Final ID: 4168838
Dual inhibition of PDE5-mTOR Enhances Chemoimmunotherapeutic Efficacy in Breast Cancer and Reduces Cardiotoxicity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The combination of HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, ErbB2)-targeted immunotherapy with anthracycline-based chemotherapy (such as Doxorubicin, DOX), has shown synergistic effects and improved progression free survival in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. However, the use of HER2 antibodies in conjunction with anthracycline-based regimens has been linked to a high incidence of heart failure. In this study, we investigated whether a novel therapy with combining phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitor (sildenafil, Sild) and an mTOR inhibitor (rapamycin, Rapa) could reduce the cardiotoxicity associated with DOX and HER2 inhibitor without compromising its potent antitumor efficacy.
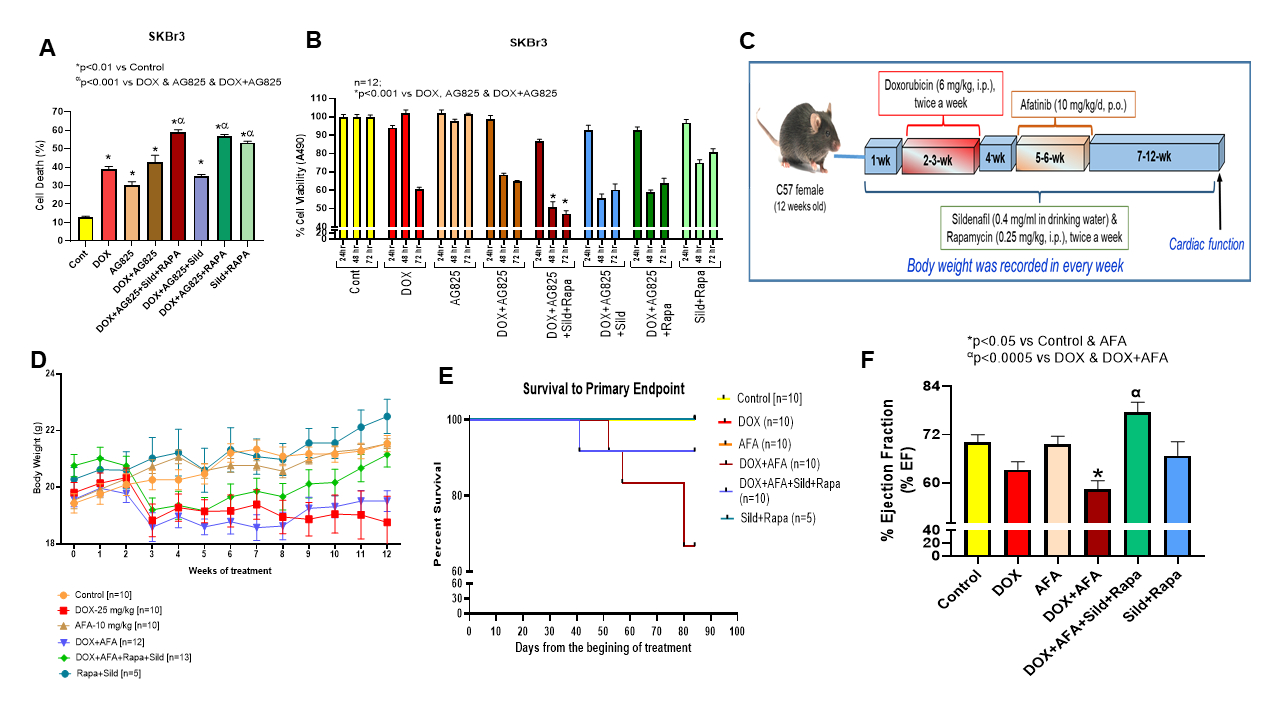
Methods & Results: ErbB2+breast cancer cells (SKBr3) were treated with DOX (1mM), AG825 (ErbB2 inhibitor, 5mM) and/or Sild (10mM) and Rapa (100 nM) for 72 hours. Cell death was elevated with DOX+AG825 treatment compared to single drug treatments, and this effect was further enhanced with the addition of Sild+Rapa treatment (Fig. 1A). Similarly, cell viability was remarkably reduced after treatment with combination of DOX+AG825 with Sild+Rapa (Fig. 1B). To evaluate therapeutic effect of Sild+Rapa against cardiotoxicity, C57BL/6J mice were treated for 2 weeks with DOX (6 mg/kg/twice/week, i.p.) (Fig. 1C). After a one-week interval, the mice were administered Afatinib (AFA, a selective ErbB inhibitor) for two weeks at a dosage of 10 mg/kg, via oral gavage. Rapa (0.25 mg/kg/twice/week, i.p.) and Sild (0.4 mg/ml in drinking water) were administered for 12 weeks. Body weight (Fig. 1D) and survival (Fig. 1E) decreased along with a reduction in cardiac function (left ventricular ejection fraction, LVEF, Fig. 1F) following sequential treatment with DOX and AFA, compared to control. However, co-treatment of Sild+Rapa significantly improved body weight and survival while restoring cardiac function in mice treated with DOX±AFA.
Conclusion: Cotreatment with Sild and Rapa may represent a novel strategy to reduce cardiotoxicity associated with chemoimmunotherapy, while simultaneously enhancing its effectiveness in breast cancer prevention.
Methods & Results: ErbB2+breast cancer cells (SKBr3) were treated with DOX (1mM), AG825 (ErbB2 inhibitor, 5mM) and/or Sild (10mM) and Rapa (100 nM) for 72 hours. Cell death was elevated with DOX+AG825 treatment compared to single drug treatments, and this effect was further enhanced with the addition of Sild+Rapa treatment (Fig. 1A). Similarly, cell viability was remarkably reduced after treatment with combination of DOX+AG825 with Sild+Rapa (Fig. 1B). To evaluate therapeutic effect of Sild+Rapa against cardiotoxicity, C57BL/6J mice were treated for 2 weeks with DOX (6 mg/kg/twice/week, i.p.) (Fig. 1C). After a one-week interval, the mice were administered Afatinib (AFA, a selective ErbB inhibitor) for two weeks at a dosage of 10 mg/kg, via oral gavage. Rapa (0.25 mg/kg/twice/week, i.p.) and Sild (0.4 mg/ml in drinking water) were administered for 12 weeks. Body weight (Fig. 1D) and survival (Fig. 1E) decreased along with a reduction in cardiac function (left ventricular ejection fraction, LVEF, Fig. 1F) following sequential treatment with DOX and AFA, compared to control. However, co-treatment of Sild+Rapa significantly improved body weight and survival while restoring cardiac function in mice treated with DOX±AFA.
Conclusion: Cotreatment with Sild and Rapa may represent a novel strategy to reduce cardiotoxicity associated with chemoimmunotherapy, while simultaneously enhancing its effectiveness in breast cancer prevention.
More abstracts on this topic:
ARA290, a small peptide non-erythropoietic Erythropoietin derivative, ameliorates heart functional deterioration in a chronic cardiac stress model
Gime Suri, Winicki Nolan, Ahmet Ismayil, Morrell Christopher, Lakatta Edward
A Rare Case of Acute Undifferentiated Leukemia Presenting as an Isolated Cardiac MassMallipeddi Tarun, Rantanen Petra, Debakey Michael, Cheng Lily, Waheed Nida