Final ID: Mo2063
Temporal Changes in High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in African Americans: The Jackson Heart Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: African Americans (AAs) face higher mortality from atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) than Whites. Inflammation plays a central role in atherosclerosis, yet the association between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and ASCVD in AAs remains unclear. This study examined serial hs-CRP measurements and incident ASCVD in the Jackson Heart Study (JHS), a community-based AA cohort.
Methods: JHS Participants without prior ASCVD were analyzed using hs-CRP measurements at Visit 1 (baseline; 2000–2004, "single-visit cohort"), Visits 1 and 2 (2005–2008, "two-visit cohort"), and Visit 1–3 (2009–2013) for joint modeling. hs-CRP was evaluated as both continuous and categorized (≥3 mg/L defined as elevated) variables. In the two-visit cohort, participants were divided by hs-CRP status as: normal at both visits, elevated at Visit 1 or 2 or both. ASCVD was defined as coronary heart disease (CHD; myocardial infarction and fatal CHD) and stroke. Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess the association between hs-CRP and incident ASCVD, adjusted for cardiovascular risk factors. Joint modeling was utilized to examine the time-dependent relationship of hs-CRP with incident ASCVD.
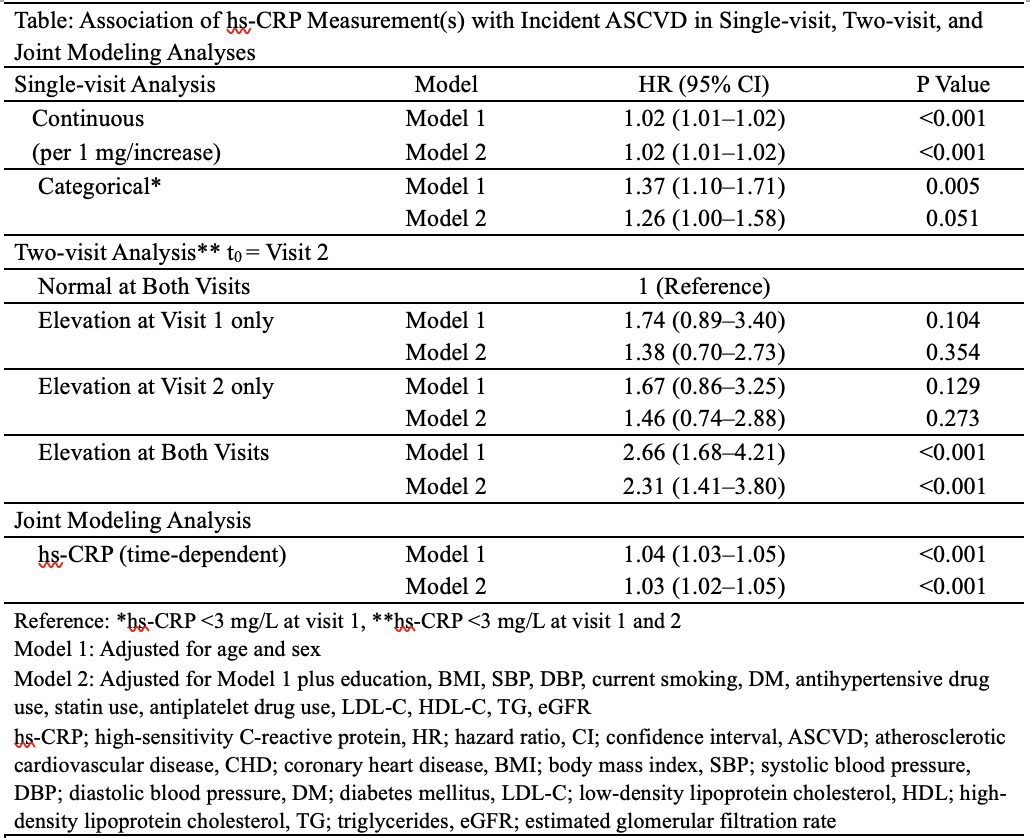
Results: In the single-visit cohort (n = 3,948, mean age (standard deviation) 53.6 (12.8), female 64.3%), 340 participants developed ASCVD (6.9 cases per 1,000 person-years) during median 13.7 years follow-up. Each unit increase in hs-CRP was associated with greater ASCVD risk (adjusted hazard ratio (HR) 1.02, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.01–1.02, P < 0.001). Elevated hs-CRP showed a trend toward increased risk. In the two-visit cohort (n = 2,324), 110 participants developed ASCVD (5.3 cases per 1,000 person-years) during median 8.9 years follow-up. Those with elevated hs-CRP were found to have a higher risk of ASCVD, with those with elevated hs-CRP at both visits the highest risk (HR 2.31, 95% CI 1.41–3.80, P < 0.001, Table). Joint modeling revealed a significant time-dependent association of hs-CRP trajectory with incident ASCVD (HR 1.03 per 1.0 mg/L increase, 95% CI 1.02–1.05, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: In the AA general cohort, temporal hs-CRP changes were associated with the risk of ASCVD.
Methods: JHS Participants without prior ASCVD were analyzed using hs-CRP measurements at Visit 1 (baseline; 2000–2004, "single-visit cohort"), Visits 1 and 2 (2005–2008, "two-visit cohort"), and Visit 1–3 (2009–2013) for joint modeling. hs-CRP was evaluated as both continuous and categorized (≥3 mg/L defined as elevated) variables. In the two-visit cohort, participants were divided by hs-CRP status as: normal at both visits, elevated at Visit 1 or 2 or both. ASCVD was defined as coronary heart disease (CHD; myocardial infarction and fatal CHD) and stroke. Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess the association between hs-CRP and incident ASCVD, adjusted for cardiovascular risk factors. Joint modeling was utilized to examine the time-dependent relationship of hs-CRP with incident ASCVD.
Results: In the single-visit cohort (n = 3,948, mean age (standard deviation) 53.6 (12.8), female 64.3%), 340 participants developed ASCVD (6.9 cases per 1,000 person-years) during median 13.7 years follow-up. Each unit increase in hs-CRP was associated with greater ASCVD risk (adjusted hazard ratio (HR) 1.02, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.01–1.02, P < 0.001). Elevated hs-CRP showed a trend toward increased risk. In the two-visit cohort (n = 2,324), 110 participants developed ASCVD (5.3 cases per 1,000 person-years) during median 8.9 years follow-up. Those with elevated hs-CRP were found to have a higher risk of ASCVD, with those with elevated hs-CRP at both visits the highest risk (HR 2.31, 95% CI 1.41–3.80, P < 0.001, Table). Joint modeling revealed a significant time-dependent association of hs-CRP trajectory with incident ASCVD (HR 1.03 per 1.0 mg/L increase, 95% CI 1.02–1.05, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: In the AA general cohort, temporal hs-CRP changes were associated with the risk of ASCVD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessment performance of the AHA PREVENT equations in disaggregated Asian and Hispanic Subgroups
Yan Xiaowei, Bacong Adrian, Huang Qiwen, Husby Hannah, Jose Powell, Palaniappan Latha, Rodriguez Fatima
A Machine Learning Approach to Simplify Risk Stratification of Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseLi Hsin Fang, Gluckman Ty, Nute Andrew, Weerasinghe Roshanthi, Wendt Staci, Wilson Eleni, Sidelnikov Eduard, Kathe Niranjan, Swihart Charissa, Jones Laney