Final ID: MP2339
Residual Learning Networks for Automated Detection of Hypertensive Retinopathy: A Multi-Institutional Validation Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Cardiovascular-retinal pathophysiology represents an emerging frontier in precision medicine, with hypertensive retinopathy (HR) serving as a critical biomarker for systemic vascular compromise. Contemporary neural architectures have revolutionized medical imaging interpretation through sophisticated feature extraction capabilities. ResNet18, distinguished by its residual learning framework and skip connections, addresses the vanishing gradient problem inherent in deep networks while maintaining computational efficiency. This architecture's unique capacity for hierarchical feature propagation makes it particularly advantageous for detecting subtle microvascular changes characteristic of hypertensive retinopathy, potentially transforming cardiovascular risk stratification paradigms.
Methods:
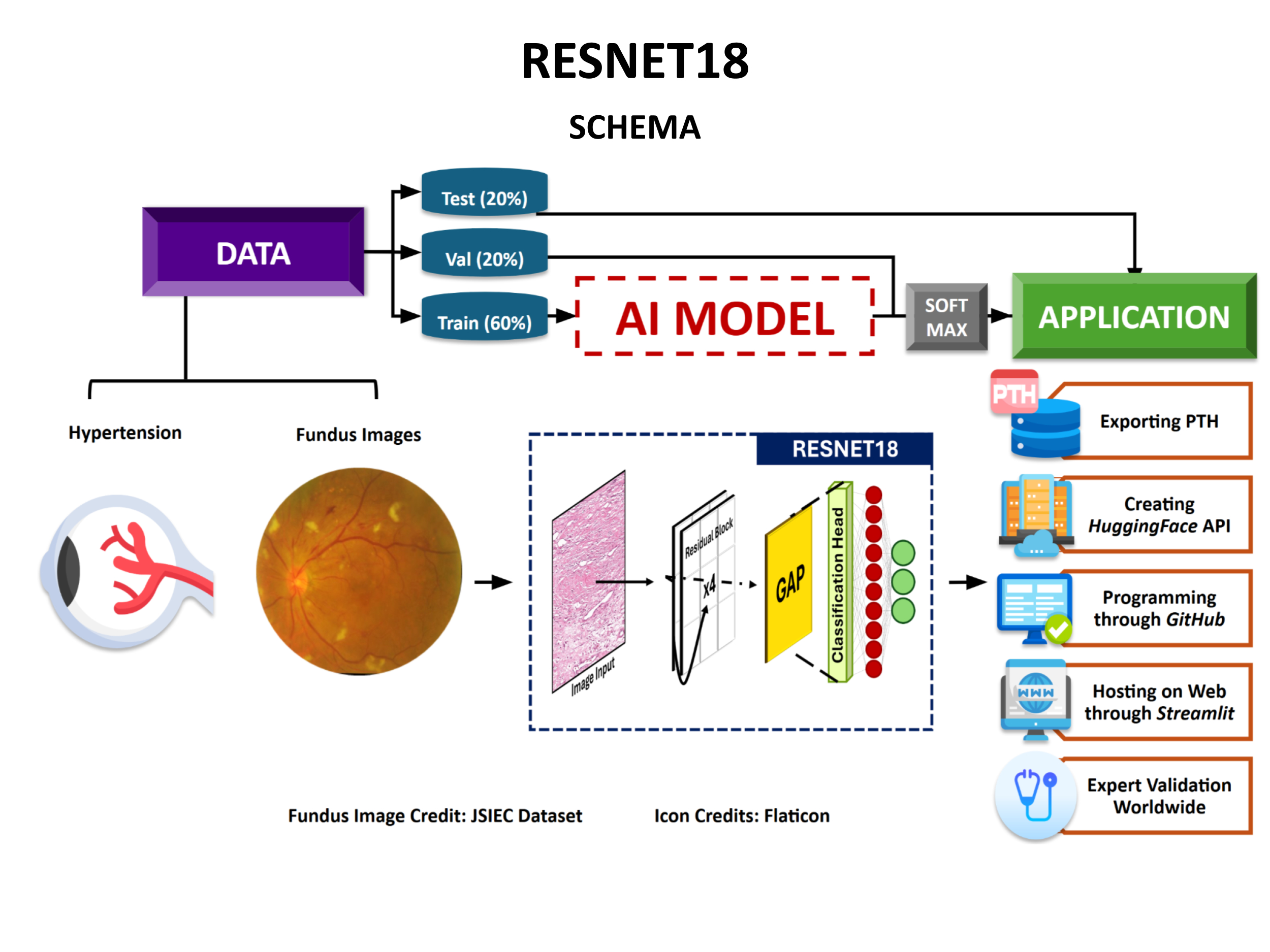
Following institutional ethics approval, a comprehensive dataset encompassing retinal fundus photographs was curated, representing seven distinct pathological entities: HR, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy (DR), cataract, glaucoma, pathological myopia, and normal variants. The ResNet18 architecture was implemented with systematic data partitioning (60% training, 20% validation, 20% testing) and standardized preprocessing protocols. Model optimization employed transfer learning with fine-tuning strategies specific to ophthalmic imaging characteristics. Performance validation utilized comprehensive metrics including area under the curve analysis and multi-class precision-recall evaluation.
Results:
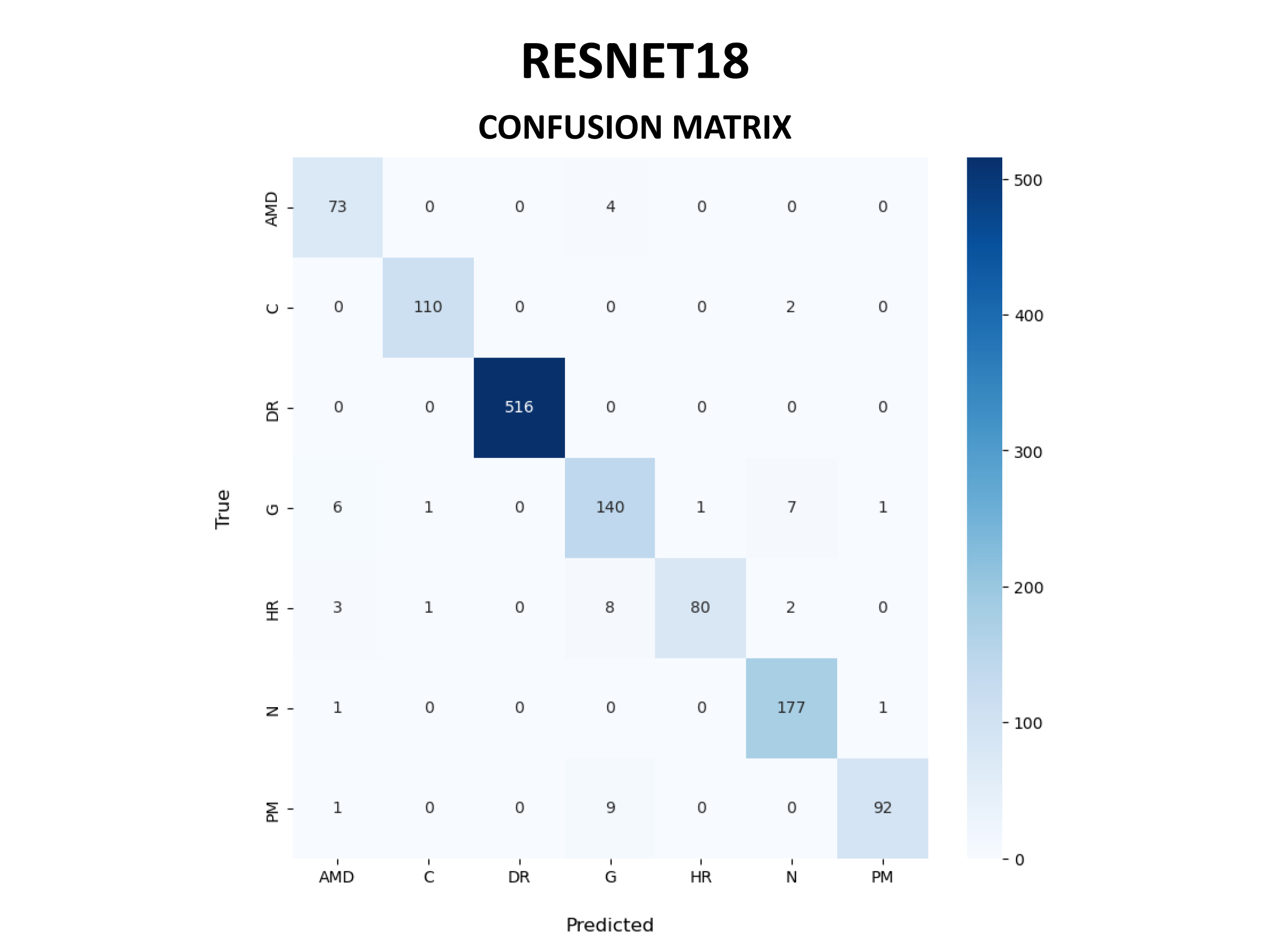
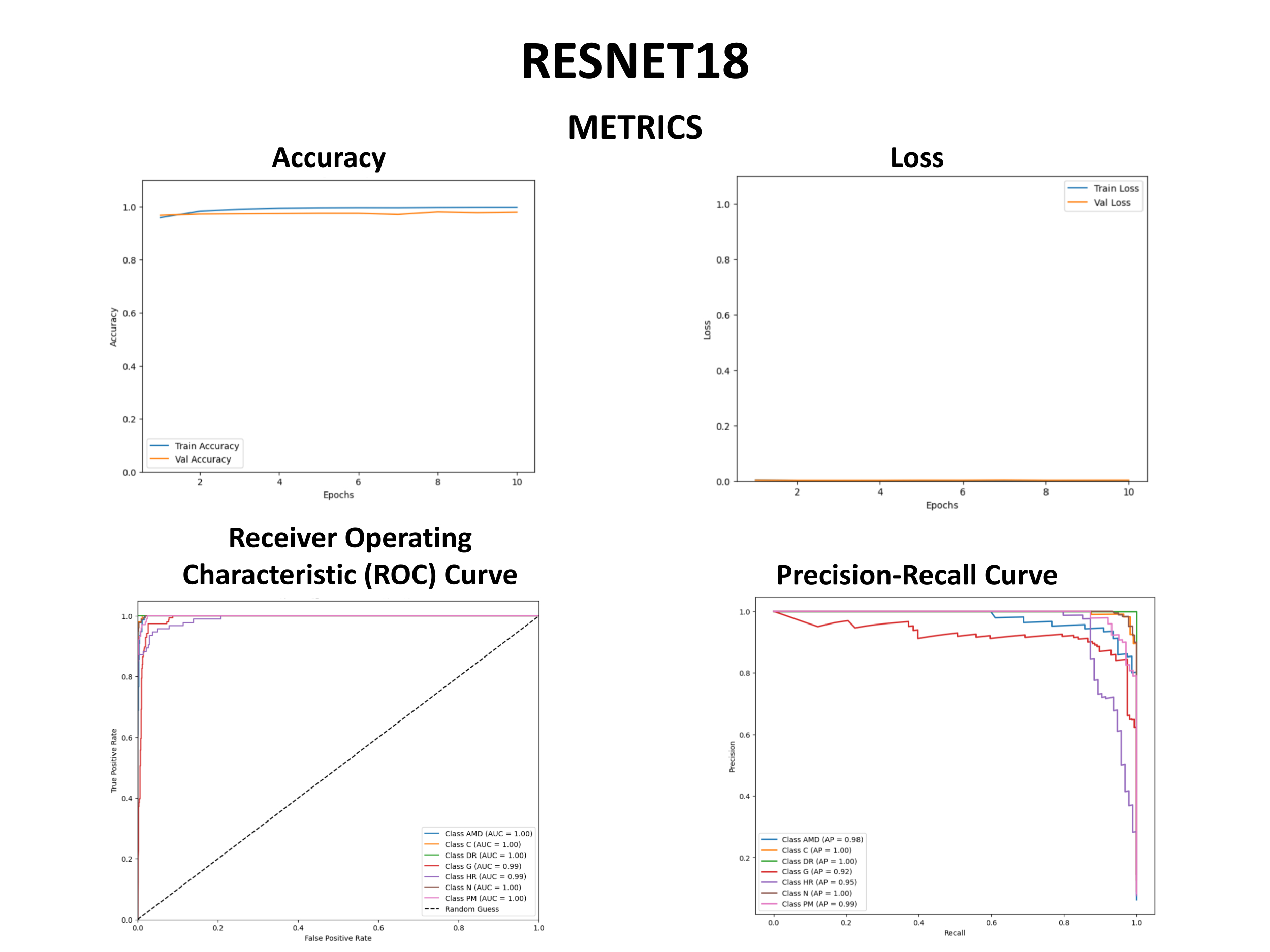
ResNet18 demonstrated exceptional discriminatory performance across all pathological categories. The confusion matrix revealed optimal classification accuracy: DR achieved perfect identification (516/516), while HR demonstrated 85.1% sensitivity (80/94 correct classifications). Cross-validation accuracy consistently exceeded 99%, with area under the receiver operating characteristic curve approaching unity for all disease categories. Precision-recall analysis confirmed robust model generalizability with minimal overfitting characteristics.
Conclusions:
These findings establish ResNet18's superiority in automated hypertensive retinopathy detection, offering scalable deployment potential for cardiovascular risk assessment. The residual learning paradigm enables precise microvascular phenotyping, advancing personalized medicine approaches in ophthalmologic and cardiologic practice.
Cardiovascular-retinal pathophysiology represents an emerging frontier in precision medicine, with hypertensive retinopathy (HR) serving as a critical biomarker for systemic vascular compromise. Contemporary neural architectures have revolutionized medical imaging interpretation through sophisticated feature extraction capabilities. ResNet18, distinguished by its residual learning framework and skip connections, addresses the vanishing gradient problem inherent in deep networks while maintaining computational efficiency. This architecture's unique capacity for hierarchical feature propagation makes it particularly advantageous for detecting subtle microvascular changes characteristic of hypertensive retinopathy, potentially transforming cardiovascular risk stratification paradigms.
Methods:
Following institutional ethics approval, a comprehensive dataset encompassing retinal fundus photographs was curated, representing seven distinct pathological entities: HR, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy (DR), cataract, glaucoma, pathological myopia, and normal variants. The ResNet18 architecture was implemented with systematic data partitioning (60% training, 20% validation, 20% testing) and standardized preprocessing protocols. Model optimization employed transfer learning with fine-tuning strategies specific to ophthalmic imaging characteristics. Performance validation utilized comprehensive metrics including area under the curve analysis and multi-class precision-recall evaluation.
Results:
ResNet18 demonstrated exceptional discriminatory performance across all pathological categories. The confusion matrix revealed optimal classification accuracy: DR achieved perfect identification (516/516), while HR demonstrated 85.1% sensitivity (80/94 correct classifications). Cross-validation accuracy consistently exceeded 99%, with area under the receiver operating characteristic curve approaching unity for all disease categories. Precision-recall analysis confirmed robust model generalizability with minimal overfitting characteristics.
Conclusions:
These findings establish ResNet18's superiority in automated hypertensive retinopathy detection, offering scalable deployment potential for cardiovascular risk assessment. The residual learning paradigm enables precise microvascular phenotyping, advancing personalized medicine approaches in ophthalmologic and cardiologic practice.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Competency-Based Screening Echocardiography Curriculum Designed for Rural American Indian Community Health Representatives
Thoroughman Rose, Riley Alan, De Loizaga Sarah, Adams David, Beaton Andrea, Buonfiglio Samantha, Danforth Kristen, Masyuko Sarah, Miller Mccall, Yadava Mrinal
A Machine Learning Algorithm to Detect Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Risk from Baseline ECGsArezoumand Amirhossein, Danala Gopichandh, Masnadi Khiabani Parisa, Ebert David, Behere Shashank