Final ID: Su3148
Non-statin Medication Utilization under Medicare Part D Population
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Statin intolerance is reported in 5–30% of patients and contributes to reduced statin adherence and persistence, as well as a higher risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes. For patients with known or suspected statin intolerance and high ASCVD risk, non-statin therapy is currently a class IIa recommendation by the National Lipid Association (NLA).
Method
We accessed publicly available datasets from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). The non-statin medications included in these studies are bempedoic acid, evolocumab, alirocumab, inclisiran, and evanicumab. Key variables, such as beneficiaries, claims, and total spending, were analyzed and presented below. We looked at the trend of medication from 2020 to 2022. All costs were adjusted for inflation and represented in 2022 US dollars.
Results
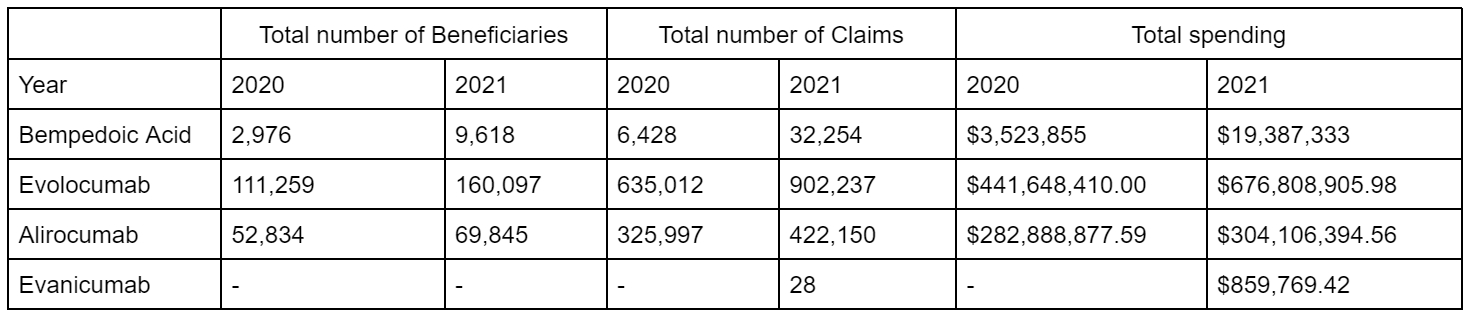
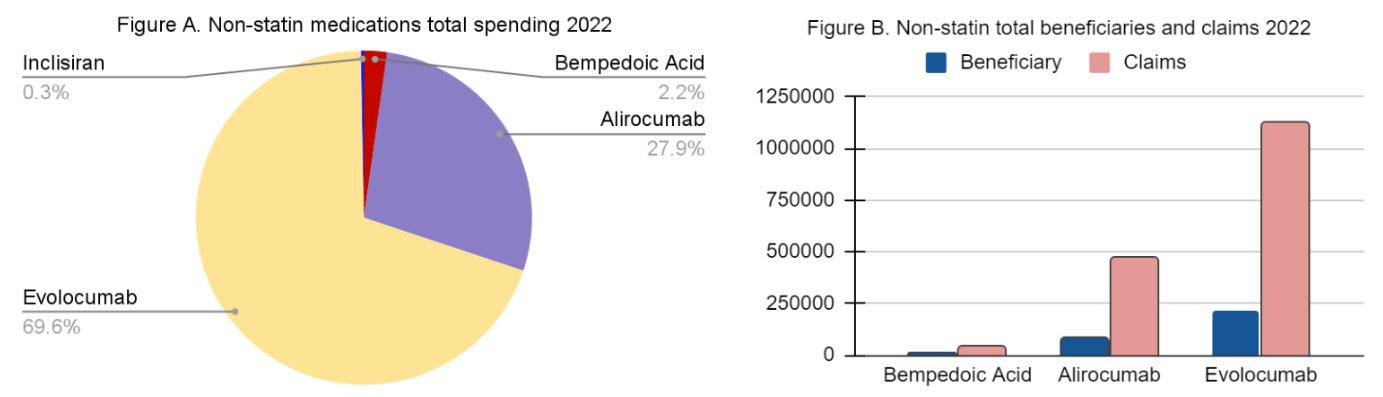
We analyzed CMS Medicare Part D plans of Bempedoic Acid, Inclisiran, Alirocumab, Evolocumab and Evanicumab, covering 2020–2022. We noticed a 3- to 4-fold increase in total beneficiaries and claims for bempedoic acid, along with a sharp rise in total spending from 3.5 million dollars to 19.4 million dollars after adjusting for inflation rate using the consumer price index inflation calculator. The trends for other non-statin medications were similar. We also created comparative graphs for 2022 and noticed a total spending of 97.5% among proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK-9) in Medicare D CMS populations.
Discussion
We can see a rise in total Medicare spending among all the drugs. Amongst different lipid-lowering agents, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK-9) inhibitors are the most commonly used, followed by bempedoic acid. Newer agents, like Evanicumab
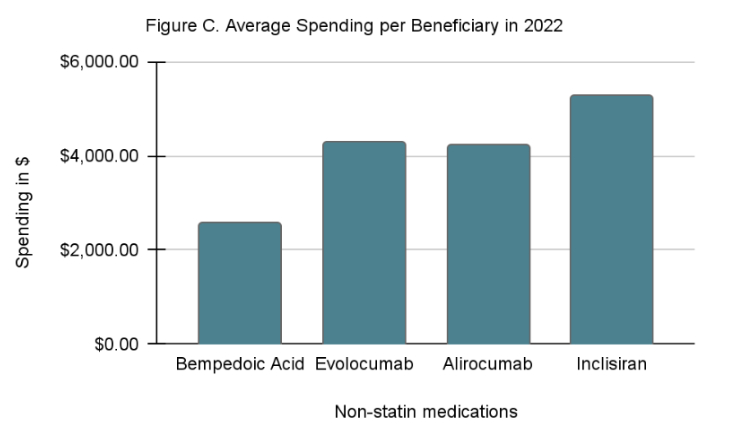
and Inclisiran are also available on the market, and their trend has not yet been determined. Inclisiran, however, has the highest average spending per beneficiary. How the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 will affect drug utilization is yet to be seen.
Limitation
The pattern of data used may not be generalizable to other payer demographics. Policy changes can affect the comparability of data over different periods.
Conclusion
From 2020 to 2022, the number of claims, beneficiaries, and total spending on various lipid-lowering agents steadily increased.
Statin intolerance is reported in 5–30% of patients and contributes to reduced statin adherence and persistence, as well as a higher risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes. For patients with known or suspected statin intolerance and high ASCVD risk, non-statin therapy is currently a class IIa recommendation by the National Lipid Association (NLA).
Method
We accessed publicly available datasets from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). The non-statin medications included in these studies are bempedoic acid, evolocumab, alirocumab, inclisiran, and evanicumab. Key variables, such as beneficiaries, claims, and total spending, were analyzed and presented below. We looked at the trend of medication from 2020 to 2022. All costs were adjusted for inflation and represented in 2022 US dollars.
Results
We analyzed CMS Medicare Part D plans of Bempedoic Acid, Inclisiran, Alirocumab, Evolocumab and Evanicumab, covering 2020–2022. We noticed a 3- to 4-fold increase in total beneficiaries and claims for bempedoic acid, along with a sharp rise in total spending from 3.5 million dollars to 19.4 million dollars after adjusting for inflation rate using the consumer price index inflation calculator. The trends for other non-statin medications were similar. We also created comparative graphs for 2022 and noticed a total spending of 97.5% among proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK-9) in Medicare D CMS populations.
Discussion
We can see a rise in total Medicare spending among all the drugs. Amongst different lipid-lowering agents, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK-9) inhibitors are the most commonly used, followed by bempedoic acid. Newer agents, like Evanicumab
and Inclisiran are also available on the market, and their trend has not yet been determined. Inclisiran, however, has the highest average spending per beneficiary. How the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 will affect drug utilization is yet to be seen.
Limitation
The pattern of data used may not be generalizable to other payer demographics. Policy changes can affect the comparability of data over different periods.
Conclusion
From 2020 to 2022, the number of claims, beneficiaries, and total spending on various lipid-lowering agents steadily increased.
More abstracts on this topic:
Clinical characteristics and treatment of high-risk cardiovascular patients without prior myocardial infarction or stroke: VESALIUS-REAL - results from US
Chan Queenie, Jernberg Tomas, Cegla Jaimini, Budoff Matthew, Wong Ian, Sakhuja Swati, Ochs Andreas, Dhalwani Nafeesa, O'kelly James, Shannon Erin, Paivadasilva Lima Gabriel, Avcil Suna, Laufs Ulrich
Access to Lipid-Lowering Therapies is Limited by Payer Coverage Restrictions and High Out-of-Pocket Costs on Medicare Prescription Drug PlansYoung Grant, Bansal Kannu, Riello Ralph, Faridi Kamil, Clark Katherine, Desai Nihar