Final ID: MP1273
Comparison of In-Hospital Outcomes Between Type 1 and Type 2 Myocardial Infarction in Patients Admitted with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: A Nationwide Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Patients with Type 2 myocardial infarction (MI) often exhibit unique characteristics and outcomes compared to those with Type 1 MI. Additionally, individuals with Type 2 MI are often underdiagnosed and undertreated in relation to their Type 1 counterparts. There is limited data regarding the clinical outcomes of patients with Myocardial Infarction Type 1 (MI1) versus those with Myocardial Infarction Type 2 (MI2), particularly among those with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). The objective of our study is to compare in-hospital outcomes, including inpatient mortality, cardiogenic shock, ablation procedures, total costs, and total length of stay.
Methods:
The National Inpatient Sample (2016-2021) was utilized to identify patients hospitalized for ADHF by querying ICD-10 codes. A propensity score matching approach, adjusted for demographics and comorbidities, was employed to calculate the adjusted odds ratio (aOR) and regression coefficients, along with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) and p-values.
Results:
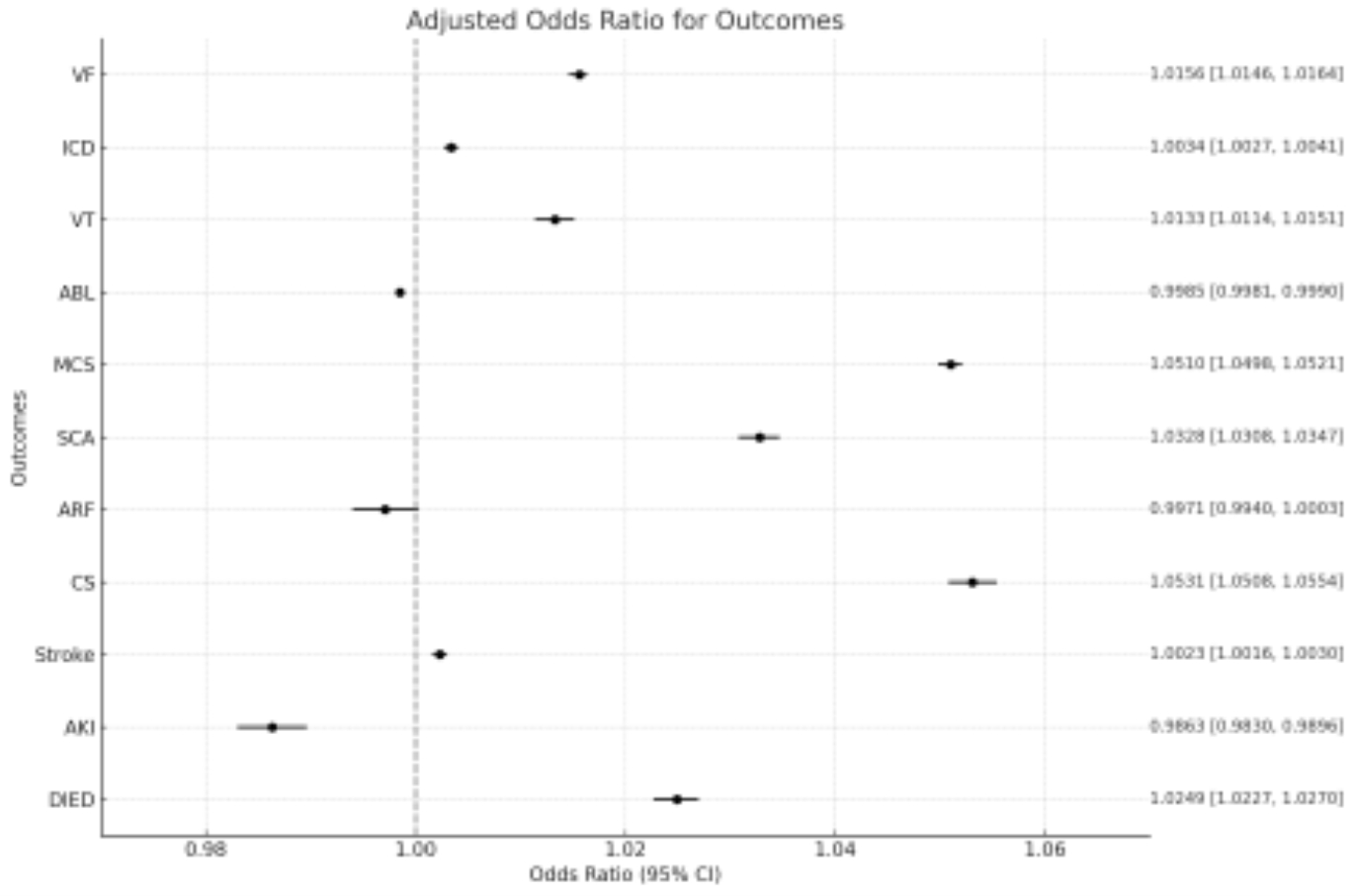
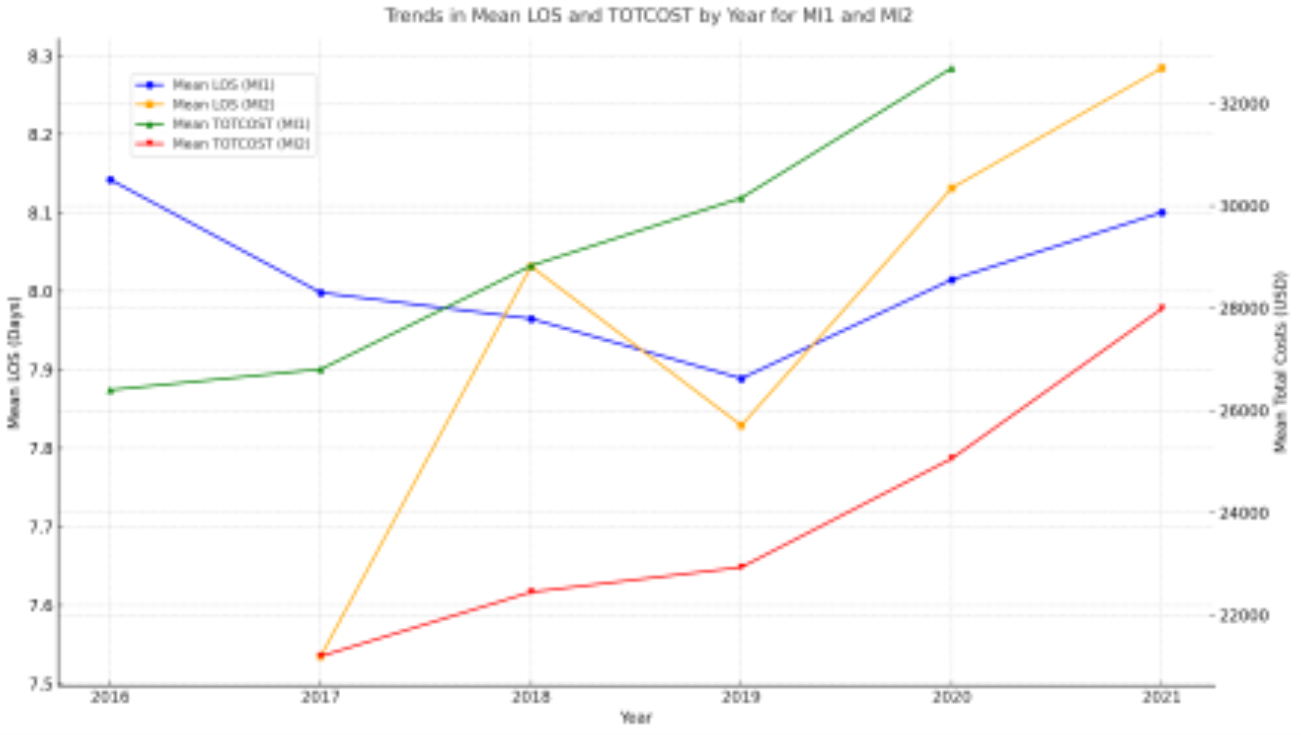
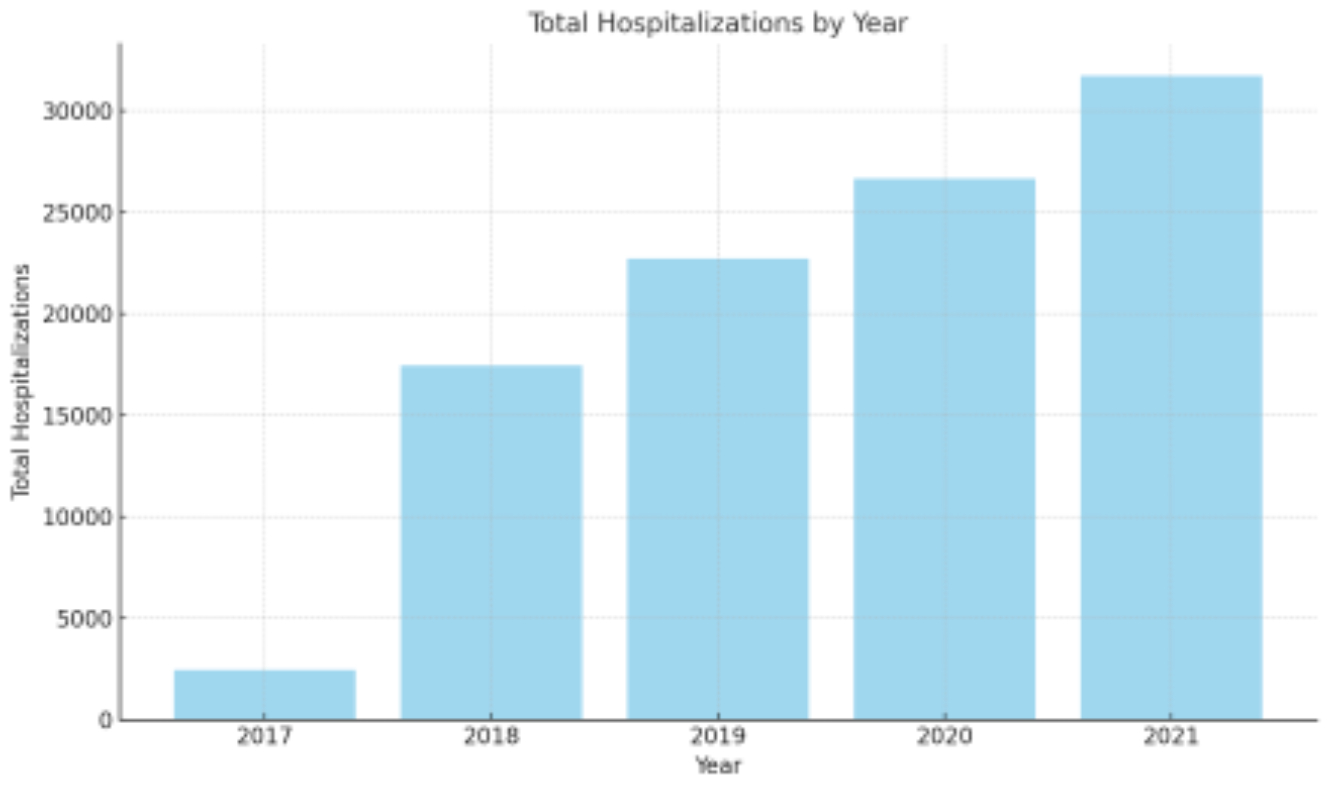
A total of 330,354 survey-weighted hospitalizations for ADHF with underlying MI were identified, of which 69.5% were due to Type 1 MI and 30.5% were due to Type 2 MI. Patients with Type 1 MI experienced a higher rate of inpatient mortality (aOR, 1.02 [95% CI, 1.022-1.027]; p < 0.001), sudden cardiac arrest (aOR, 1.03 [95% CI, 1.030-1.034]; p < 0.001), cardiogenic shock (aOR, 1.05 [95% CI, 1.050-1.055]; p < 0.001), mechanical circulatory support (aOR, 1.051 [95% CI, 1.049-1.052]; p < 0.001), and ventricular fibrillation (aOR, 1.01 [95% CI, 1.014-1.016]; p < 0.001) after propensity score matching. Additionally, total costs, total length of stay, and overall hospitalization rates have been progressively increasing over the years.
Conclusions:
Patients admitted with ADHF who have underlying Type 2 MI experience more favorable in-hospital clinical outcomes compared to those with Type 1 MI.
Patients with Type 2 myocardial infarction (MI) often exhibit unique characteristics and outcomes compared to those with Type 1 MI. Additionally, individuals with Type 2 MI are often underdiagnosed and undertreated in relation to their Type 1 counterparts. There is limited data regarding the clinical outcomes of patients with Myocardial Infarction Type 1 (MI1) versus those with Myocardial Infarction Type 2 (MI2), particularly among those with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). The objective of our study is to compare in-hospital outcomes, including inpatient mortality, cardiogenic shock, ablation procedures, total costs, and total length of stay.
Methods:
The National Inpatient Sample (2016-2021) was utilized to identify patients hospitalized for ADHF by querying ICD-10 codes. A propensity score matching approach, adjusted for demographics and comorbidities, was employed to calculate the adjusted odds ratio (aOR) and regression coefficients, along with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) and p-values.
Results:
A total of 330,354 survey-weighted hospitalizations for ADHF with underlying MI were identified, of which 69.5% were due to Type 1 MI and 30.5% were due to Type 2 MI. Patients with Type 1 MI experienced a higher rate of inpatient mortality (aOR, 1.02 [95% CI, 1.022-1.027]; p < 0.001), sudden cardiac arrest (aOR, 1.03 [95% CI, 1.030-1.034]; p < 0.001), cardiogenic shock (aOR, 1.05 [95% CI, 1.050-1.055]; p < 0.001), mechanical circulatory support (aOR, 1.051 [95% CI, 1.049-1.052]; p < 0.001), and ventricular fibrillation (aOR, 1.01 [95% CI, 1.014-1.016]; p < 0.001) after propensity score matching. Additionally, total costs, total length of stay, and overall hospitalization rates have been progressively increasing over the years.
Conclusions:
Patients admitted with ADHF who have underlying Type 2 MI experience more favorable in-hospital clinical outcomes compared to those with Type 1 MI.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Recurrent Acute Coronary Syndrome and Cardiogenic Shock due to Apolipoprotein A-IV Amyloidosis
Muthukkumar Rashmi, Holmes Taylor, Friede Kevin
Acute Administration of The Novel Cardiac Sarcomere Modulator EDG-7500, Improves Ventricular Filling While Preserving LVEF In Dogs with Pacing Induced Left-Ventricular Systolic DysfunctionEvanchik Marc, Emter Craig, Del Rio Carlos, Roof Steve, St Clair Sydney, Russell Alan, Henze Marcus, Semigran Marc