Final ID: MP986
Analysing the Capabilities of Recent Artificial Intelligence Models in Detecting Atrial Fibrillation Using Patient Electrocardiograms
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background:
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia and it imparts significant morbidity and mortality. A substantial proportion of AF remains undiagnosed. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative tool to enhance early AF detection. This systematic review and meta-analysis critically evaluates the diagnostic performance of AI models for AF by using patient electrocardiograms (ECGs).
Objectives:
To systematically appraise and quantitatively synthesize the diagnostic accuracy of AI algorithms for AF detection, using databases of patient ECGs previously validated by cardiologists.
Methods:
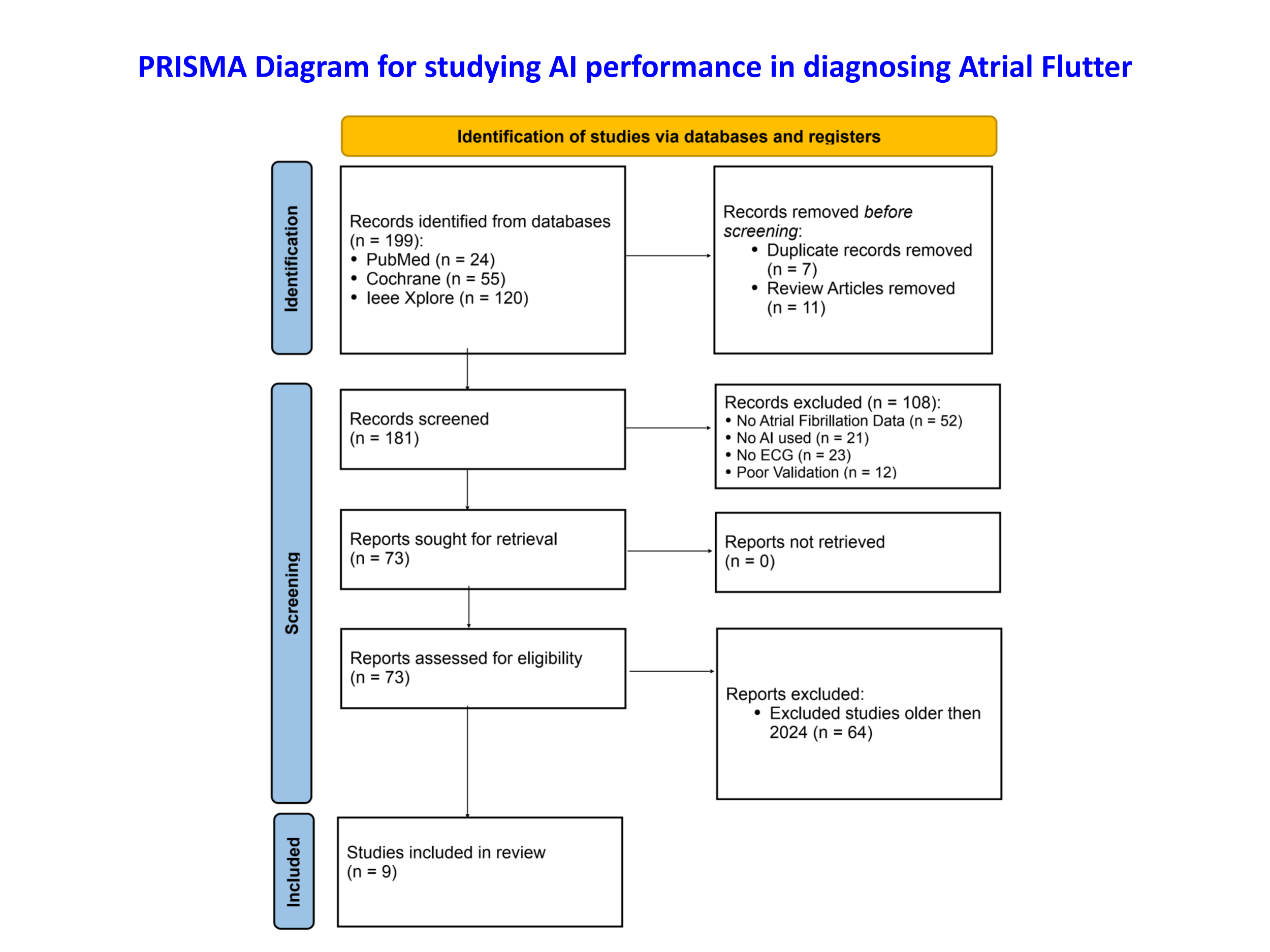
Comprehensive searches were performed in PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, and IEEE Xplore from January 2016 - June 2025 to identify studies evaluating the diagnostic performance of AI algorithms for AF detection, only using databases consisting of patient ECGs with prior cardiologist validation, irrespective of comparator. 73 quality studies were included for the study. Only the 9 most recent publications (January 2024–June 2025) were included in this analysis Two independent reviewers screened titles, abstracts, and full texts, extracted data, and assessed risk of bias using the QUADAS-2 tool; discrepancies were resolved by consensus. Pooled accuracy estimates were synthesized using random-effects meta-analysis in R, adhering to PRISMA-DTA guidelines.
Results:
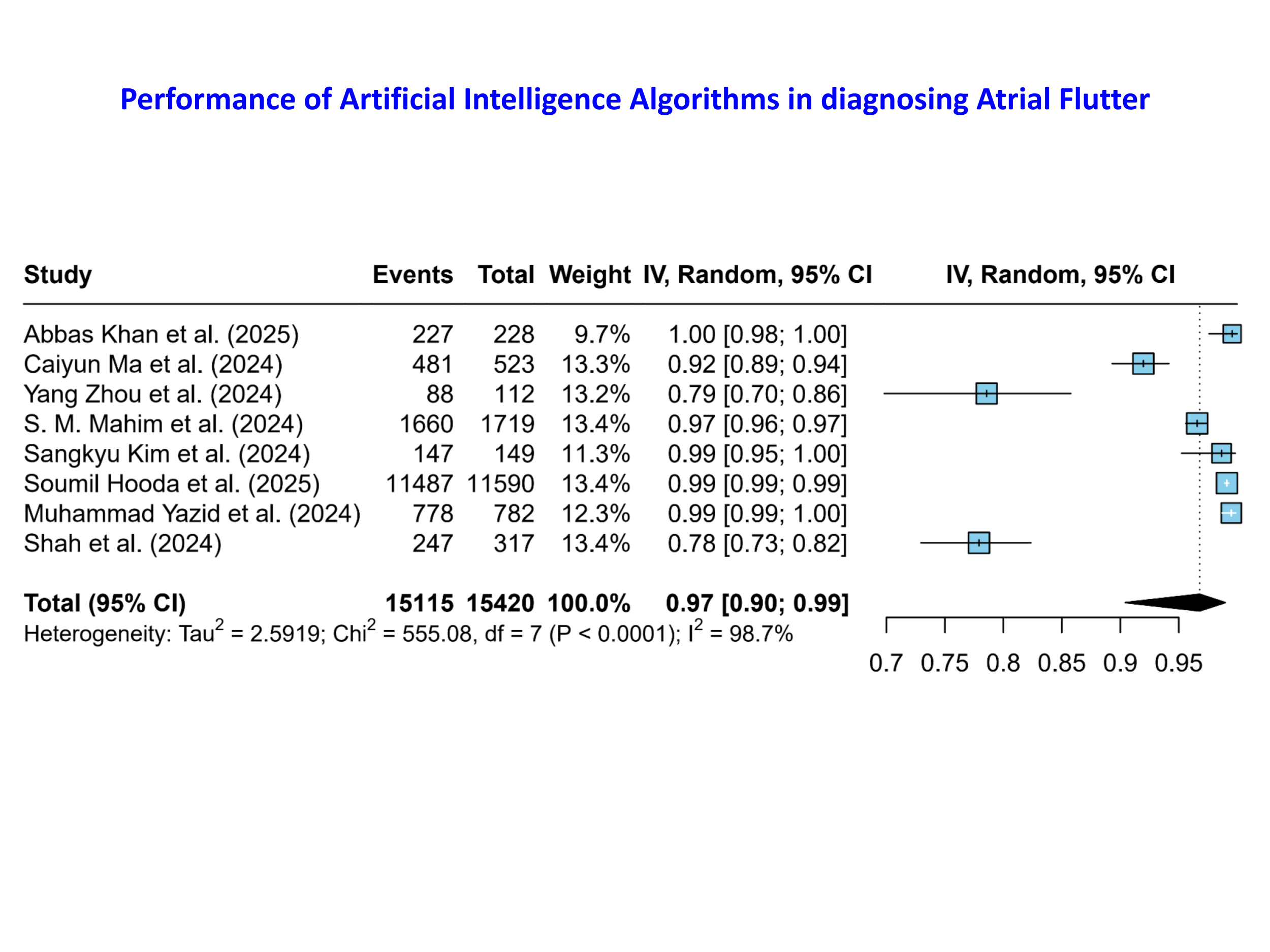
Nine studies were included. AI algorithms demonstrated robust diagnostic accuracy for AF, yielding a pooled accuracy of 0.97 (95% CI, 0.90 to 0.99; p < 0.0001). Individual study estimates ranged from 0.78 to 1.00, with the majority exceeding 0.95, underscoring the high discriminative capacity of contemporary AI models. Heterogeneity was substantial (I2 = 98.7%), reflecting variability in algorithmic architecture and validation cohorts.
Conclusions:
AI and deep learning algorithms represent a paradigm shift in AF detection, addressing limitations of conventional diagnostic approaches. Our synthesis demonstrates that AI models achieve exceptional diagnostic accuracy using patient ECGs as samples, highlighting their transformative potential for scalable, early detection. However, substantial heterogeneity underscores the necessity for rigorous external validation, algorithmic transparency, and bias mitigation to ensure equitable clinical integration and to fully realize the promise of AI-driven cardiovascular diagnostics.
Background:
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia and it imparts significant morbidity and mortality. A substantial proportion of AF remains undiagnosed. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative tool to enhance early AF detection. This systematic review and meta-analysis critically evaluates the diagnostic performance of AI models for AF by using patient electrocardiograms (ECGs).
Objectives:
To systematically appraise and quantitatively synthesize the diagnostic accuracy of AI algorithms for AF detection, using databases of patient ECGs previously validated by cardiologists.
Methods:
Comprehensive searches were performed in PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, and IEEE Xplore from January 2016 - June 2025 to identify studies evaluating the diagnostic performance of AI algorithms for AF detection, only using databases consisting of patient ECGs with prior cardiologist validation, irrespective of comparator. 73 quality studies were included for the study. Only the 9 most recent publications (January 2024–June 2025) were included in this analysis Two independent reviewers screened titles, abstracts, and full texts, extracted data, and assessed risk of bias using the QUADAS-2 tool; discrepancies were resolved by consensus. Pooled accuracy estimates were synthesized using random-effects meta-analysis in R, adhering to PRISMA-DTA guidelines.
Results:
Nine studies were included. AI algorithms demonstrated robust diagnostic accuracy for AF, yielding a pooled accuracy of 0.97 (95% CI, 0.90 to 0.99; p < 0.0001). Individual study estimates ranged from 0.78 to 1.00, with the majority exceeding 0.95, underscoring the high discriminative capacity of contemporary AI models. Heterogeneity was substantial (I2 = 98.7%), reflecting variability in algorithmic architecture and validation cohorts.
Conclusions:
AI and deep learning algorithms represent a paradigm shift in AF detection, addressing limitations of conventional diagnostic approaches. Our synthesis demonstrates that AI models achieve exceptional diagnostic accuracy using patient ECGs as samples, highlighting their transformative potential for scalable, early detection. However, substantial heterogeneity underscores the necessity for rigorous external validation, algorithmic transparency, and bias mitigation to ensure equitable clinical integration and to fully realize the promise of AI-driven cardiovascular diagnostics.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Algorithm to Detect Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Risk from Baseline ECGs
Arezoumand Amirhossein, Danala Gopichandh, Masnadi Khiabani Parisa, Ebert David, Behere Shashank
A large-scale multi-view deep learning-based assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction in echocardiographyJing Linyuan, Metser Gil, Mawson Thomas, Tat Emily, Jiang Nona, Duffy Eamon, Hahn Rebecca, Homma Shunichi, Haggerty Christopher, Poterucha Timothy, Elias Pierre, Long Aaron, Vanmaanen David, Rocha Daniel, Hartzel Dustin, Kelsey Christopher, Ruhl Jeffrey, Beecy Ashley, Elnabawi Youssef