Final ID: LBP29
Novel Combination Therapy with Sildenafil and Rapamycin Potentiates Chemotherapeutic Efficacy of Doxorubicin in Breast Cancer while Suppressing its Cardiotoxicity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Doxorubicin (DOX) is a cornerstone of chemotherapy regimens for breast cancer, but it leads to development of drug resistance and multi-organ dysfunction including cardiotoxicity. Our previous studies revealed that Sildenafil (Sild, Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor) potentiated antitumor efficacy of DOX, while ameliorating DOX-induced cardiotoxicity and Rapamycin (Rapa, mammalian target of rapamycin, mTOR, inhibitor) also protected heart against myocardial injuries. In the present study, we examined whether a novel combination therapy with Sild and Rapa can mitigate DOX-induced cardiotoxicity, while potentiating its chemotherapeutic efficacy.
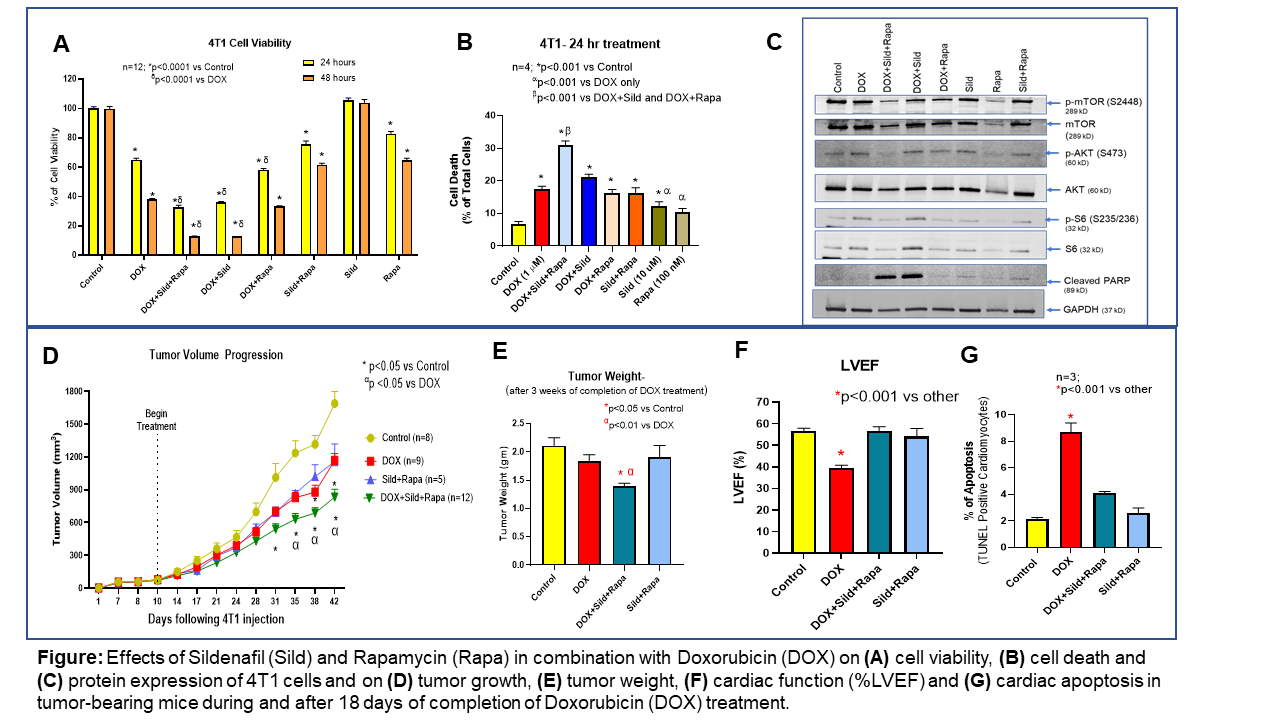
Methods & Results: Murine breast cancer cells, 4T1, were treated with DOX (1mM), and/or Sild (10mM) and Rapa (100nM) for 24-hr or 48-hr. Combination of Sild and Rapa significantly suppressed cell viability (Fig. A) with enhanced cell death (Fig. B) as compared to DOX treatment alone in 4T1 cells. Western blot analysis showed Sild+Rapa in presence of DOX suppressed phosphorylation as well as total expression of mTOR, AKT and S6, but induced cleaved-PARP level in 4T1 cells (Fig. C). Female Balb/c mice engrafted with orthotopic 4T1 tumors were treated with DOX (3mg/kg, twice/week, i.p., 5 times) and/or Sild (1.4mg/kg/daily, p.o.) and Rapa (0.25 mg/kg, twice a week, i.p.). After 18 days of completion of DOX treatment, tumor growth and weight were significantly reduced compared to control, which was further attenuated by cotreatment with Sild+Rapa (Fig. D&E). DOX treatment significantly reduced cardiac systolic function (Fig. F) in tumor bearing mice (left ventricular ejection fraction, LVEF:39±1.2%) compared to control (LVEF:57±1.4%) with higher cardiac apoptosis (Fig. G). Importantly, cotreatment of Sild+Rapa with DOX effectively restored the cardiac function in the tumor-bearing mice (LVEF of 57±2.1%) with reduction of apoptosis.
Conclusion: Cotreatment with Sild and Rapa may represent a novel strategy to reduce cardiotoxicity associated with DOX, while simultaneously enhancing its chemosensitivity, which would have a significant impact on breast cancer patients subjected to chemotherapy.
Methods & Results: Murine breast cancer cells, 4T1, were treated with DOX (1mM), and/or Sild (10mM) and Rapa (100nM) for 24-hr or 48-hr. Combination of Sild and Rapa significantly suppressed cell viability (Fig. A) with enhanced cell death (Fig. B) as compared to DOX treatment alone in 4T1 cells. Western blot analysis showed Sild+Rapa in presence of DOX suppressed phosphorylation as well as total expression of mTOR, AKT and S6, but induced cleaved-PARP level in 4T1 cells (Fig. C). Female Balb/c mice engrafted with orthotopic 4T1 tumors were treated with DOX (3mg/kg, twice/week, i.p., 5 times) and/or Sild (1.4mg/kg/daily, p.o.) and Rapa (0.25 mg/kg, twice a week, i.p.). After 18 days of completion of DOX treatment, tumor growth and weight were significantly reduced compared to control, which was further attenuated by cotreatment with Sild+Rapa (Fig. D&E). DOX treatment significantly reduced cardiac systolic function (Fig. F) in tumor bearing mice (left ventricular ejection fraction, LVEF:39±1.2%) compared to control (LVEF:57±1.4%) with higher cardiac apoptosis (Fig. G). Importantly, cotreatment of Sild+Rapa with DOX effectively restored the cardiac function in the tumor-bearing mice (LVEF of 57±2.1%) with reduction of apoptosis.
Conclusion: Cotreatment with Sild and Rapa may represent a novel strategy to reduce cardiotoxicity associated with DOX, while simultaneously enhancing its chemosensitivity, which would have a significant impact on breast cancer patients subjected to chemotherapy.
More abstracts on this topic:
A RETRO-ENANTIOMER OF ANGIOTENSIN-(1-9) PREVENTS THE DEVELOPMENT OF HEART FAILURE WITH PRESERVED EJECTION FRACTION.
Ocaranza Maria Paz, Jimenez Veronica, Yanez Osvaldo, Jalil Jorge, Venegas Camilo, Candia Camila, Hermoso Marcela, Gabrielli Luigi, Morales Javier, Oyarzun Felipe, Torres Cristian, Lillo Pablo
Lactate Levels as a Prognostic Marker in Postpartum Hemorrhage: A Comparison with Shock Index, MEWS, and mREMS in the Emergency DepartmentCha Young Suk, Yang Eunjin