Final ID: 4138955
Artificial intelligence-guided screening of rheumatic heart disease from single-view two-dimensional echocardiography
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is the most common acquired heart disorder in children and adolescents worldwide. We developed and validated an automated artificial intelligence (AI)-guided RHD screening algorithm adapted for point-of-care ultrasonography (POCUS) in school-aged children.
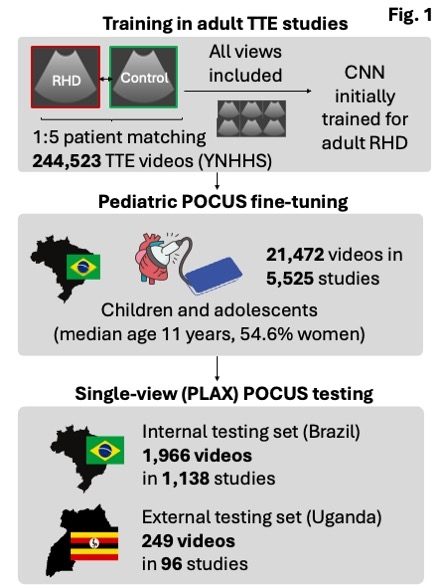
Methods: We employed a cross-domain transfer learning approach, in which a 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) was first trained to detect structural RHD deformation of the mitral or aortic valves in 244,523 videos, representing all views from 5,614 adult transthoracic echocardiograms (1:5 age and sex-matched cases and controls; median age 69 [58-80] years, 76.4% female) in a large US health system. The model was fine-tuned for stage ≥B (“definite”) RHD in 21,472 POCUS videos (2D parasternal and apical acquisitions) from 5,525 studies (75% training, 25% validation) in a pediatric screening program (median age 11 [IQR 10-13] years, 54.6% female) in Brazilian low-income schools. Testing was performed in a held-out set of 1,966 parasternal long-axis (PLAX) videos from 1,138 studies in Brazil (14 [1.2%] with stage ≥B RHD) as well as in an external pediatric screening set in Uganda consisting of 249 videos from 96 studies (34 [35.4%] with stage ≥B RHD) (Fig. 1).
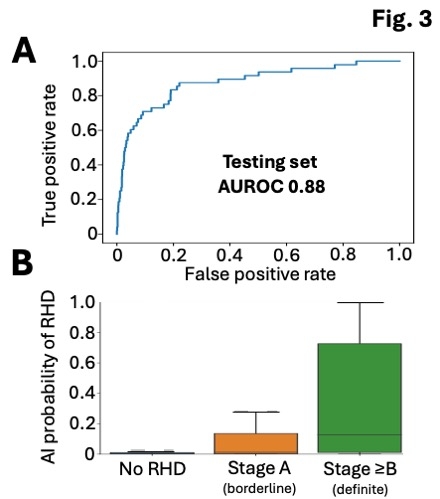
Results: Our model (Fig. 2) achieved a study-level AUROC (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve) of 0.88 across the held-out/external testing sets for identifying stage ≥B RHD from cardiac POCUS (Fig. 3A). On a video-level the model learned a continuous spectrum of phenotypes on PLAX acquisitions spanning stage ≥B (“definite”) and stage A (“borderline”) cases, ranging from a median video-level AI probability of 0.13 [0.01-0.73] for stage ≥B to 0.00 [0.00-0.01] for non-RHD POCUS (Fig. 3B). At the threshold that maximized Youden’s J in the held-out Brazil set, our algorithm’s performance in the set from Uganda showed 97% recall (sensitivity), a positive predictive value (precision) of 46%, and a negative predictive value of 95%.
Conclusions: A transfer learning approach that employs multi-view learning achieves excellent performance for RHD on single-view two-dimensional cardiac POCUS without Doppler. Our study suggests a scalable approach to AI-enabled RHD detection with images that can be acquired by individuals with modest training.
Methods: We employed a cross-domain transfer learning approach, in which a 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) was first trained to detect structural RHD deformation of the mitral or aortic valves in 244,523 videos, representing all views from 5,614 adult transthoracic echocardiograms (1:5 age and sex-matched cases and controls; median age 69 [58-80] years, 76.4% female) in a large US health system. The model was fine-tuned for stage ≥B (“definite”) RHD in 21,472 POCUS videos (2D parasternal and apical acquisitions) from 5,525 studies (75% training, 25% validation) in a pediatric screening program (median age 11 [IQR 10-13] years, 54.6% female) in Brazilian low-income schools. Testing was performed in a held-out set of 1,966 parasternal long-axis (PLAX) videos from 1,138 studies in Brazil (14 [1.2%] with stage ≥B RHD) as well as in an external pediatric screening set in Uganda consisting of 249 videos from 96 studies (34 [35.4%] with stage ≥B RHD) (Fig. 1).
Results: Our model (Fig. 2) achieved a study-level AUROC (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve) of 0.88 across the held-out/external testing sets for identifying stage ≥B RHD from cardiac POCUS (Fig. 3A). On a video-level the model learned a continuous spectrum of phenotypes on PLAX acquisitions spanning stage ≥B (“definite”) and stage A (“borderline”) cases, ranging from a median video-level AI probability of 0.13 [0.01-0.73] for stage ≥B to 0.00 [0.00-0.01] for non-RHD POCUS (Fig. 3B). At the threshold that maximized Youden’s J in the held-out Brazil set, our algorithm’s performance in the set from Uganda showed 97% recall (sensitivity), a positive predictive value (precision) of 46%, and a negative predictive value of 95%.
Conclusions: A transfer learning approach that employs multi-view learning achieves excellent performance for RHD on single-view two-dimensional cardiac POCUS without Doppler. Our study suggests a scalable approach to AI-enabled RHD detection with images that can be acquired by individuals with modest training.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Bleeding Heart: Chronic Pericarditis Manifesting as Recurrent Hemorrhagic Pericardial Effusion - Diagnostic Considerations with a PFO Closure Device and the Role of CT Imaging
Patel Zeel, Liu Yang, Wengrofsky Perry, Yoon Sung-han
18F-NaF and 18F-FDG and calcification predict the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms and is attenuated by drug therapyNakahara Takehiro, Miyazawa Raita, Iwabuchi Yu, Tonda Kai, Narula Nupoor, Strauss Harry, Narula Jagat, Jinzaki Masahiro