Final ID: MDP932
5-oxoproline/ OPLAH Axis Alleviates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy By Inhibiting Ferroptosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The clinical utility of doxorubicin (DOX) is constrained by its cardiotoxicity, known as DOX-induced cardiomyopathy (DIC). 5-oxoproline (5-OXO), a degradation product of glutathione, can be converted into glutathione by OPLAH (5-oxoprolinase). However, the role of 5-oxoproline/OPLAH in DIC remains largely unknown.
Methods:By analyzing murine DIC metabolomics, we identified 5-oxoproline as an important metabolite involved in DIC. To investigate the role of 5-oxoproline/OPLAH axis in DIC, we adopted 5-OXO (5μmol/L; 28 days) and used global OPLAH-knockout mice in DIC mouse models induced with DOX.
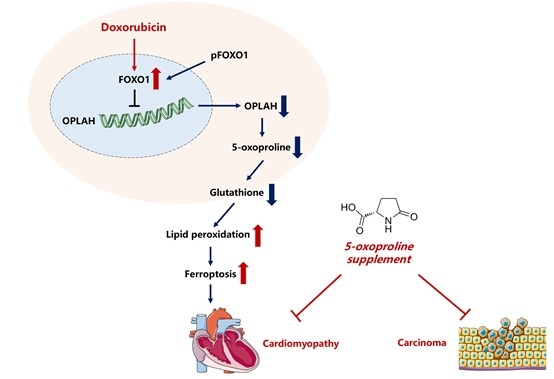
Results: 5-oxoproline exhibited the highest fold change among all metabolites in murine DIC tissues and 5-oxoproline was downregulated in both serum and myocardial tissues of DIC mice. In DIC mouse model, administration of 5-oxoproline significantly alleviated heart dysfunction, oxidative stress and ferroptosis, while OPLAH knockout exacerbated DOX-induced heart dysfunction, oxidative stress and ferroptosis in mice. Moreover, OPLAH knockout abolished the cardioprotective effect of 5-OXO in DIC model. Mechanistically, doxorubicin induced the translocation of FOXO1 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, facilitating FOXO1’s transcriptional inhibitory effect on OPLAH (5-oxoprolinase) and downregulated the expression of OPLAH. Reduced OPLAH expression in cardiomyocytes decreases the conversion of 5-oxoproline to glutathione, thus aggravated oxidative stress and ferroptosis. Interestingly, 5-OXO supplement inhibited tumor growth while protecting DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in nude mice with implanted breast cancer. Regarding clinical significance, we found that downregulated expression of 5-OXO correlated with high risk in breast cancer patients with DOX treatment.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate a previously unrecognized role of 5-oxoproline in DIC treatment and an undescribed 5-oxoproline/OPLAH axis involved in regulating therapeutic metabolism in cardiomyocytes. It is important that our findings suggest 5-oxoproline can be used as a potential therapeutic agent for DIC and simultaneously antagonizing cancer growth.
Methods:By analyzing murine DIC metabolomics, we identified 5-oxoproline as an important metabolite involved in DIC. To investigate the role of 5-oxoproline/OPLAH axis in DIC, we adopted 5-OXO (5μmol/L; 28 days) and used global OPLAH-knockout mice in DIC mouse models induced with DOX.
Results: 5-oxoproline exhibited the highest fold change among all metabolites in murine DIC tissues and 5-oxoproline was downregulated in both serum and myocardial tissues of DIC mice. In DIC mouse model, administration of 5-oxoproline significantly alleviated heart dysfunction, oxidative stress and ferroptosis, while OPLAH knockout exacerbated DOX-induced heart dysfunction, oxidative stress and ferroptosis in mice. Moreover, OPLAH knockout abolished the cardioprotective effect of 5-OXO in DIC model. Mechanistically, doxorubicin induced the translocation of FOXO1 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, facilitating FOXO1’s transcriptional inhibitory effect on OPLAH (5-oxoprolinase) and downregulated the expression of OPLAH. Reduced OPLAH expression in cardiomyocytes decreases the conversion of 5-oxoproline to glutathione, thus aggravated oxidative stress and ferroptosis. Interestingly, 5-OXO supplement inhibited tumor growth while protecting DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in nude mice with implanted breast cancer. Regarding clinical significance, we found that downregulated expression of 5-OXO correlated with high risk in breast cancer patients with DOX treatment.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate a previously unrecognized role of 5-oxoproline in DIC treatment and an undescribed 5-oxoproline/OPLAH axis involved in regulating therapeutic metabolism in cardiomyocytes. It is important that our findings suggest 5-oxoproline can be used as a potential therapeutic agent for DIC and simultaneously antagonizing cancer growth.
More abstracts on this topic:
90 days readmission rates, predictors, and causes of readmission in heart failure patients with history of irradiation: nationwide retrospective analysis
Teaima Taha, Quevedo Ramirez Andres, Jha Vivek, Ibarra Joshua, Soon-shiong Raquel, Gomez Valencia Javier
β1-adrenergic autoantibodies (β1-AA) augment macropinocytosis in CD4+ T cells, leading to the expansion of CD4+CD28− T cell subsets in heart failure.Sun Fei, Yao Junyan, Li Bingjie, Zhang Suli, Liu Huirong