Final ID: MP743
A Machine Learning Algorithm to Detect Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Risk from Baseline ECGs
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is a common form of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in childhood resulting from dual AV nodal physiology (DAVNP) substrate. Children with AVNRT present with episodic chest discomfort or palpitations. The baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) in children with AVNRT appears normal. The ability to identify AVNRT risk from a baseline ECG may help during evaluation of children for palpitations with otherwise normal ECG.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that machine learning (ML) algorithms would be able to identify subtle ECG markers of DAVNP substrate on baseline ECG.
Methods
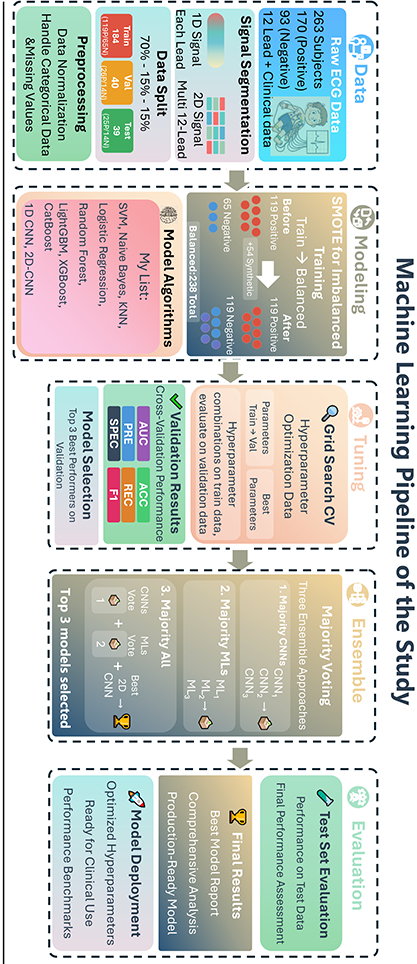
Retrospective single center case-control study from 2020 to 2025, including 12 lead ECG data from children 5-18 years of age who had a confirmed diagnosis of AVNRT through electrophysiological study. Patients with congenital heart disease were excluded. The control group consisted of children 5-18 years presenting to clinic for chest pain or palpitations and had normal cardiac findings. ECGs were processed to extract 12×65 biomarkers. Preprocessing included normalization, handling categorical and missing values. SMOTE was used during training to prevent bias. The dataset was split into 70% train, 15% validation, and 15% test. Both 1D and 2D lead data were assessed during model building. The models included 1 dimensional and 2 dimensional convolutional neural networks (CNN), Support Vector Machines (SVM), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Logistic Regression, and Boosting techniques. We implemented 10 ML models for 1D data: 9 traditional and a 1D CNN and used 2D CNNs for 2D data. Three ensemble models were also built using majority voting from the top performers. Optimal hyperparameters were determined using Bayesian optimization integrated with a grid search approach on the train/validation and evaluated on the test set. We used AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity to evaluate performance and compared the best models for statistical significance.
Results
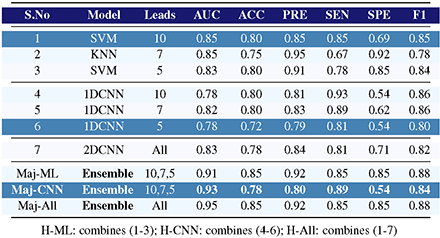
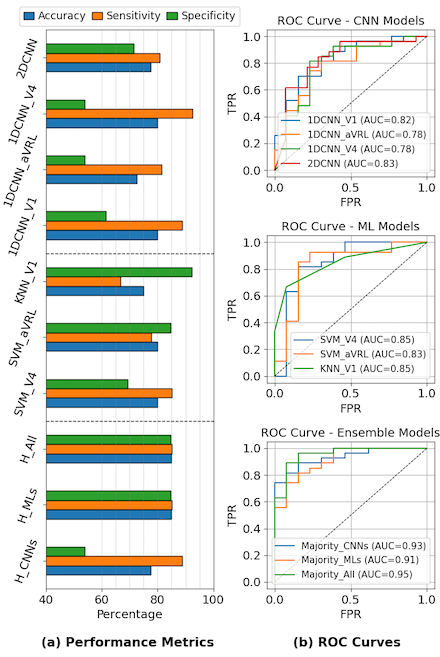
The case group included 170 children, control group included 93. Models using individual leads aVRL, V1, and V4 showed promising results with AUC as high as 0.85. Consistent improvement is observed by using ensemble models combining three leads in both traditional ML and CNN approaches, with AUC reaching 0.95 and maintaining balanced sensitivity and specificity of 0.85 each.
Conclusion
ML algorithms can successfully identify subtle findings of DAVNP on baseline ECG that predict AVNRT risk.
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is a common form of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in childhood resulting from dual AV nodal physiology (DAVNP) substrate. Children with AVNRT present with episodic chest discomfort or palpitations. The baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) in children with AVNRT appears normal. The ability to identify AVNRT risk from a baseline ECG may help during evaluation of children for palpitations with otherwise normal ECG.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that machine learning (ML) algorithms would be able to identify subtle ECG markers of DAVNP substrate on baseline ECG.
Methods
Retrospective single center case-control study from 2020 to 2025, including 12 lead ECG data from children 5-18 years of age who had a confirmed diagnosis of AVNRT through electrophysiological study. Patients with congenital heart disease were excluded. The control group consisted of children 5-18 years presenting to clinic for chest pain or palpitations and had normal cardiac findings. ECGs were processed to extract 12×65 biomarkers. Preprocessing included normalization, handling categorical and missing values. SMOTE was used during training to prevent bias. The dataset was split into 70% train, 15% validation, and 15% test. Both 1D and 2D lead data were assessed during model building. The models included 1 dimensional and 2 dimensional convolutional neural networks (CNN), Support Vector Machines (SVM), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Logistic Regression, and Boosting techniques. We implemented 10 ML models for 1D data: 9 traditional and a 1D CNN and used 2D CNNs for 2D data. Three ensemble models were also built using majority voting from the top performers. Optimal hyperparameters were determined using Bayesian optimization integrated with a grid search approach on the train/validation and evaluated on the test set. We used AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity to evaluate performance and compared the best models for statistical significance.
Results
The case group included 170 children, control group included 93. Models using individual leads aVRL, V1, and V4 showed promising results with AUC as high as 0.85. Consistent improvement is observed by using ensemble models combining three leads in both traditional ML and CNN approaches, with AUC reaching 0.95 and maintaining balanced sensitivity and specificity of 0.85 each.
Conclusion
ML algorithms can successfully identify subtle findings of DAVNP on baseline ECG that predict AVNRT risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
A blood test based on RNA-seq and machine learning for the detection of steatotic liver disease: A Pilot Study on Cardiometabolic Health
Poggio Rosana, Berdiñas Ignacio, La Greca Alejandro, Luzzani Carlos, Miriuka Santiago, Rodriguez-granillo Gaston, De Lillo Florencia, Rubilar Bibiana, Hijazi Razan, Solari Claudia, Rodríguez Varela María Soledad, Mobbs Alan, Manchini Estefania
A Comparison of Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients with and without Adult Congenital Heart Disease Undergoing Catheter Ablation for Ventricular TachycardiaFutela Pragyat, Poddar Aastha, Kowlgi Gurukripa