Final ID: Su3109
Non-Invasive Prediction Tools of Elevated Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure in HFpEF: A Machine Learning Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Diagnosing heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) remains challenging and invasive hemodynamic assessment is not easily available. A non-invasive tool for prediction of elevated PCWP could facilitate earlier identification of HFpEF and reduce the need for right heart catheterization (RHC).
Methods
We analyzed 279 patients from the JHU HFpEF Clinic who underwent RHC. Patients were separated by PCWP (≥15 mmHg versus <15 mmHg) and compared clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic variables, including the H2PEF score. Five feature sets were defined: (1) clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic variables; (2) echocardiographic variables only; (3) clinical and laboratory variables only; (4) H2PEF score alone; and (5) E/e′ ratio alone. Categorical variables were one-hot encoded; continuous variables were standardized. Feature selection used correlation with PCWP and AUC-based forward-backward optimization. Five classifiers were trained and evaluated using cross-validated and test-set AUC, with performance compared using DeLong’s test.
Results
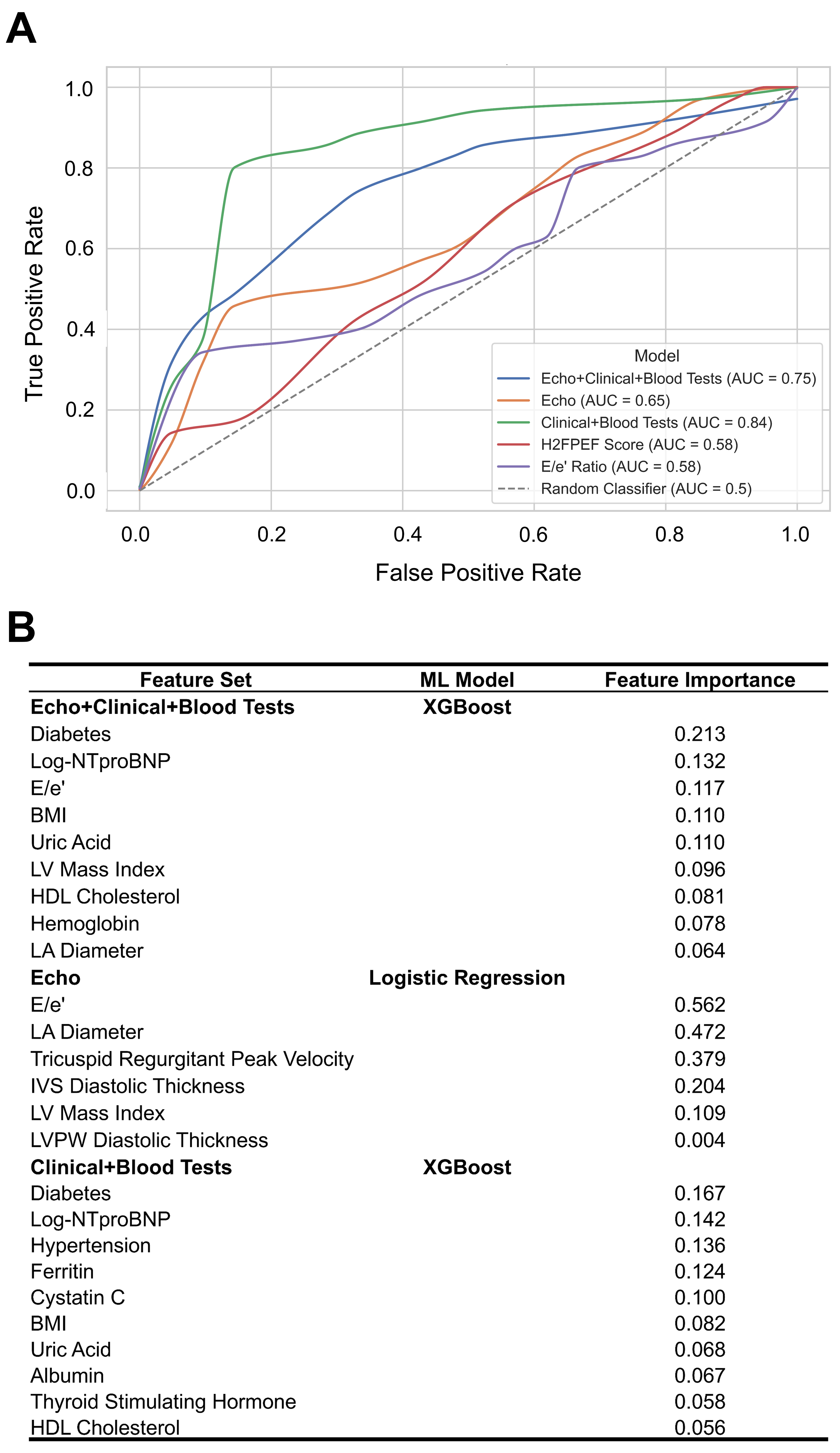
All models showed moderate to high discrimination with test set AUCs ranging from 0.65 to 0.84 (P < 0.001; Figure A). The top-performing model used only clinical and laboratory variables, achieving AUC of 0.84, outperforming the other models though differences were not statistically significant. In contrast, traditional diagnostic tools—the H2PEF score and E/e′ ratio—performed worse (AUCs both 0.58), with significant differences in DeLong comparisons (z = 3.72, P < 0.001 and z = 3.31, P < 0.001). Key clinical predictors in the highest performing model were diabetes, hypertension, NT-proBNP, ferritin, and cystatin C, along with E/e′, LA diameter, and LVMI (Figure B).
Conclusion
Machine learning models built on routinely available clinical, laboratory and echo data can accurately predict elevated PCWP in HFpEF and outperform existing diagnostic tools such as the H2PEF score. Such models can serve as effective surrogates for invasive hemodynamic assessment in HFpEF; prospective validation is needed in the future.
Diagnosing heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) remains challenging and invasive hemodynamic assessment is not easily available. A non-invasive tool for prediction of elevated PCWP could facilitate earlier identification of HFpEF and reduce the need for right heart catheterization (RHC).
Methods
We analyzed 279 patients from the JHU HFpEF Clinic who underwent RHC. Patients were separated by PCWP (≥15 mmHg versus <15 mmHg) and compared clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic variables, including the H2PEF score. Five feature sets were defined: (1) clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic variables; (2) echocardiographic variables only; (3) clinical and laboratory variables only; (4) H2PEF score alone; and (5) E/e′ ratio alone. Categorical variables were one-hot encoded; continuous variables were standardized. Feature selection used correlation with PCWP and AUC-based forward-backward optimization. Five classifiers were trained and evaluated using cross-validated and test-set AUC, with performance compared using DeLong’s test.
Results
All models showed moderate to high discrimination with test set AUCs ranging from 0.65 to 0.84 (P < 0.001; Figure A). The top-performing model used only clinical and laboratory variables, achieving AUC of 0.84, outperforming the other models though differences were not statistically significant. In contrast, traditional diagnostic tools—the H2PEF score and E/e′ ratio—performed worse (AUCs both 0.58), with significant differences in DeLong comparisons (z = 3.72, P < 0.001 and z = 3.31, P < 0.001). Key clinical predictors in the highest performing model were diabetes, hypertension, NT-proBNP, ferritin, and cystatin C, along with E/e′, LA diameter, and LVMI (Figure B).
Conclusion
Machine learning models built on routinely available clinical, laboratory and echo data can accurately predict elevated PCWP in HFpEF and outperform existing diagnostic tools such as the H2PEF score. Such models can serve as effective surrogates for invasive hemodynamic assessment in HFpEF; prospective validation is needed in the future.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Critical Illness and Signs of Myocardial Injury
Mueller Joshua, Stepanova Daria, Chidambaram Vignesh, Nakarmi Ukash, Al'aref Subhi
3-Mercaptopyruvate Sulfurtransferase is a Critical Regulator of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Catabolism in Cardiometabolic HFpEFLi Zhen, Doiron Jake, Xia Huijing, Lapenna Kyle, Sharp Thomas, Yu Xiaoman, Nagahara Noriyuki, Goodchild Traci, Lefer David