 participants (44.1%) never had elevated hs-CRP, while 1,379 (55.9%) had elevated hs-CRP at Visit 1 or 2. hs-CRP at baseline was significantly associated with incident AF in Model 1 (age and sex-adjusted), but not in Model 2 (further adjusted) (Table). Elevated hs-CRP at Visit 1or 2 was associated with higher risk of AF incidence in both Model 1 (HR 1.81, 95% CI 1.28-2.58, P < 0.005) and Model 2 (HR 1.61, 95% CI 1.11-2.32, p<0.05).
Conclusion: In a community AA cohort, baseline hs-CRP was not associated with incident AF. On the other hand, individuals with elevated hs-CRP at Visit 1 or 2 had a higher risk of AF incidence. This might suggest usefulness of serial hs-CRP measurements to identify those with lower AF risk.
Methods: Participants of the JHS with hs-CRP assessment and without previous AF at baseline were included in the study. hs-CRP measurement at Visit 1 (baseline) and Visit 2 were used. Elevated hs-CRP was defined as 3 mg/L per guidelines. Incident AF was defined as having 12 lead electrocardiogram evidence at a subsequent follow up, or a documented diagnosis code at the time of hospital discharge from 2000 to 2016. Cox proportional hazards models were used to evaluate the association between baseline hs-CRP as a continuous variable and AF risk (t0=Visit 1), and the risk of AF in those with elevated hs-CRP at Visit 1 or 2, compared to those who had never had elevated hs-CRP (t0=Visit 2).
Results: Of the 4,169 participants followed for a median of 13.7 years, 351 participants developed AF (6.7 cases per 1,000 person-years). 1,089 participants (44.1%) never had elevated hs-CRP, while 1,379 (55.9%) had elevated hs-CRP at Visit 1 or 2. hs-CRP at baseline was significantly associated with incident AF in Model 1 (age and sex-adjusted), but not in Model 2 (further adjusted) (Table). Elevated hs-CRP at Visit 1or 2 was associated with higher risk of AF incidence in both Model 1 (HR 1.81, 95% CI 1.28-2.58, P < 0.005) and Model 2 (HR 1.61, 95% CI 1.11-2.32, p<0.05).
Conclusion: In a community AA cohort, baseline hs-CRP was not associated with incident AF. On the other hand, individuals with elevated hs-CRP at Visit 1 or 2 had a higher risk of AF incidence. This might suggest usefulness of serial hs-CRP measurements to identify those with lower AF risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel method for measuring HDL-bound unconjugated bilirubin using an eel fluorescent protein reveals its association with reduced coronary artery disease
Fujioka Tomoo, Iino Takuya, Toh Ryuji, Harada Amane, Nagao Manabu, Shinohara Masakazu, Ishida Tatsuro, Otake Hiromasa
1-Year Outcomes After Cardioversion With and Without Anticoagulation in Patients With Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion: A Propensity-Matched AnalysisThangjui Sittinun, Trongtorsak Angkawipa, Kewcharoen Jakrin, Thyagaturu Harshith, Watson Hangyu, Mensah Samuel, Balla Sudarshan, Navaravong Leenhapong