Final ID: MP1689
India as the Epicenter of Global Rheumatic Heart Disease: A Subnational and Temporal Analysis from 1990 to 2021
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) continues to impose a significant public health burden globally,primarily as a sequela of untreated or recurrent streptococcal infections. Despite being preventable, RHD remains endemic in low- and middle-income countries.India, with its vast and diverse population, has emerged as a global hub for RHD, contributing a disproportionate share of the worldwide burden.
Methods:
We used the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 framework to estimate RHD prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) among all age groups in India from 1990 to 2021. Temporal trends were assessed using total percentage change(TPC). Subnational patterns were examined across states and union territories. Age-specific incidence and YLDs per 100,000 population were reported.Gender-based disparities were also evaluated.
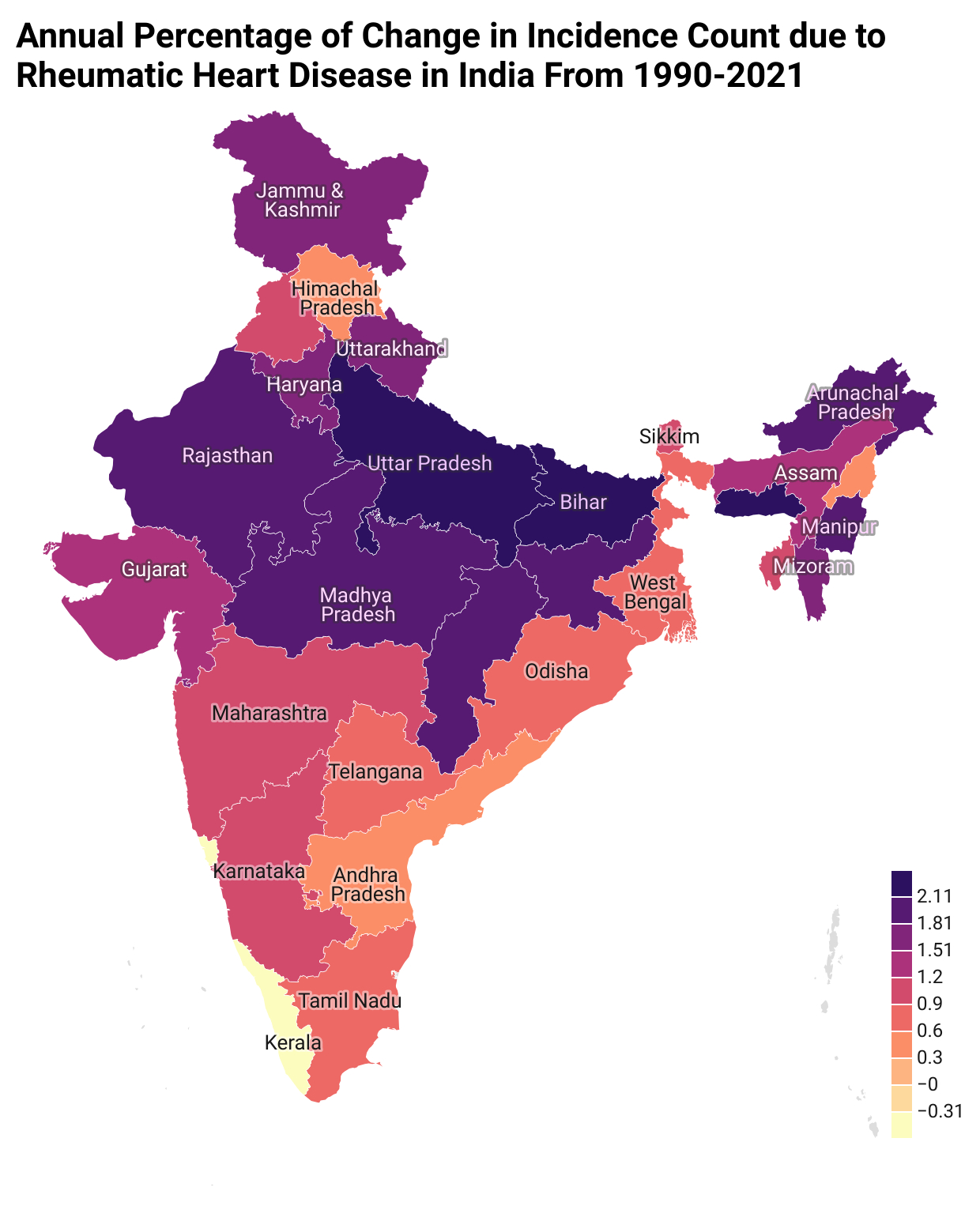
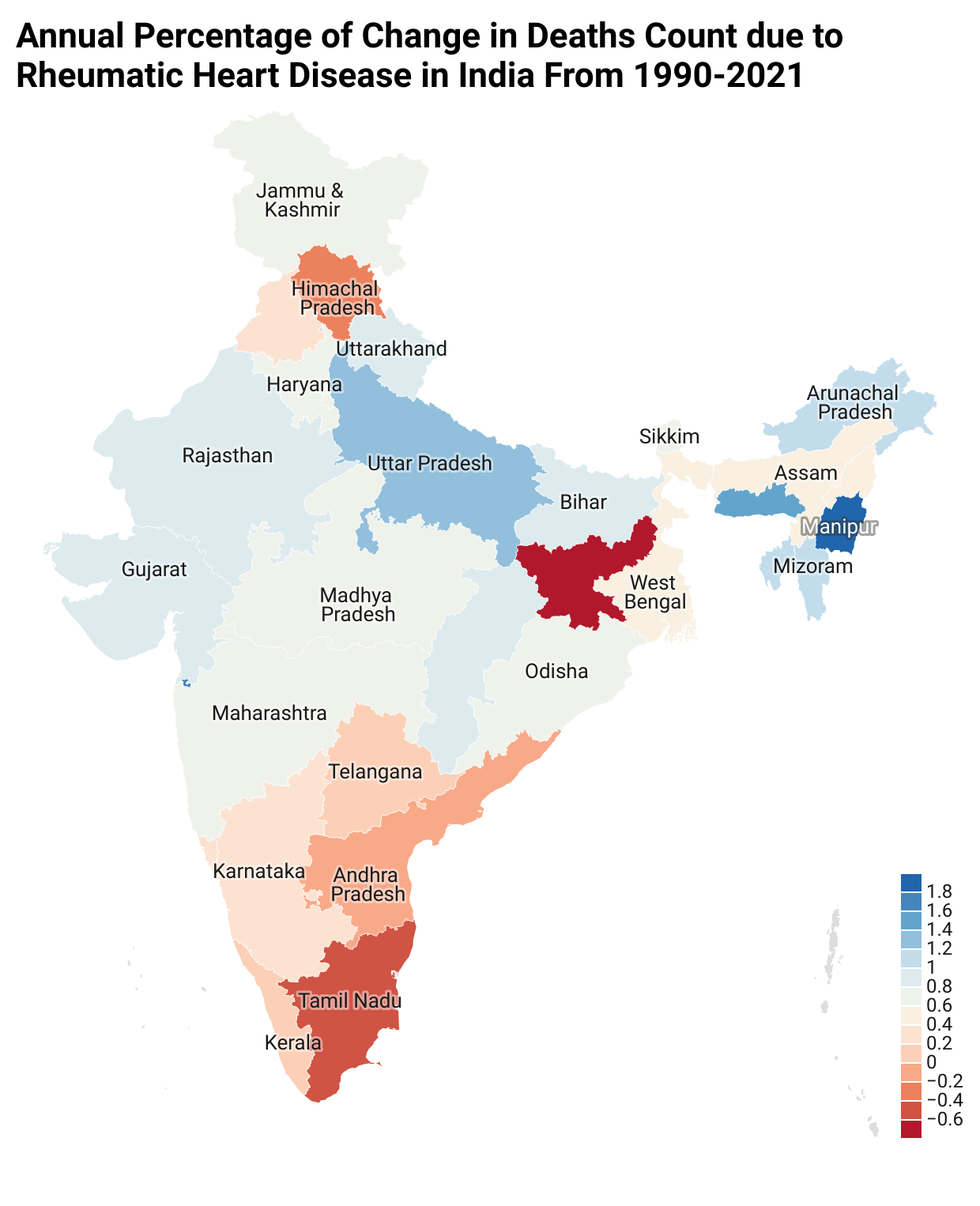
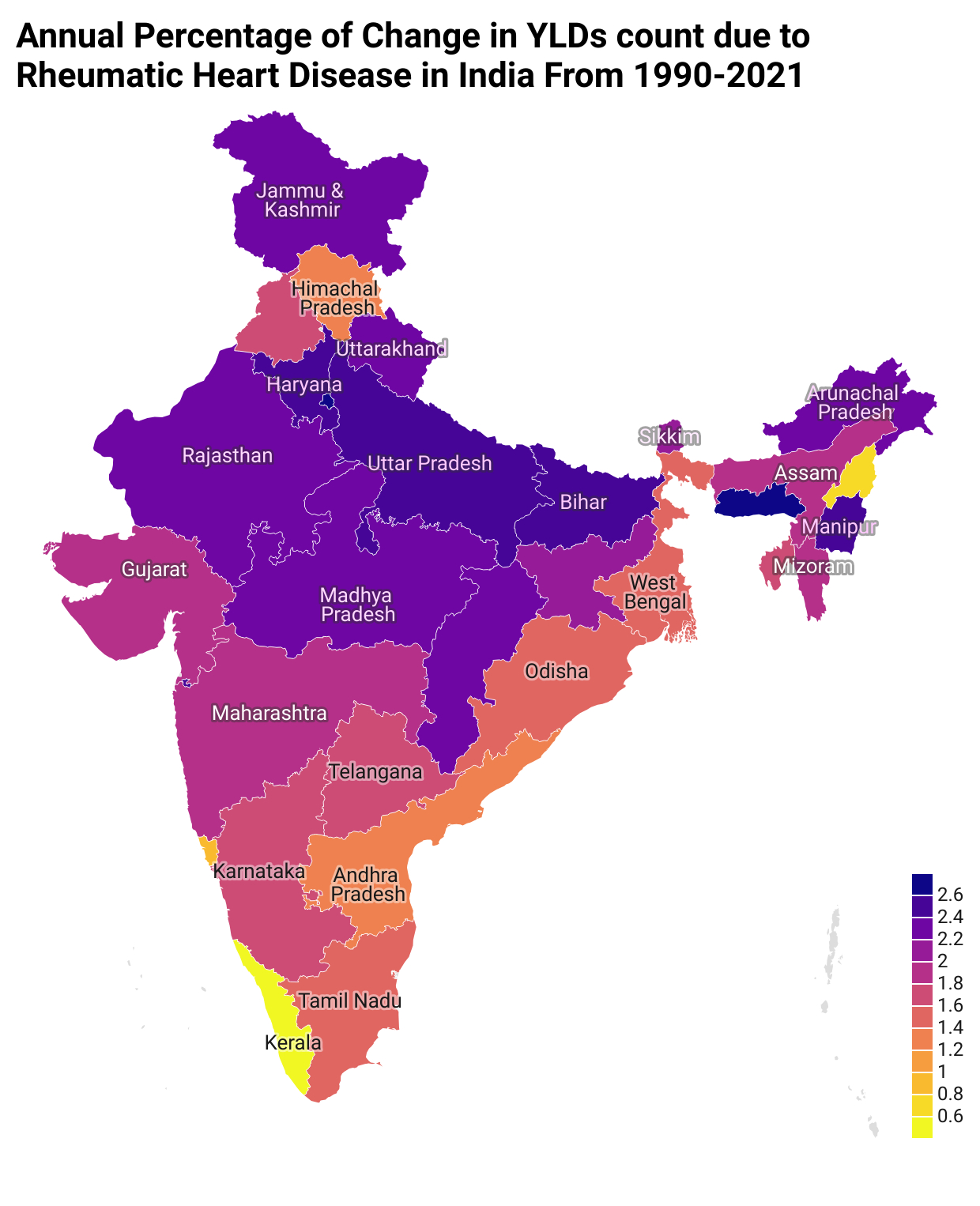
Result: In 2021,India accounted for 19.17% of global rheumatic heart disease(RHD) prevalence(10.5 million out of 54.7 million cases), 44.46% of total global RHD deaths, and 42.79% of global DALYs. From 1990 to 2021, the total percentage change (TPC) in prevalence increased by 85% (95% UI: 80%–89%), while deaths rose by 20% (95% UI: 6%–49%). At the sub-national level, the greatest rise in TPC of incidence was observed in Meghalaya (109%), followed by Bihar (104%) and Uttar Pradesh (95%). In contrast, Goa and Kerala experienced declines of 9% and 17%, respectively. Regarding mortality, Manipur reported the highest increase in deaths (78%), followed by the Union Territories (64%), Meghalaya (58%), and Uttar Pradesh (49%). By age, the highest incidence rate in 2021 was recorded in the 20–24 years group at 110 (63–176) per 100,000, closely followed by 15–19 years at 109 per 100,000. For YLDs, the 30–34 years age group had the highest rate of 61 (37–96) per 100,000, followed by 25–29 years at 61 (36–96). Gender-wise, women experienced a disproportionately higher rise in RHD burden over the past three decades. The TPC in incidence (56% vs. 55%), deaths (39% vs. 2%), and YLDs (86% vs. 78%)—highlighting a disproportionately higher burden in women from 1990-2021.
Conclusion:
India bears the highest localized burden of RHD globally, with widening subnational and gender disparities. Despite declining trends in some states, the growing burden in others—especially among young adults and women—underscores the urgent need for targeted prevention, early diagnosis, and streptococcal infection control strategies across high-risk regions.
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) continues to impose a significant public health burden globally,primarily as a sequela of untreated or recurrent streptococcal infections. Despite being preventable, RHD remains endemic in low- and middle-income countries.India, with its vast and diverse population, has emerged as a global hub for RHD, contributing a disproportionate share of the worldwide burden.
Methods:
We used the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 framework to estimate RHD prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) among all age groups in India from 1990 to 2021. Temporal trends were assessed using total percentage change(TPC). Subnational patterns were examined across states and union territories. Age-specific incidence and YLDs per 100,000 population were reported.Gender-based disparities were also evaluated.
Result: In 2021,India accounted for 19.17% of global rheumatic heart disease(RHD) prevalence(10.5 million out of 54.7 million cases), 44.46% of total global RHD deaths, and 42.79% of global DALYs. From 1990 to 2021, the total percentage change (TPC) in prevalence increased by 85% (95% UI: 80%–89%), while deaths rose by 20% (95% UI: 6%–49%). At the sub-national level, the greatest rise in TPC of incidence was observed in Meghalaya (109%), followed by Bihar (104%) and Uttar Pradesh (95%). In contrast, Goa and Kerala experienced declines of 9% and 17%, respectively. Regarding mortality, Manipur reported the highest increase in deaths (78%), followed by the Union Territories (64%), Meghalaya (58%), and Uttar Pradesh (49%). By age, the highest incidence rate in 2021 was recorded in the 20–24 years group at 110 (63–176) per 100,000, closely followed by 15–19 years at 109 per 100,000. For YLDs, the 30–34 years age group had the highest rate of 61 (37–96) per 100,000, followed by 25–29 years at 61 (36–96). Gender-wise, women experienced a disproportionately higher rise in RHD burden over the past three decades. The TPC in incidence (56% vs. 55%), deaths (39% vs. 2%), and YLDs (86% vs. 78%)—highlighting a disproportionately higher burden in women from 1990-2021.
Conclusion:
India bears the highest localized burden of RHD globally, with widening subnational and gender disparities. Despite declining trends in some states, the growing burden in others—especially among young adults and women—underscores the urgent need for targeted prevention, early diagnosis, and streptococcal infection control strategies across high-risk regions.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comparative Analysis of 30-Day Surgical Outcomes: Univalvular vs. Multivalvular Procedures in Contemporary Practice
Tessari Fernanda, Sampaio Roney, Tarasoutchi Flavio, Rosa Vitor, Nazzetta Daniella, Lopes Mariana, Vicente Pereira Lipari Layara Fernanda, Campos Carlos, Andrade Camila, Alves De Souza Giovanna, Vieira Ferola Laura Beatriz
A machine learning approach to classifying ischemic stroke etiology using variables available in the Get-with-the-Guidelines Stroke RegistryLee Ho-joon, Schwamm Lee, Turner Ashby, De Havenon Adam, Kamel Hooman, Brandt Cynthia, Zhao Hongyu, Krumholz Harlan, Sharma Richa