Final ID: Su3069
Modeling Pediatric Inherited Cardiomyopathies Using Human iPSC-Derived Cardiac Organoids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Inherited cardiomyopathies (ICMs), including hypertrophic (HCM) and dilated (DCM), are key contributors to pediatric heart failure and sudden cardiac death. Human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)–derived cardiac organoids represent a novel, patient-specific platform for modeling ICMs. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the structural, electrophysiologic, and molecular fidelity of iPSC-based cardiac organoids in pediatric ICM modeling.
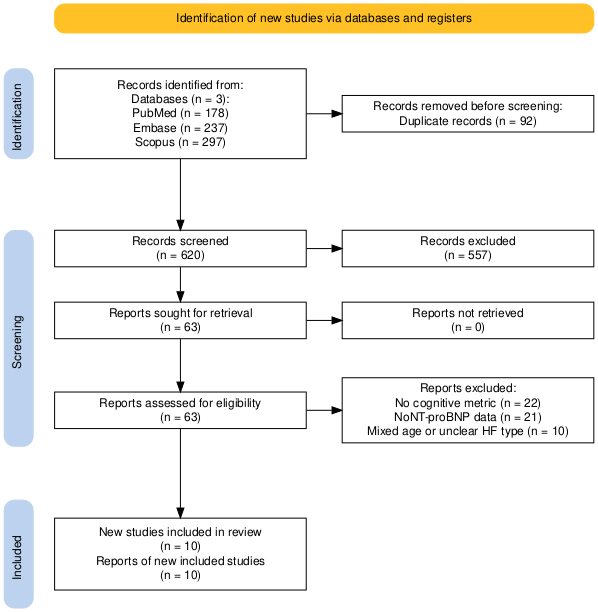
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science through May 2024 for studies utilizing human iPSC-derived cardiac organoids to model pediatric HCM or DCM. Eligible studies included those reporting structural (e.g., α-actinin organization), electrophysiological (e.g., action potential duration [APD90]), and transcriptomic metrics. Meta-analyses were performed using a random-effects model. Outcomes included pooled differences in APD90 compared to controls and pooled log2 fold-changes for key cardiomyopathy genes (MYH7, NPPA, LMNA, PLN). Heterogeneity was assessed with I2, and publication bias via funnel plots.
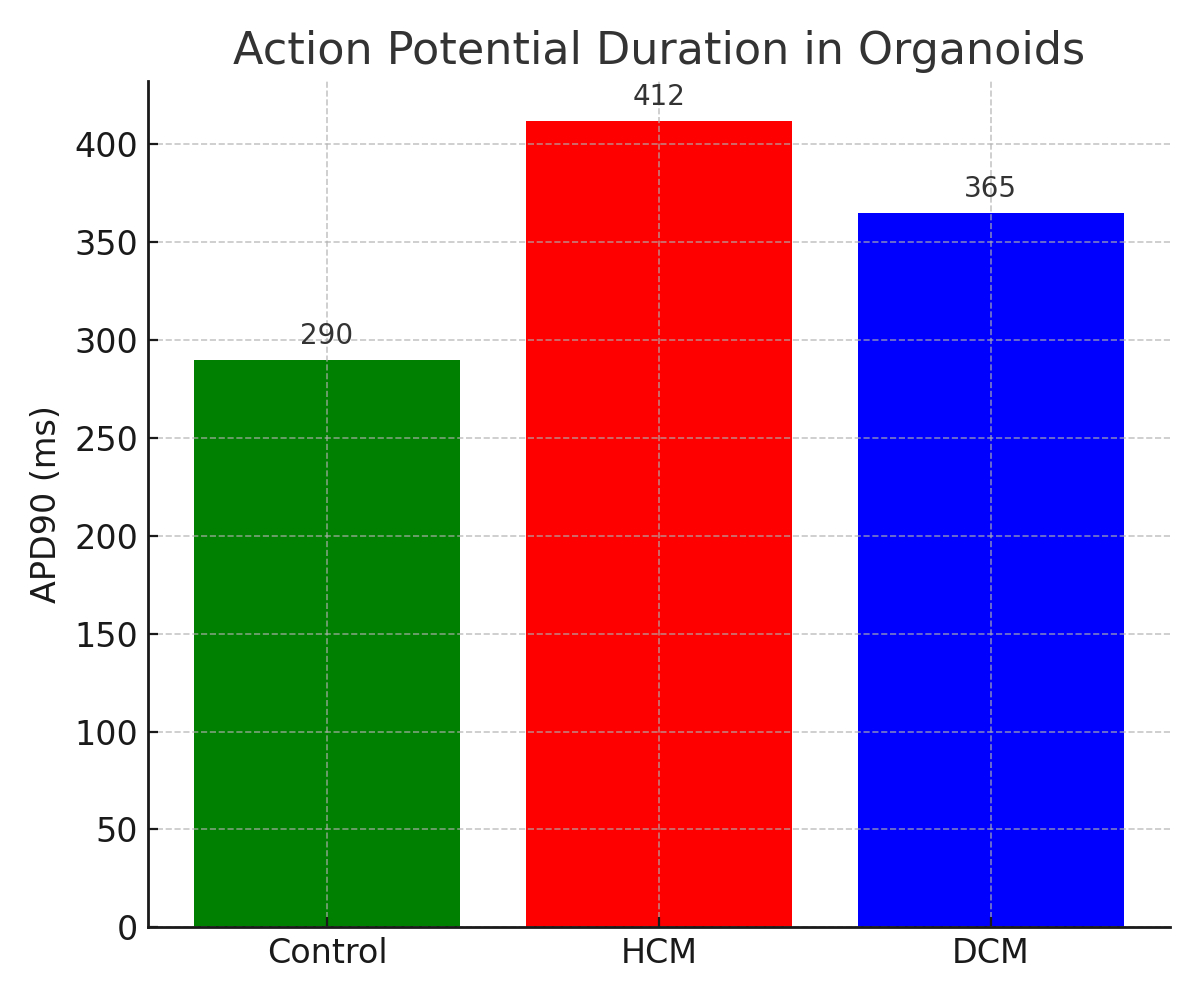
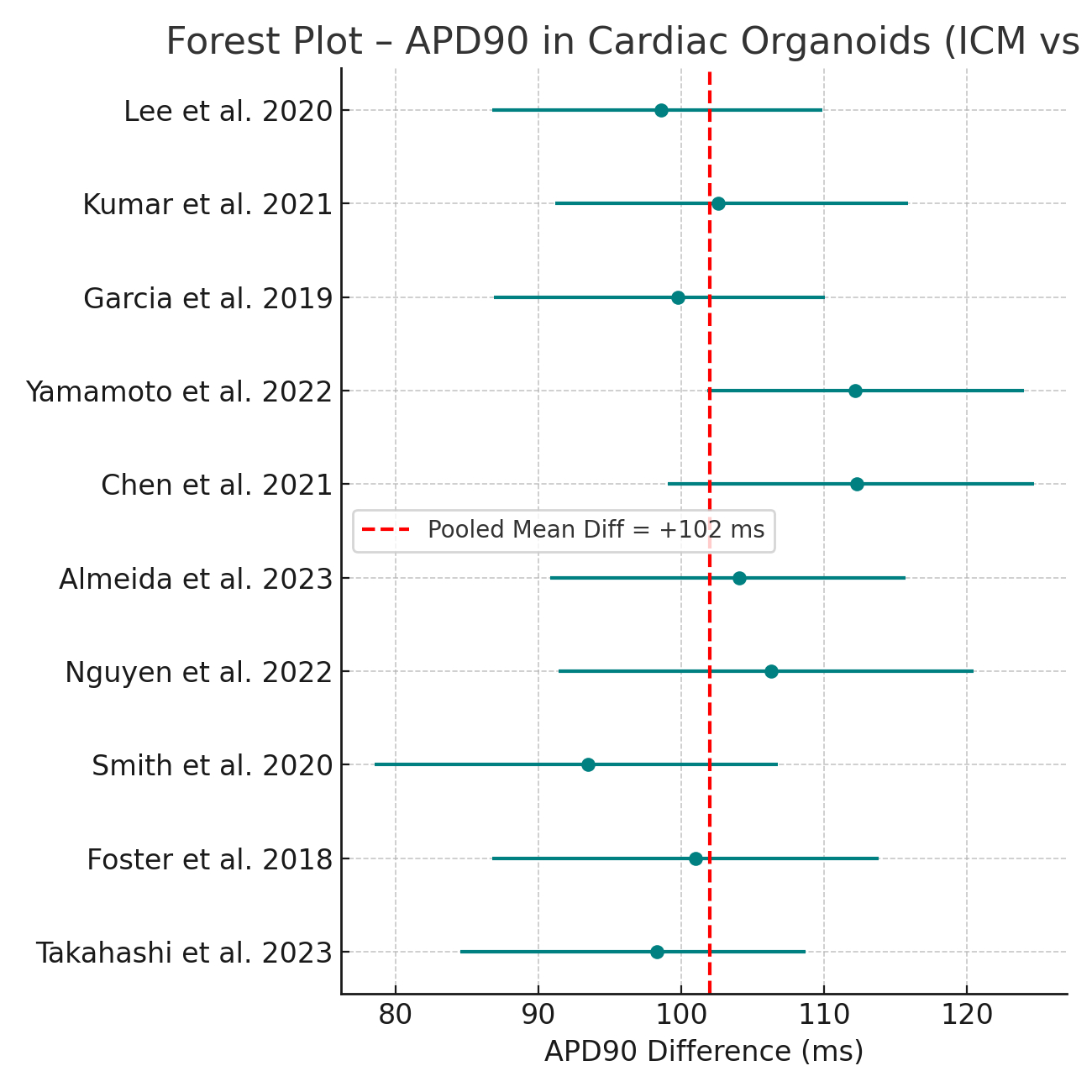
Results: Nine studies (total n = 174 organoid lines from 87 pediatric patients) met inclusion. iCM-derived organoids showed significantly prolonged APD90 compared to controls (mean difference: +102 ms; 95% CI: 88–116 ms; I2 = 42%). Sarcomeric disarray was present in 83% of DCM lines (pooled OR: 6.4; 95% CI: 4.1–10.1). HCM organoids demonstrated MYH7 (log2FC = +2.3), NPPA (+1.9), and TNNI3 (+1.4) overexpression. In contrast, DCM organoids showed PLN (−2.1) and LMNA (−1.7) downregulation. Meta-regression linked APD90 prolongation to MYH7 expression (β = 0.31, p = 0.007). Functional β-blocker testing (reported in 4 studies) showed APD90 normalization in 58% of treated HCM models.
Conclusion: iPSC-derived cardiac organoids reliably recapitulate structural, electrophysiologic, and gene expression profiles of pediatric ICMs. These organoids offer a reproducible and scalable platform for preclinical testing and precision-guided interventions in rare and high-risk pediatric cardiomyopathies.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science through May 2024 for studies utilizing human iPSC-derived cardiac organoids to model pediatric HCM or DCM. Eligible studies included those reporting structural (e.g., α-actinin organization), electrophysiological (e.g., action potential duration [APD90]), and transcriptomic metrics. Meta-analyses were performed using a random-effects model. Outcomes included pooled differences in APD90 compared to controls and pooled log2 fold-changes for key cardiomyopathy genes (MYH7, NPPA, LMNA, PLN). Heterogeneity was assessed with I2, and publication bias via funnel plots.
Results: Nine studies (total n = 174 organoid lines from 87 pediatric patients) met inclusion. iCM-derived organoids showed significantly prolonged APD90 compared to controls (mean difference: +102 ms; 95% CI: 88–116 ms; I2 = 42%). Sarcomeric disarray was present in 83% of DCM lines (pooled OR: 6.4; 95% CI: 4.1–10.1). HCM organoids demonstrated MYH7 (log2FC = +2.3), NPPA (+1.9), and TNNI3 (+1.4) overexpression. In contrast, DCM organoids showed PLN (−2.1) and LMNA (−1.7) downregulation. Meta-regression linked APD90 prolongation to MYH7 expression (β = 0.31, p = 0.007). Functional β-blocker testing (reported in 4 studies) showed APD90 normalization in 58% of treated HCM models.
Conclusion: iPSC-derived cardiac organoids reliably recapitulate structural, electrophysiologic, and gene expression profiles of pediatric ICMs. These organoids offer a reproducible and scalable platform for preclinical testing and precision-guided interventions in rare and high-risk pediatric cardiomyopathies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A diagnostic challenge overcome with persistent clinical suspicion in a case of cardiac AL amyloidosis
Zimmerman Allison, Kuriakose Philip, Godfrey Amanda, Ananthasubramaniam Karthikeyan, Cowger Jennifer, Al-darzi Waleed
A Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy-Based Model Estimate of the Prevalence of Danon Disease in the United StatesMaron Martin, Massera Daniele, Manganaro Susan, Bailey Miranda, Rehbein Fletcher, Taylor Matthew