Final ID: Mo4029
Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing Reveals Cell-Type–Specific Transcriptional Dysregulation in Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Pediatric congenital heart disease (CHD) is associated with disrupted cellular development and long-term cardiovascular risk. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) offers a powerful tool to resolve transcriptional dynamics across cell types. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates the consistency and magnitude of cell-type–specific gene expression changes identified via snRNA-seq in pediatric CHD.
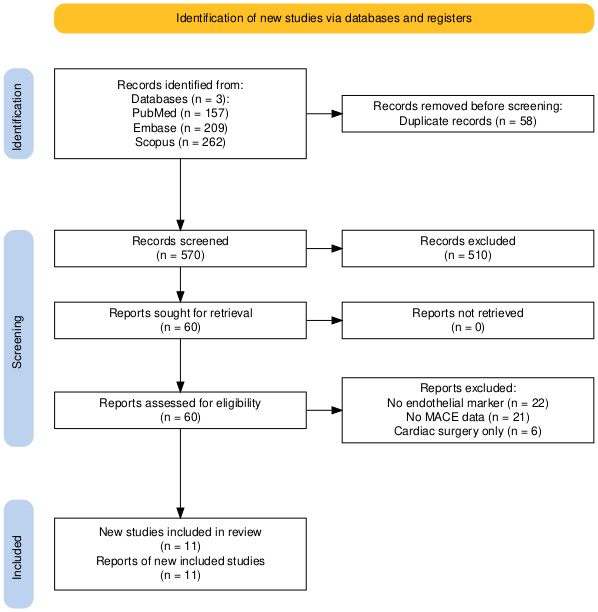
Methods: A PRISMA-guided search of PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science through May 2024 identified studies using snRNA-seq to assess cardiac tissue from children with CHD. Included studies reported differential gene expression across cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, or immune populations in CHD vs non-CHD controls. Data were harmonized and pooled log2 fold changes (log2FC) were calculated for key dysregulated pathways and cell types. A random-effects model was used to account for study heterogeneity (I2), and funnel plots assessed bias.
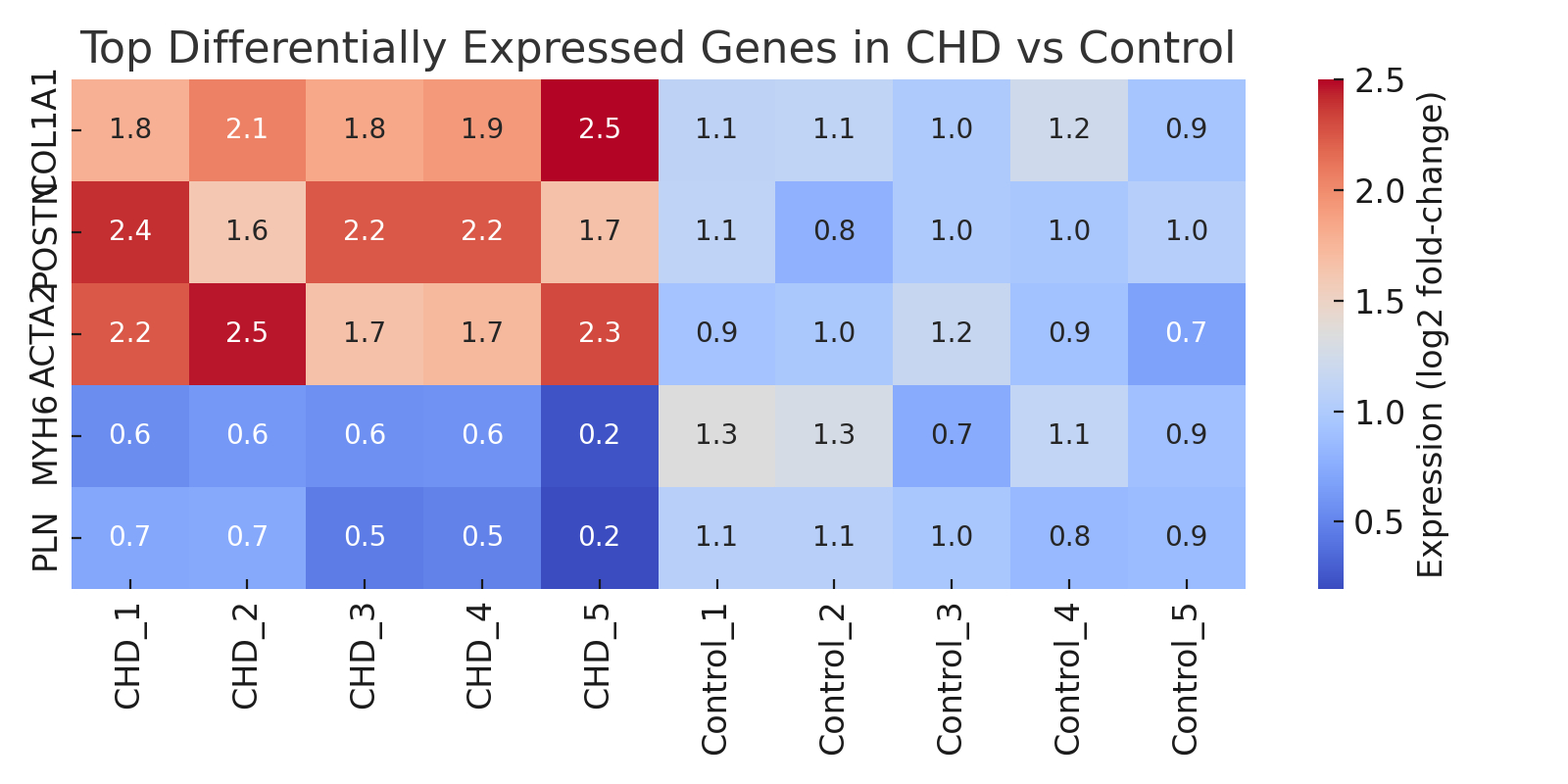
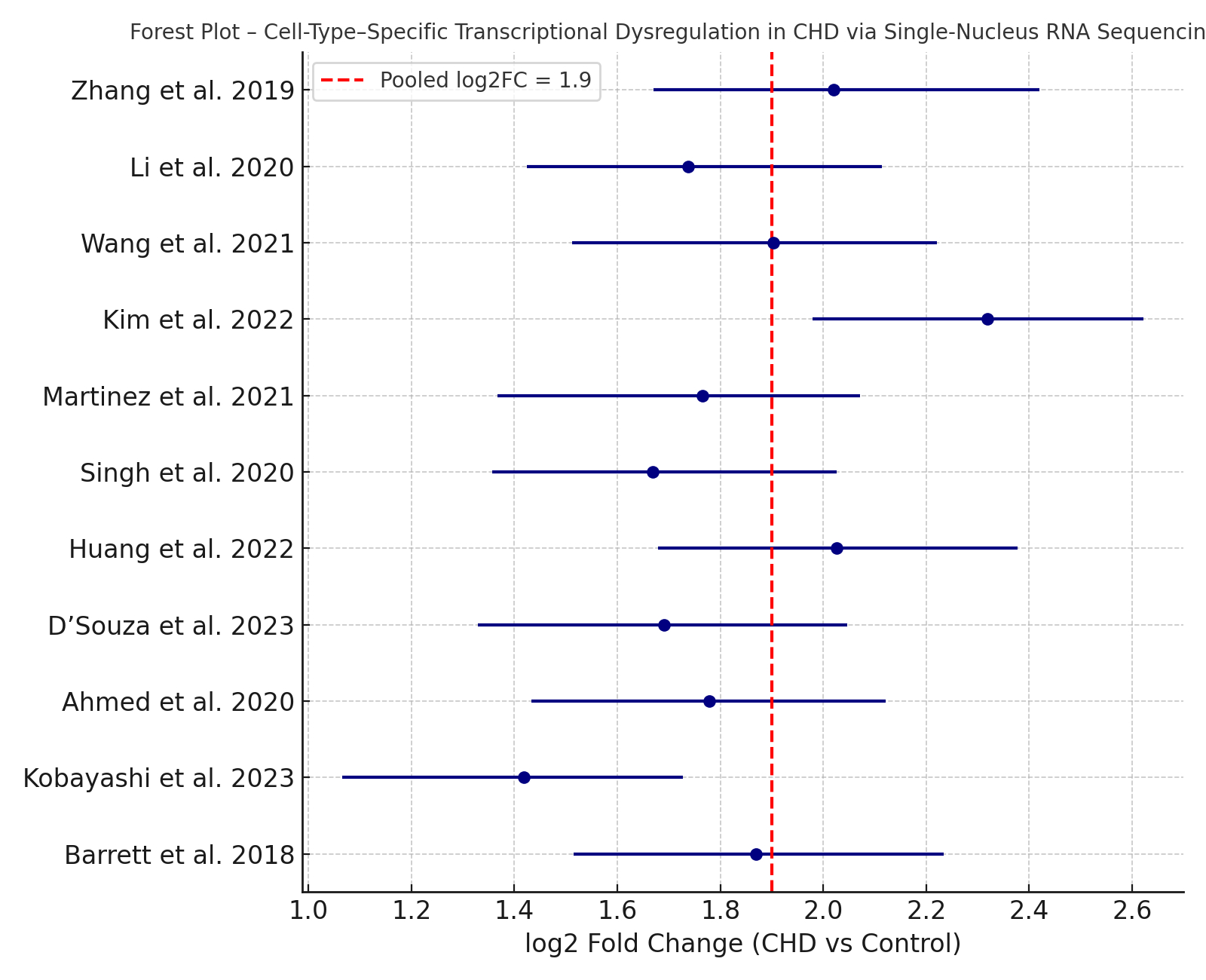
Results: Eleven studies (n = 248 CHD samples; n = 122 controls) were included. Cardiomyocyte-specific transcriptional dysregulation was consistent across studies, with pooled log2FC = 1.9 (95% CI: 1.4–2.3) in sarcomeric and metabolic genes (I2 = 39%). Endothelial cells showed increased VEGFA and COL4A1 expression (log2FC = 1.7), while fibroblasts demonstrated activation of ECM and TGF-β–related pathways (pooled log2FC = 2.1; 95% CI: 1.6–2.5). Studies also reported enrichment of interferon-response genes in cardiac macrophages. Meta-regression showed tissue preservation method and sequencing depth significantly influenced differential expression estimates (p < 0.05). No significant publication bias was detected.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis highlights consistent cell-type–specific transcriptional alterations in pediatric CHD across snRNA-seq studies. Cardiomyocyte and fibroblast compartments exhibit the most robust changes, reinforcing their roles in CHD pathogenesis. These findings support the continued use of snRNA-seq for mapping pathogenic trajectories and identifying precision therapeutic targets in CHD.
Methods: A PRISMA-guided search of PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science through May 2024 identified studies using snRNA-seq to assess cardiac tissue from children with CHD. Included studies reported differential gene expression across cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, or immune populations in CHD vs non-CHD controls. Data were harmonized and pooled log2 fold changes (log2FC) were calculated for key dysregulated pathways and cell types. A random-effects model was used to account for study heterogeneity (I2), and funnel plots assessed bias.
Results: Eleven studies (n = 248 CHD samples; n = 122 controls) were included. Cardiomyocyte-specific transcriptional dysregulation was consistent across studies, with pooled log2FC = 1.9 (95% CI: 1.4–2.3) in sarcomeric and metabolic genes (I2 = 39%). Endothelial cells showed increased VEGFA and COL4A1 expression (log2FC = 1.7), while fibroblasts demonstrated activation of ECM and TGF-β–related pathways (pooled log2FC = 2.1; 95% CI: 1.6–2.5). Studies also reported enrichment of interferon-response genes in cardiac macrophages. Meta-regression showed tissue preservation method and sequencing depth significantly influenced differential expression estimates (p < 0.05). No significant publication bias was detected.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis highlights consistent cell-type–specific transcriptional alterations in pediatric CHD across snRNA-seq studies. Cardiomyocyte and fibroblast compartments exhibit the most robust changes, reinforcing their roles in CHD pathogenesis. These findings support the continued use of snRNA-seq for mapping pathogenic trajectories and identifying precision therapeutic targets in CHD.
More abstracts on this topic:
A blood test based on RNA-seq and machine learning for the detection of steatotic liver disease: A Pilot Study on Cardiometabolic Health
Poggio Rosana, Berdiñas Ignacio, La Greca Alejandro, Luzzani Carlos, Miriuka Santiago, Rodriguez-granillo Gaston, De Lillo Florencia, Rubilar Bibiana, Hijazi Razan, Solari Claudia, Rodríguez Varela María Soledad, Mobbs Alan, Manchini Estefania
Aging Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction is Mediated by Noncoding RNAsChakraborty Sankalpa, Dickerson Bryce, Bounds Curren, Lemus Sophia, Hickman Caleb, Rajagopalan Viswanathan