Final ID: MP1536
Seasonal Patterns and Geographic Disparities in United States Cardiovascular Mortality between 1999-2020
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Seasonal, geographic, and socioeconomic factors all influence cardiovascular (CV) mortality. Long-term seasonal trends across United States regions remain insufficiently characterized.
Research Question:
We evaluated longitudinal trends in CV mortality across seasons in the U.S., stratified by geographic region and degree of urbanisation, from 1999 through 2020.
Methods:
Data on CV mortality (ICD-10: I00-I99) were extracted from the CDC WONDER database and stratified by season (Winter, Spring, Summer, Fall), U.S. Census region (Northeast, Midwest, South, West), and degree of urbanisation (6-level National Center for Health Statistics classification). Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) were calculated, and Joinpoint regression was used to estimate annual percent change (APC) and average annual percent change (AAPC) with 95% confidence intervals.
Results
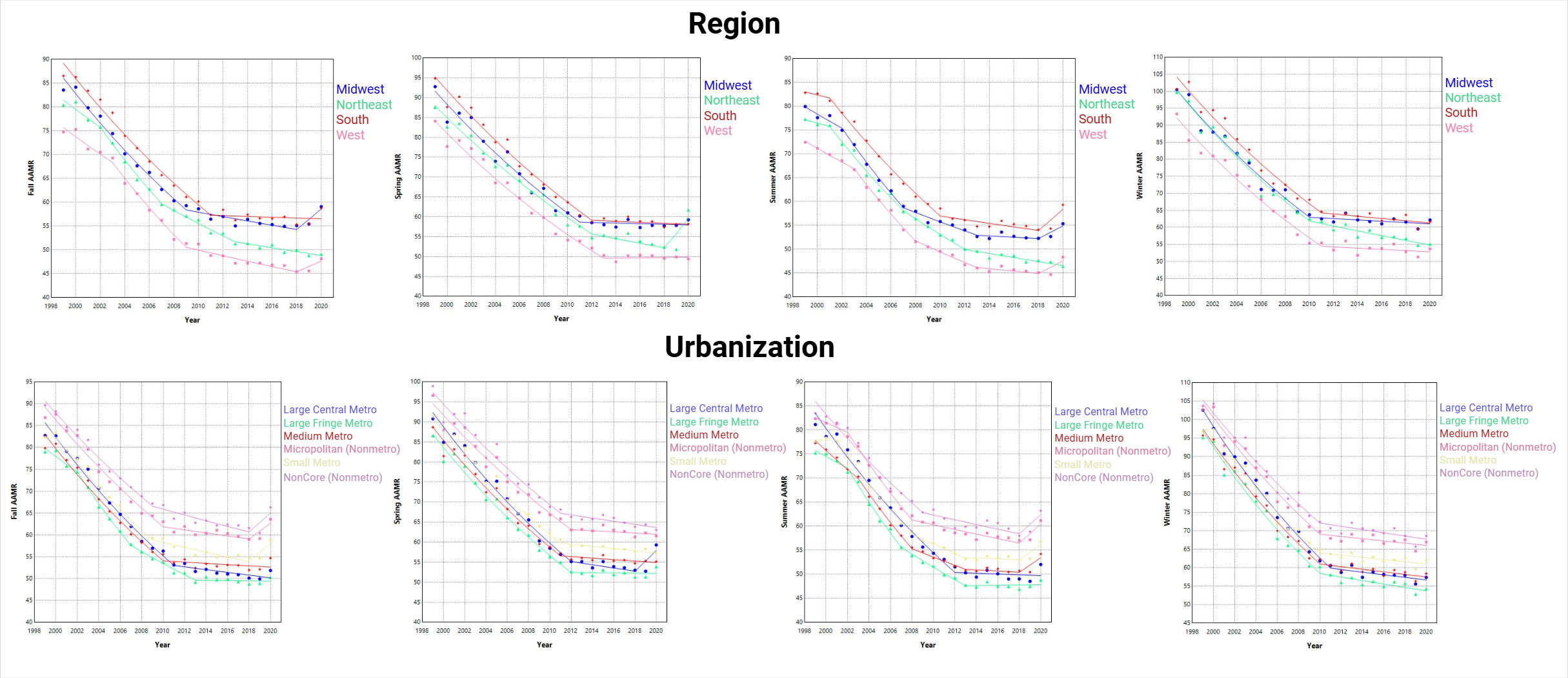
From 1999 to 2020, 18.8 million CV deaths were recorded (Table 1). Winter accounted for the highest mortality burden across all regions and urban settings but also showed the greatest improvement of the the 20-year study period, with AAPC reductions most pronounced in the Northeast (–2.83%) and Large Central Metro areas (–2.79%; p < 0.000001 for all trends; Figure 1). Summer and Fall, while associated with fewer deaths, showed slower progress, particularly in the Midwest (Fall AAPC: –1.81%; Summer: –1.77%) and rural areas (NonMetro Fall AAPC: –1.56%). Notably, Midwest Fall mortality demonstrated a statistically significant reversal, with an APC increase of +3.87% from 2018 to 2020 (p = 0.02)(Figure 1).
Conclusion
CV mortality in the U.S. follows a distinct and evolving seasonal pattern. Although winter remains the deadliest season, it has seen the most substantial mortality reductions, likely tied to improved awareness, continuity of care, and cold-weather adaptations. However, slower progress during summer and fall, particularly in the Midwest and rural areas, reveals growing seasonal and geographic disparities. Most notably, the recent and statistically significant rise in Midwest fall mortality signals an urgent concern. This reversal may reflect emerging climate stressors such as prolonged heat, air pollution, and environmental volatility during transitional months compounded by reduced healthcare access or changing behavioral risk factors. These findings call for year-round, seasonally tailored public health strategies especially for underserved and climate-vulnerable populations.
Seasonal, geographic, and socioeconomic factors all influence cardiovascular (CV) mortality. Long-term seasonal trends across United States regions remain insufficiently characterized.
Research Question:
We evaluated longitudinal trends in CV mortality across seasons in the U.S., stratified by geographic region and degree of urbanisation, from 1999 through 2020.
Methods:
Data on CV mortality (ICD-10: I00-I99) were extracted from the CDC WONDER database and stratified by season (Winter, Spring, Summer, Fall), U.S. Census region (Northeast, Midwest, South, West), and degree of urbanisation (6-level National Center for Health Statistics classification). Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) were calculated, and Joinpoint regression was used to estimate annual percent change (APC) and average annual percent change (AAPC) with 95% confidence intervals.
Results
From 1999 to 2020, 18.8 million CV deaths were recorded (Table 1). Winter accounted for the highest mortality burden across all regions and urban settings but also showed the greatest improvement of the the 20-year study period, with AAPC reductions most pronounced in the Northeast (–2.83%) and Large Central Metro areas (–2.79%; p < 0.000001 for all trends; Figure 1). Summer and Fall, while associated with fewer deaths, showed slower progress, particularly in the Midwest (Fall AAPC: –1.81%; Summer: –1.77%) and rural areas (NonMetro Fall AAPC: –1.56%). Notably, Midwest Fall mortality demonstrated a statistically significant reversal, with an APC increase of +3.87% from 2018 to 2020 (p = 0.02)(Figure 1).
Conclusion
CV mortality in the U.S. follows a distinct and evolving seasonal pattern. Although winter remains the deadliest season, it has seen the most substantial mortality reductions, likely tied to improved awareness, continuity of care, and cold-weather adaptations. However, slower progress during summer and fall, particularly in the Midwest and rural areas, reveals growing seasonal and geographic disparities. Most notably, the recent and statistically significant rise in Midwest fall mortality signals an urgent concern. This reversal may reflect emerging climate stressors such as prolonged heat, air pollution, and environmental volatility during transitional months compounded by reduced healthcare access or changing behavioral risk factors. These findings call for year-round, seasonally tailored public health strategies especially for underserved and climate-vulnerable populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Approach to Simplify Risk Stratification of Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Li Hsin Fang, Gluckman Ty, Nute Andrew, Weerasinghe Roshanthi, Wendt Staci, Wilson Eleni, Sidelnikov Eduard, Kathe Niranjan, Swihart Charissa, Jones Laney
A Pressure-Volume Loops Approach Predicts Outcomes After Double Switch Operation For Congenitally Corrected Transposition Of The Great Arteries with Intact Ventricular SeptumThatte Nikhil, Del Nido Pedro, Ghelani Sunil, Hammer Peter, Marx Gerald, Beroukhim Rebecca, Gauvreau Kimberlee, Callahan Ryan, Prakash Ashwin, Emani Sitaram, Hoganson David